Table of Contents
Today we look in detail about two most powerful and distinct architectures Cisco ACI Multi Pod vs Multi-site, major differences between the two, purpose for which they are deployed and use cases.
Application centric architectures are core of networking which help to derive maximum value from data center networks powered by them. Application centric architectures (ACIs) provide flexibility to leverage ACIs policy model in single data center, multiple data centers or in public cloud environments. They let organizations expand, secure and interconnect data centers located all over the world.
About Cisco ACI Multi-Pod
Before we deep dive into these two distinct architectures we need to understand two terminologies commonly used or associated with them. A ‘Fabric’ is a spine leaf topology of Nexus 9000 series switches with a single cluster of application policy infrastructure controllers (APIC); it is a single point of management for ACI fabric. A ‘Pod’ is a set of interconnected ACI leaf and spine switches that are under the control of a specific APIC cluster.
ACI fabric could have multiple Pods and all these Pods are part of the same fabric and are under the control of the same APIC cluster. If you have multiple fabrics, each with its own APIC cluster then independent ACI clusters are referred to as ‘Sites’. A ‘Site’ is a single fabric in the ACI world.
The ACI multi-Pod architecture is an extension of pre-existing ACI fabric without the need to set up new fabric from the start. ACI Multi-pod fabric comprises two to twelve ACI Pods which are connected via an inter Pod network and managed under a single APIC cluster. It is an evaluation of what was earlier called as ‘stretched fabric’.
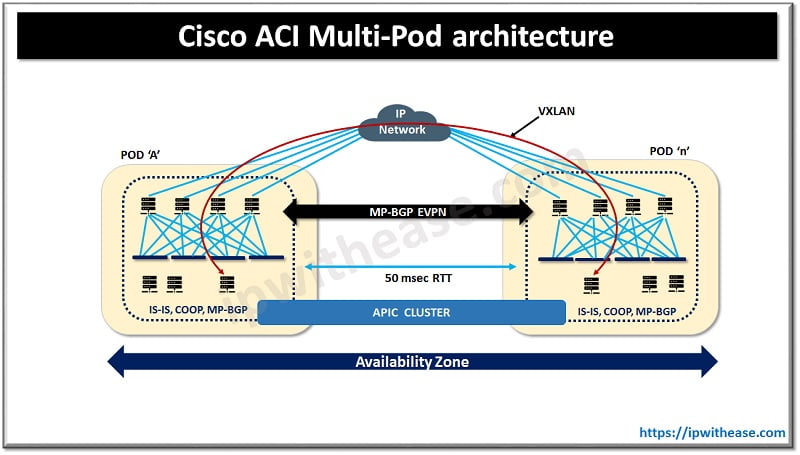
Features of Cisco ACI Multi-Pod
- Multi-Pod offers resiliency at network level across Pods and rest of the functionality remains with Single ACI fabric. Administrative overhead is minimal while extending data center network
- Connectivity and control – all Pods within topology are interconnected using an IP routed inter-Pod network (IPN) which is not managed by APIC but user can configure it separately. All inter-Pod traffic is encapsulated with VXLAN. Control plane between Pod leverages MP-BGP EVPN so endpoint information is propagated in one Pod to an endpoint to another Pod in a seamless manner.
- Ease of administration – All leaf and Spine switches deployed across Pod come under one Single APIC cluster which means they are considered a single administrative domain.
Use cases for Cisco ACI Multi-Pod
- Enhanced scalability for a large data centre footprint
- Campus data centre deployments
- Setting up disaster recovery sites
About Cisco ACI Multi-Site
ACI Multi-site is two or more fabrics (having its own APIC cluster) that are managed as a unit using ACI multi-site orchestrator. Each ACI site has a single APIC cluster managing spine leaf fabric. This is ideal where complete isolation is a requirement both at network and tenant change domain levels across ACI network setups.
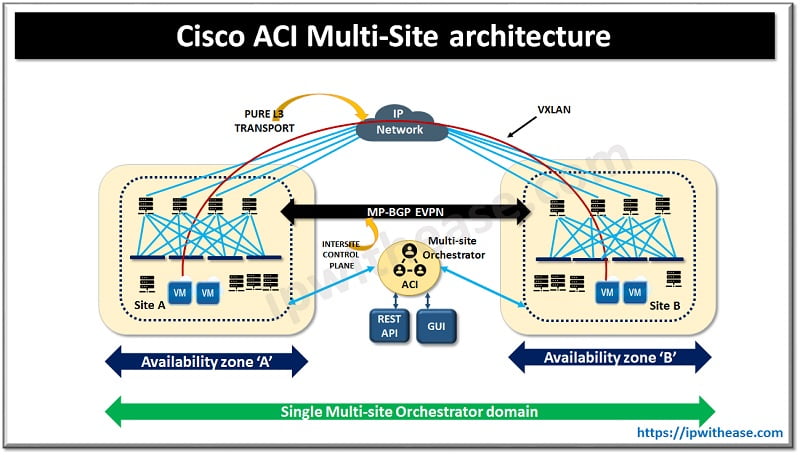
Components of Cisco ACI Multi-Site Architecture
Cisco Multi-site architecture has several functional components we will look into them more in detail as under:
- Cisco Multi-site orchestrator – is the intersite policy manager providing single pane of glass for centralized policy manager to push all intersite policy to different APIC domains, monitoring health status and score of all interconnected sites and also provides single pane of management.
- Intersite control plane is – reachability details of endpoints is exchanged across MP-BGV EVPN protocol using MAC and IP Address
- Intersite data plane is multi-site , site to site VXLAN tunnel to provide layer 2 and layer 3 endpoint communication
- Shadow EPG is specific copy of each EPG (also known as shadow EPG) are create automatically for each APIC domain when contracts between two different EPGs at each site is defined at MSO.
Features of Cisco ACI Multi-Site
- It comes complementary with Cisco APIC
- MP-BGP EVPN is used as the control plane between sites with across sites VXLAN data encapsulation
- Extends policy domain end to end across fabrics
- Enablement of global view of sites health
- Muti site policy manager GUI interface to launch site APICs
- Cross site namespace normalization is supported by connecting spine switches
- Disaster recovery scenarios to offer IP mobility through sites
Use cases for Cisco ACI Multi-Site
- Centralized data center which requires to create separate availability zones
- Disaster recovery scenarios
- Geographically distributed data centers across countries, cities, continents require a single pane of management for provisioning, monitoring and management , deployment of stretched policies across availability zones.
Comparison Table: Cisco ACI Multi-Pod vs Multi-Site
Below able summarizes the difference between the two:
| PARAMETER | CISCO ACI MULTI-POD | CISCO ACI MULTI-SITE |
|---|---|---|
| Management | APIC cluster offers the central point of management for entire multi-pod fabric | Central point of configuration and management of fabric. |
| ACI Functionality | Full ACI functionality across Mult-Pod fabric | Multi-sites have tenants, Applications, VREs, BDs, Subnets, EPGs, policies pushed across ACI fabrics |
| Availability | Single availability zone with one APIC cluster | Multiple availability zones , each fabric with its separate APIC cluster |
| Replication | Uses multicast in inter-pod network | Uses head end replication |
| VM Migration | Supports live VM migration within and across Pods | Supports live VM migration within and across sites (vSphere 6 and above) with support of IP mobility across sites |
| Traffic handling | Multi-Pod utilize multicast in inter-pod network | Handles multi-destination traffic |
| Redundancy | Redundant nodes, interfaces and devices within a fabric | Full site active / active or active/standby deployment |
| Configuration Changes | APIC cluster pushes configuration changes to Pods fabric (Preserving tenant isolation) | Selectively pushing configuration changes to specific sites enable staging/validation (preserving tenant isolation) |
| Node Count | Node count scales as per limits of a single fabric | Node count scales as per number of connected sites |
| Interconnects | Uses lower latency IP networks | It can deploy policies across continents |
| Authentication And Role-based Access Control | Authentication and RBAC enforced within all Pods of fabric | Authentication and RBAC enforced across sites |
Download the comparison table: Multi-pod vs Multi-site
Continue Reading
Cisco ACI Network Centric vs Application Centric approach
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj