Full Virtualization vs Para Virtualization vs Hardware Assisted Virtualization
Virtualization is about abstracting application, operating system, network or storage away from the genuine basic software and hardware.
It makes the illusion of physical hardware to accomplish the objective of operating system isolation. In a decade ago, server farms were involved by countless physical servers, network switches, storage gadgets. It expended a great deal of intensity and labour to keep up the server farms.
In that period, there were many organizations were inquiring about the hardware simulation/emulation like QEMU, virtual PC and so on.
It’s extremely difficult to list all the virtualization types here. So, I have recorded down key server virtualization types.
Full virtualization
Para-virtualization
Hardware-assistant virtualization
Why you should be aware of Virtualization?
As a principal innovation for the cloud computing industry, figuring out how Virtualization works will give you a few favourable circumstances for your career and for the organization you are working for.
You will get to understand the economic and technical advantage presented by Virtualization in the cutting edge of open cloud conditions.
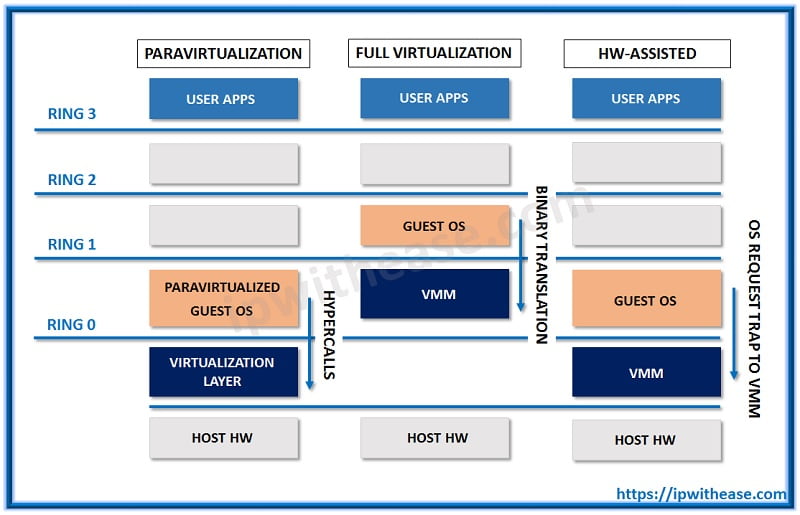
Full virtualization:
In this scenario, data is completely abstracted from the underlying hardware by the virtualization layer. In this technique guest, OS is unaware that it is a guest and hypervisor translate all OS calls on-the-fly. It provides flexibility and no hardware assistance or modification is required.
The advantages of full virtualization are that the emulation layer isolates VMs from the host OS and from each other. It also controls individual VM access to system resources, preventing an unstable VM from impacting system performance.
It also provides the total VM portability by emulating a consistent set of system hardware, VMs have the ability to transparently move between hosts with dissimilar hardware without any problems. The products support this virtualization are VMware, Microsoft, and KVM.
Para-virtualization:
It is an enhancement of virtualization technology in which a guest OS is recompiled prior to installation inside a virtual machine. In para-virtualization, the guest OS is modified to enable communication with the hypervisor to improve performance and efficiency.
Its advantages are that the guest system comes closer to native performance than a fully virtualized guest and also it does nor require the latest virtualization CPU support. It also allows for an interface to the virtual machine that can differ somewhat from that of the underlying hardware.
VMware and Xen are supported by this type of virtualization.
Hardware-assistant virtualization:
In enables full virtualization with help of utilizing of a computer’s physical components to support the software that creates and manages virtual machines. In this technique of virtualization unmodified guest is OS and no API are made. The sensitive calls are trapped by the hypervisor and in 2006 it was added to x86 processors (Intel VT-x or AMD-V).
The products supporting hardware-assisted virtualization are VMware, Xen, Microsoft, and Parallels.
There is additionally a mix of para-virtualization and full virtualization called Hybrid Virtualization where parts of the visitor working on paravirtualization for certain hardware drivers, and the host utilizes full virtualization for different highlights. This frequently delivers prevalent execution on the visitor without the requirement for the visitor to be totally par- virtualized.
Every virtualization innovation has its own focal points and burdens. The decision of virtualization vigorously relies upon use and cost. There are a ton of advances are developing and enterprise products support various virtualization types to enhance the performance and reduce the asset overhead.
Full Virtualization vs Para Virtualization vs Hardware-Assisted Virtualization
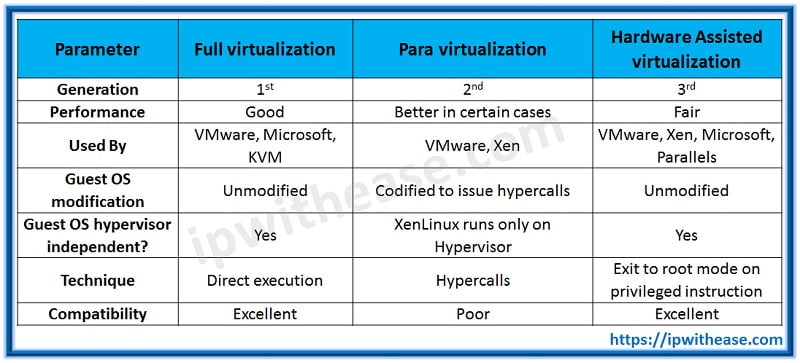
Below table summarizes the difference between Full Virtualization, Para Virtualization and Hardware-Assisted Virtualization:
| PARAMETER | FULL VIRTUALIZATION | PARA VIRTUALIZATION | HARDWARE ASSISTED VIRTUALIZATION |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generation | 1st | 2nd | 3rd |
| Performance | Good | Better in certain cases | Fair |
| Used By | VMware, Microsoft, KVM | VMware, Xen | VMware, Xen, Microsoft, Parallels |
| Guest OS modification | Unmodified | Codified to issue hypercalls | Unmodified |
| Guest OS hypervisor independent? | Yes | XenLinux runs only on Hypervisor | Yes |
| Technique | Direct execution | Hypercalls | Exit to root mode on privileged instruction |
| Compatibility | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj