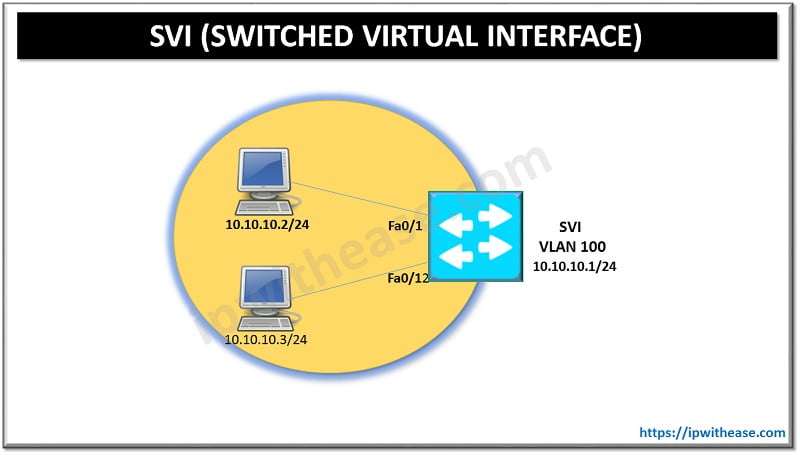
When Router is in Connect State, it’s waiting for a completed TCP connection. To do this task, the two neighbors must perform the standard TCP three-way handshake and open a TCP connection to port 179.Below is a scenario where 3-way handshake happens between client and web server.
In the same way, BGP also utilizes TCP 3-way handshake to form neighborship.
All BGP message are unicast to the one neighbor over the TCP connection.
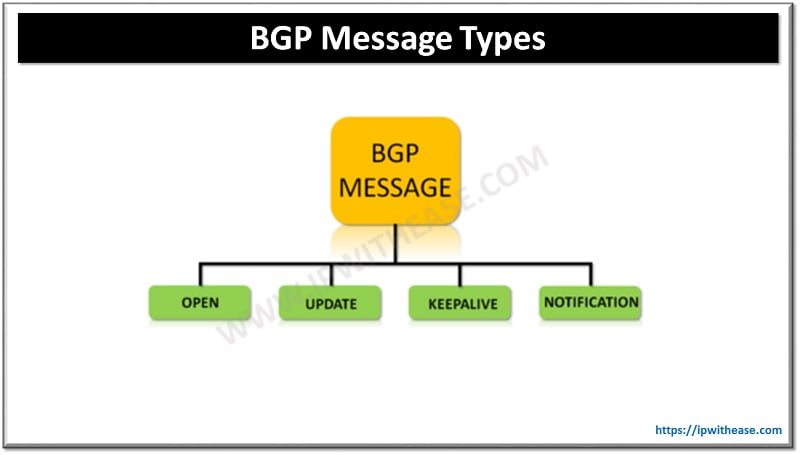
BGP Message Types
The different types of BGP message are:
- Open
- Keepalive
- Update
- Notification
BGP Message Type I: OPEN
Open messages are used to start a BGP session by requesting that a BGP session be opened over an existing TCP/IP session. Once two BGP routers have completed a TCP 3-way handshake they will attempt to establish a BGP session, this is done using open messages. In the open message information about BGP router will be available.
Routers use this message to identify itself and to specify its BGP operational parameters. Open message is always send when the TCP session is established between neighbors.
Open message include following fields: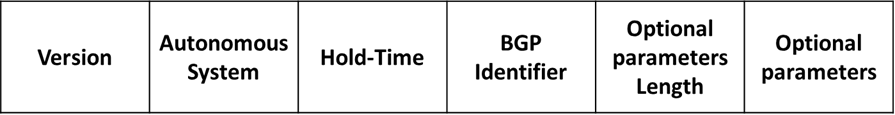
- Version – specifies the version (2, 3 or 4), default being version 4.
- Autonomous System – provides AS number of the sender. It determines whether the BGP session is EBGP or IBPG (if the AS number are the same )
- Hold-Time – indicates the maximum number of seconds that can elapse without receipt of message before transmitter is assumed to be nonfunctional. The default hold time is 180 sec. If the neighbors hold time differ, the lower of the two times become the accepted hold time.
- BGP Identifier – Provides the BGP identifier of the sender (an IP address). IOS determines identifier in exactly the same way as OSPF router ID. The highest loopback interface address is used, if there is no loopback the numerically highest IP address on a physical interface is selected.
- Optional Parameters Length – indicates the length or absence (with a zero value) of the optional parameters filed
- Optional Parameters – contains a list of optional parameters as authentication, multiprotocol support and route refresh. It includes
- Support for MP-BGP (Multi-Protocol BGP).
- Support for Route Refresh.
- Support for 4-octet AS numbers.
BGP Message Type II: KEEPALIVE
If a router accepts the parameters specified in Open message, it responds Keepalive. By default Cisco sends keepalive every 60 sec or a period equal to 1/3 the hold time.
BGP Message Type III: UPDATE MESSAGE
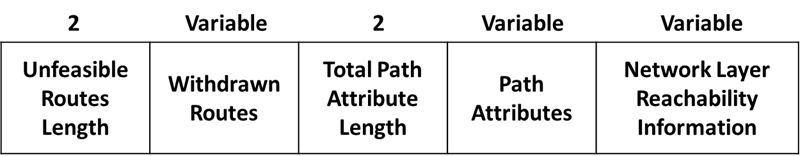
Advertises feasible routes, withdrawn routes or both. Update message contains five fields:
- Unfeasible Routes Length – Indicates the total length of the withdrawn routes field or that the field is not present.
- Withdrawn Routes — Contains a list of IP address prefixes for routes being withdrawn from. These are (Length, Prefix) tuples describing destinations that have become unreachable and are being withdrawn from service.
- Total Path Attribute Length — Indicates the total length of the path attributes field or that the field is not present.
- Path Attributes — Describes the characteristics of the advertised path. The following are possible attributes for a path.
- Origin: Mandatory attribute that defines the origin of the path information
- AS Path: Mandatory attribute composed of a sequence of autonomous system path segments
- Next Hop: Mandatory attribute that defines the IP address of the border router that should be used as the next hop to destinations listed in the network layer reachability information field
- Multi Exit Disc: Optional attribute used to discriminate between multiple exit points to a neighboring autonomous system
- Local Pref: Discretionary attribute used to specify the degree of preference for an advertised route
- Atomic Aggregate: Discretionary attribute used to disclose information about route selections
- Aggregator: Optional attribute that contains information about aggregate routes
- Network Layer Reachability Information (NLRI) — Contains a list of IP address prefixes for the advertised routes.
BGP Message Type IV: NOTIFICATION MESSAGE
This message is sent whenever something bad has happened, e.g. an error is detected and causes the BGP connection to close.
Field Length in Bytes
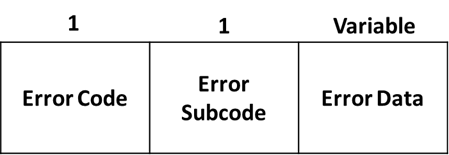
- Error Code — indicates the type of error that occurred. The following are the error types defined by the field:
- Message Header Error: Indicates a problem with a message header, such as unacceptable message length, unacceptable marker field value, or unacceptable message type.
- Open Message Error: Indicates a problem with an open message, such as unsupported version number, unacceptable autonomous system number or IP address, or unsupported authentication code.
- Update Message Error: Indicates a problem with an update message, such as a malformed attribute list, attribute list error, or invalid next-hop attribute.
- Hold Time Expired: Indicates that the hold-time has expired, after which time a BGP node will be considered nonfunctional.
- Finite State Machine Error: Indicates an unexpected event.
- Cease: Closes a BGP connection at the request of a BGP device in the absence of any fatal errors.
- Error Subcode — Provides more specific information about the nature of the reported error.
- Error Data — Contains data based on the error code and error subcode fields. This field is used to diagnose the reason for the notification message.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj