Table of Contents
Cloudflare is a world largest Anycast ‘zero trust’ global network used by organizations to secure their assets. ‘Zero trust security’ is a new buzz word and relies on the fundamental principle of ‘trust no one, check everything’ opposed to the earlier concept of ‘trust once and allow’. Earlier office spaces looked like a store house of some hardware infrastructure, servers, cables, end user machines, firewalls and security appliances to create traditional data centres which operated within the perimeter of corporate and protected everything inside that space. As organizations started moving their key services and applications over cloud and end users were no longer confined to a particular space or building it became difficult to secure things outside the closed perimeter.
‘Zero trust’ security principles became more relevant as businesses started growing outside the confined boundaries or spaces.
In this article we will learn about how zero trust security is implemented with Cloudflare global network.
Zero Trust Security
Moving away from perimeter-based security, ‘Zero trust’ security focuses on verifying each and every user and device access request and is tightly coupled with the principle of ‘least privileges’. The ‘zero trust’ strategy involves implementation of Multi-factor (MFA) authentication, continuous monitoring of environment security. Each principle reduces attack surface, prevents unauthorized access and reduces impact of breaches. However, implementation of ‘zero trust’ security is a bit challenging due to mixed infrastructure, cultural hurdles and vendor and solution sprawls and cost is one of the major factors here.
Cloudflare: Zero Trust Security
Cloudflare is a global anycast network sprawl across 300 data centres operating on ‘zero trust’ security principles. Cloudflare has several components to support ‘zero trust’ security such as policy engine (Cloudflare zero trust), policy administrator (Cloudflare zero trust), policy enforcement point (cloudflared) and enterprise resources (GCP VM/ Web applications).
Before we start building a ‘Zero trust’ security in Cloudflare we have to start setting up the foundation which is the ‘Asset’.
Asset Inventory
Taking stock of current assets before building their access mechanism. Mapping physical and virtual infrastructure is essential. How many virtual clouds are there? How do they communicate with each other? How and why do users access those virtual clouds and its services? All access is via console or browser based? Are there public IP addresses for HTTPS or SSH services? Are resource access permissible over the Internet? Do you have a traditional VPN to allow remote access and how is it gated?
Once the list is ready, the next step is to know what you need to protect and rank these services by risk level in the event of security breaches. For example an internal tool is less critical than a customer production database and requires better protection such as access via a corporate device and MFA.
Identity
It is the core of ‘zero trust’ security. Most customers use a central source for authentication, authorization, validation and logging of actions taken by users. Phishing resistant MFA using physical keys, local authenticator apps, and biometric authentication are valuable tools.
SSO Integration
Single sign on (SSO) solutions offered by directory services help in integrating SaaS applications and solutions like Okta also offer machine certification as part of authentication.
Third Party Access
Zero trust solutions need to identify identities beyond which are not owned by you such as third-party service providers or suppliers.
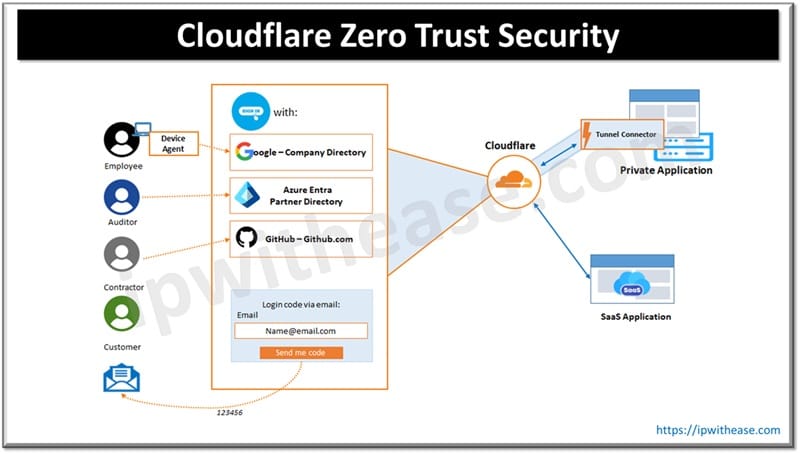
Where does Cloudflare fit in?
Cloudflare simplifies your network architecture acting as a single point of enforcement of identity for your applications and services, networks, developer services and SaaS applications. Cloud flare provides ‘zero trust’ security and authentication as a web proxy (layer 7) as VPN (layer ¾) and a secured web gateway.
Cloudflare becomes a point of policy enforcement for device posture security management. The Cloudflare device agent evaluates security posture of device ownership and its health and use combined it with user identity policies to evaluate user has proper identity and device compliance.
Cloudflare overlay network provides network tunnels and application tunnels to grant users administrative access to services on internal networks and allow only an authenticated user explicit access to a singular service in the tunnel.
References: https://developers.cloudflare.com/reference-architecture/design-guides/zero-trust-for-startups/
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj