Table of Contents
Private IP is used within a local network and isn’t accessible from the internet. Public IP is assigned by an ISP and is used to identify devices on the internet. Private IPs are reusable across networks, while public IPs must be unique globally. In this blog, we discuss the differences between the two types of IP addresses, i.e. Public IP vs Private IP Address in detail.
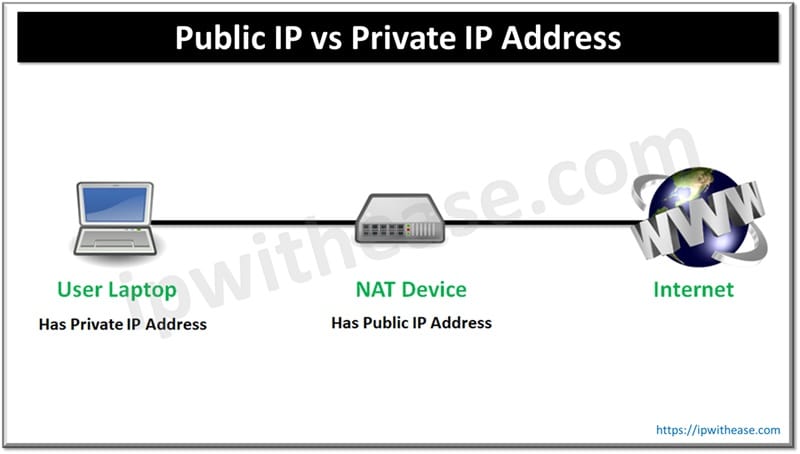
IP address is a unique string of numbers assigned to each device connected to a network. It acts like a mailing address, ensuring data gets to the right place. There are two main types of IP addresses in networking – Public IP address and Private IP address.
What is a Public IP Address
A Public IP address is the one which is globally recognizable and our ISP (Internet Service Provider) or IANA provides the same. Public IP identifies our home network to the outside world. It is an IP address that is unique throughout the entire Internet. Each customer who uses the Global/Public IP Block needs to pay the Service Provider or IANA.
Features
- It is Globally unique, no two devices on the public internet can have the same public IP.
- This is the address websites and services “see” when you connect to them.
- Your ISP gives you a public IP when you connect to the internet.
- E.g. – If you search “what is my IP” on Google, the result is your public IP.
What is a Private IP Address
Unlike Public Addresses, Private IP addresses never leave the LAN network, just as the public IP address is never used inside your network. Additionally, customer need not pay for private IP blocks used inside the LAN environment.
Features
- Only used inside local networks
- Cannot be accessed directly from the internet
- Assigned by your router (via DHCP)
Difference: Public IP vs Private IP
Further, below table details on the difference between Public IP Addresses and Private IP addresses:
| Private IP | Public IP |
|---|---|
| Used with LAN or Network | Used with Public Network |
| Not recognized over Internet | Recognized over internet |
| Assigned by LAN administrator | Assigned by service Provider/IANA |
| Unique only to LAN | Unique globally |
| Free of charge | Cost associated with using Public IP |
| Range – Class A – 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 Class B – 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 Class C – 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 | Range – Class A – 1.0.0.0 to 9.255.255.255 11.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255 Class B – 128.0.0.0 to 172.15.255.255 172.32.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 Class C – 192.0.0.0 to 192.167.255.255 192.169.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 |
Download the comparison table: Private IP vs Public IP
Reason to use a Private IP
- Private IPs add a layer of security as they keep internal devices hidden from the public internet. For example, you don’t want your printer or smart fridge exposed to hackers online!
- They also help conserve the limited number of public IPv4 addresses by allowing multiple devices to share one public IP using NAT.
Continue Reading
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj