Table of Contents
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. It is classified as a path-vector protocol, designed to manage how packets are routed across the web by providing routing and reachability information.
Troubleshooting in network routing is essential to ensure a network’s stability, reliability, and efficiency. It helps identify, diagnose, and resolve issues that can disrupt communication and data flow.
In this blog, we will discuss some of the common BGP troubleshooting scenarios with possible causes and appropriate solutions.
BGP Troubleshooting
Scenario 1: Neighbor Not Establishing (Idle State)
A BGP neighbor remains in the Idle state, indicating no TCP session establishment.
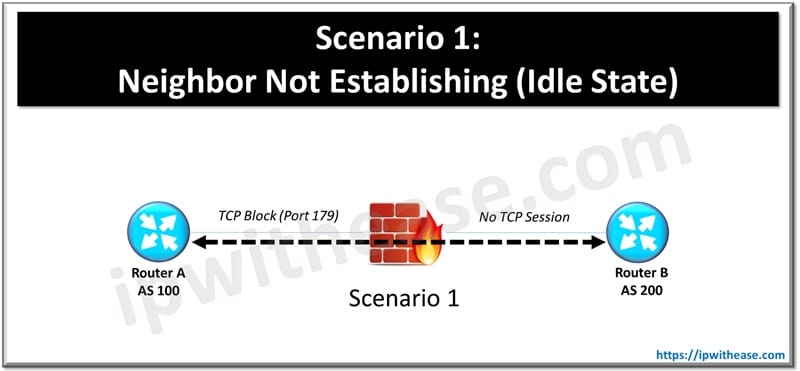
Possible Causes
- TCP port 179 blocked by a firewall.
- Incorrect neighbor IP address or AS number.
Solution
- Verify reachability using ping or telnet [neighbor-IP] 179.
- Check the BGP configuration on both routers.
- Ensure firewalls or ACLs are not blocking port 179.
Related: Common TCP FIN Issues and How to Troubleshoot Them
Scenario 2: Missing Prefixes in Routing Table
Certain prefixes are missing from the BGP table on a router.
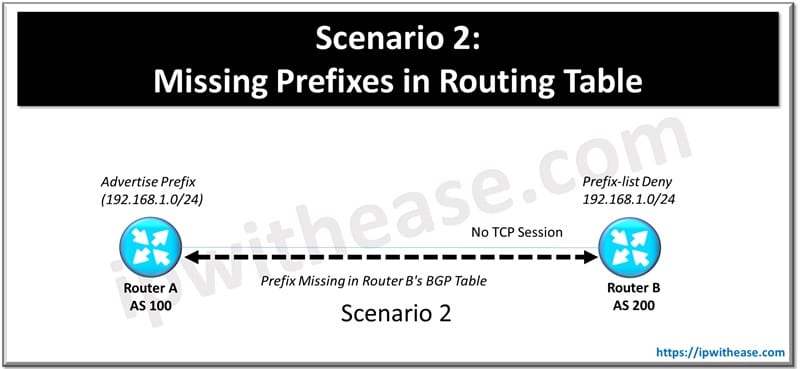
Possible Causes
- Filters (prefix-lists, route-maps) are blocking routes.
- The advertised route is not in the neighbor’s routing table.
Solution
- Check the neighbor’s advertised prefixes:
show ip bgp neighbor [neighbor-IP] advertised-routes- Verify filters with:
show run | include prefix-list- Ensure the route exists in the source router’s routing table.
Scenario 3: Flapping BGP Routes
A prefix keeps appearing and disappearing in the BGP routing table, causing instability.
