Table of Contents
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have now become the de facto standard for a company’s employees or its partners/contractors.
In fact, with the concept of “Work from Home” picking up pace and employees preferring to work from their home locations, it becomes more so important that VPN technologies like IPsec and SSL VPNs be leveraged. This way VPN addresses the security policy and confidentiality of company data over unsecured Internet.
Access to your office resources like Files, websites, applications, administrative tools and business from any location is something that has been possible for many years – thanks to VPN Technology.
It’s worth mentioning that in the early days of remote access, we had to use a dial up modem and phone line and call into your office using a serial line which was both slow and expensive. High speed domestic broadband has resolved this issue as they are cheap high bandwidth circuits. There have been quite a few VPN technologies over the years and keep getting better and better in terms of functionality and security.
There are two types that are the most popular VPN of choice – IPsec VPN and SSL VPN. Let’s understand their differences, features and how they protect and add security to our access.
Related- DMVPN Over IPSEC
What is SSL VPN
SSL, also known as Secure Sockets Layer, functions at the application layer within the OSI model. Its primary purpose is to secure and encrypt the data that is transmitted between a user’s web browser and the web server.
Features
- Its purpose is to provide remote access from anywhere to company’s headquarters or head office by to secure transmissions between servers and client.
- IPsec originally was intended for securing the communications between locations using site-to-site tunneling and it therefore had its limitations when it was used in securing the remote access. SSL VPN solves this problem; it operates using the Secure Sockets Layer protocol which also secures HTTPS and which makes the most common VPN solution that is in use today for user access.
- SSL encrypts the data generated by applications.
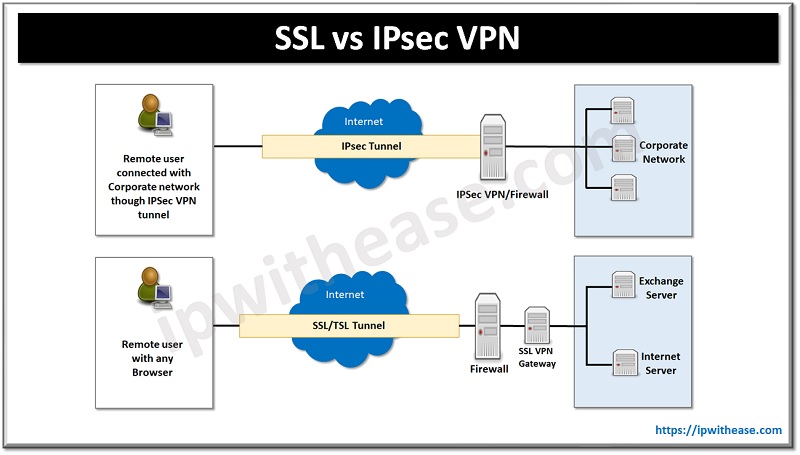
What is IPsec VPN
IPsec, also known as Internet Protocol Security, provides security for internet communication on the network layer. It consists of a collection of protocols that encrypt and authenticate network traffic.
Features
- Simply creates an IPsec tunnel between branch offices to a company’s headquarters or head office or different branch offices by providing secure connection.
- Lowers the cost by using the internet rather than a dedicated private network.
- Data is digitally signed and encrypted prior to transmission, this provides end-to-end protection, which means transportation is secured until it reaches its destination.
- IPsec is an extension to the IP protocol; any traffic that takes the form of IP datagrams can be encrypted and it doesn’t matter type of information is carried within, this means any layer above network layer are not aware that the traffic has been encrypted or part of a VPN in the first place.
Comparison: IPsec vs SSL
Now, we attempt to explain the difference between two popular VPN types and how to decide between them.
IPsec and SSL VPN work on different types of security sets. Let’s walk through their mechanisms of protection/ security of data –
| Security/ Protection | SSL VPN | IPSec VPN |
| Spoofing Prevention | Server and clients provide credentials in order to confirm the identity of both systems | Recipient cannot be tricked as the identity of each end point is verified. |
| Modification Prevention | Every packet is signed with a hash function called HMAC which ensures that there has not been any modification to the packet. | Packet cannot be ·Captured ·Payload modified And then sent further without it being detected. |
| Protection | Data is encrypted by the public key which makes sure that only the recipient is able to decrypt and receive the information. | Data is encrypted and one cannot read the content of the packet payload. |
| Reuse Prevention | Packets cannot be re-used or any passwords or keys discovered. | Packets cannot be re-used or discover any passwords or keys. |
Download the comparison table: ssl vs ipsec vpn
Let’s further have a feature comparison for these two VPN’s for much better understanding –
| Features | SSL | IPSEC |
|---|---|---|
| Application for | Web based applications | IP based applications |
| VPN Type | Client to Site only (Remote Access) | Site to Site or Client to Site (Remote Access) |
| Encryption | Moderate to Strong | Strong |
| Encryption Key Length | 40 bits to 256 bits | 56 bits to 256 bits |
| Authentication | One way or two-way authentication | Two-way authentication using shared leys or digital certificates. |
| Connection Complexity | Low Requires only web browser | Medium Full configuration, end-to-end tunnel establishment |
| Connection Options | Any device can connect | Only specific devices |
| Encryption of TCP and Application Layer | Application Layer | Both TCP and Application layer |
| IP Header Authentication | No | Yes |
| Pre-shared Key | No | Yes |
| UDP Support | No | Yes |
| Handshake Time | Fast | Slow |
| Connectivity | Connects users to specific applications and services | Connects remote hosts to entire networks |
| Scalability | High | Low |
| Configuration | Easy | Hard |
Download the comparison table: ssl vs ipsec
Continue Reading
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj