Uncertainty regarding personal cyber security and the risks of falling victim to data breaches makes users worried about protecting their networks and devices.
A recent study showed that around 86% of all respondents are concerned about their data privacy. This led to the growing popularity of security tools to keep personal data safe. But can VPN completely bulletproof your new network and device from getting hacked? Read on to find out.
What is VPN?
Knowing what VPN is and how it works is essential for understanding how it can protect your data. A virtual private network, also known as VPN, is a service that secures and protects communications over the Internet. It does so by creating an encrypted tunnel between your device and the Internet. VPN transfers all the data through encrypted servers and changes your IP to hide your online identity from websites, companies, and hackers.
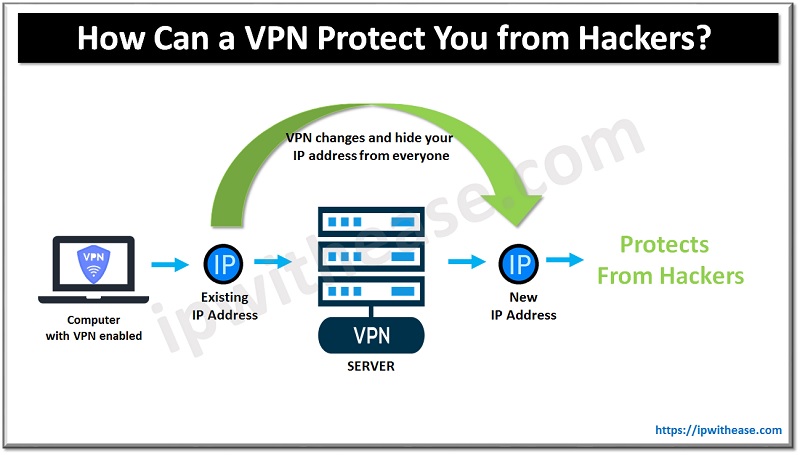
How Can a VPN Protect You from Hackers?
As mentioned above, VPNs change and hide your IP address from everyone. The software protects you from hackers by encrypting your connection and making it impossible to disguised and track you online. This doesn’t mean that VPN can protect you from any kind of attack, but it secures against specific hacker techniques that require access to your IP address.
Remote Hacking
This type of attack is focused on gaining access to your IP address by hacking into a website and stealing its logs. The hackers don’t target specific users but simply get ahold of the list of everyone who visited the hacked website. Once they have your IP address, they can find a weakness in your system and access everything connected to your Wi-Fi, including computers, laptops, mobile phones, tables, etc.
VPN masks your IP address, so it is recommended to turn it on when browsing the Internet. This way, the website logs won’t include any real data about you. With a changed IP address, hackers can’t track your online presence and target your devices and network.
Man-in-the-middle attack
As the name implies, a man-in-the-middle attack means someone else is between your connection with you and the website. You might not even notice it, but the hacker can view or tamper all data in transit that is sent over the Internet at any moment. This way, criminals can steal your personal information, including login credentials and credit card details.
Nowadays, most networks are set up with an encrypted security standard to prevent this kind of attack. But even the most secure ones, like WPA3, are only partially safe. Since VPN encrypts your online activity, it adds an additional security layer to protect your network from intercepting.
DDoS/DoS Attack
A distributed denial of service is a commonly used type of attack. It requires a hacker to know your IP address and then flood it with huge amounts of unwanted traffic and requests. The result of a DDoS/DoS attack can make you offline for some time and crash your network connection or the website you are trying to visit. This type of attack is usually done on purpose to target a specific victim.
As mentioned above, VPN masks your IP address making it almost impossible for the hacker to target your network unless they already know your actual IP address.
Fake Wi-Fi hotspots
It is a common understanding that public Wi-Fi brings certain risks since it usually uses outdated security protocols that can be easily hacked. But fake Wi-Fi hotspots that can be masked as real cafes or bus stations are even more dangerous. Usually, hackers create these hotspots without a password, making it easy for users to join. Once connected, criminals can see everything you do online and steal your data.
The only way to protect your online identity in such cases is to use a VPN. It encrypts the data before it sends and leaves your device, so the hackers can’t see or intercept any personal information.
Attacks that VPN Can’t Protect You from
A VPN is a powerful tool that protects your network and device from hackers by hiding your IP address and encrypting your connection. So it is helpful when protecting against cyber-attacks that target your IP address and Internet connection. Unfortunately, many other types of attacks fall outside of those criteria. A VPN can’t safeguard against malware, phishing, and human errors.
Malware attack
A hacker can gain control over your device and network by using malware to inject malicious software and code into the system. Usually, malware is downloaded when you download third-party apps from untrustworthy vendors, visit unsecured websites and click on fake virus messages or pop-up ads on the web. Antivirus software like Clario, Avast, and Norton is designed to protect you from malware.
Phishing attack
A phishing attack starts with a hacker who sends tons of phishing emails pretending to be from legitimate businesses. So it might be hard to spot a dangerous email if you receive many unwanted or spam messages every day. But usually, the content of the phishing emails will try to convince you to do some actions, like clicking on a link or downloading an attachment. Once you do, malware will get downloaded on your computer, giving a hacker access to your system.
Human error
Almost any action on our computers requires user authorization. So even the best cybersecurity tool won’t protect your device and network if you make mistakes that lead to hacking. You might become a victim of a cyber attack by clicking suspicious links, downloading unsecure apps, or forgetting to turn on a VPN while connecting to a public Wi-Fi.
Additional Steps to Protect from Hackers
A VPN brings a strong level of security to your device and network. But as mentioned, it can’t prevent all types of attacks. So there are some additional ways to improve your security:
- Install apps from secure sources: it is recommended to download software from AppStore or trusted websites and vendors.
- Use two-factor verification: always enable multifactor authentication when possible to add one more step to your login process.
- Use antivirus: regularly run antivirus scans to identify and remove viruses and malware before they hurt your device.
- Pay attention to suspicious activity: unexpected shutdowns, freezes, overheating, strange apps, and pop-ups appearing on your device could be a sign of malware infection or hacking. Use a special mobe hack code if you notice these signs on your phone.
- Use complex passwords: you should use a different one for every account and create strong password combinations that will not be easy to guess. It should consist of at least 16 characters, with uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols.
Continue Reading:
Types of Virtual Private Network (VPN) & its Protocol
VPN vs Proxy: Detailed Comparison
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.