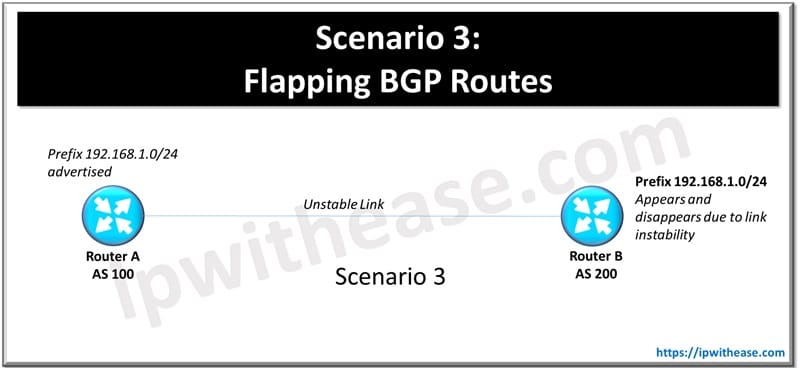
Possible Causes
- Unstable link between peers.
- Fluctuating IGP route (OSPF/EIGRP) being redistributed into BGP.
Solution
- Stabilize the link.
- Use BGP route dampening:
bgp dampening- Adjust IGP timers to reduce route changes.
Scenario 4: High CPU Usage on Router
A router experiences high CPU usage due to excessive BGP updates or large routing tables.
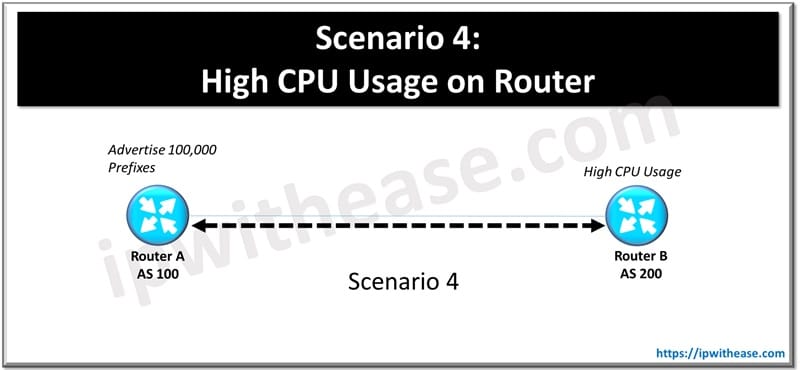
Possible Causes
- Multiple BGP peers with large numbers of prefixes.
- Inefficient filters or route summarization.
Solution
- Use summarization to reduce the number of advertised routes:
aggregate-address [summary-prefix] [mask]- Apply filters to limit received prefixes:
ip prefix-list limit-permissions- Optimize BGP timers if updates are frequent.
Scenario 5: AS Path Loop Prevention
A router rejects a route due to AS path loop detection.
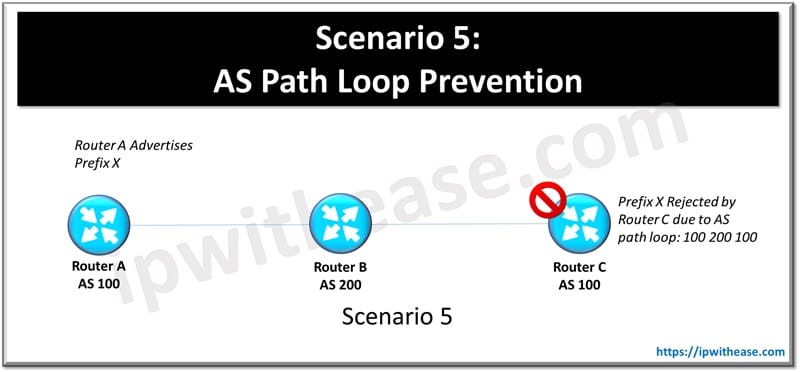
Possible Cause
The same AS appears in the AS path due to improper configuration or route reflection.
Solution
- Use the allowas-in command if the loop is intentional and safe.
- Recheck route-reflector configurations.
Effective and timely troubleshooting helps to minimize the down time as network routing problems can cause significant outages, disrupting business operations and user experience. It optimizes the network performance and enhance data integrity by rectifying and eliminating any networking anomalies like route hijacking or rogue advertisements, that can be exploited by attackers.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj