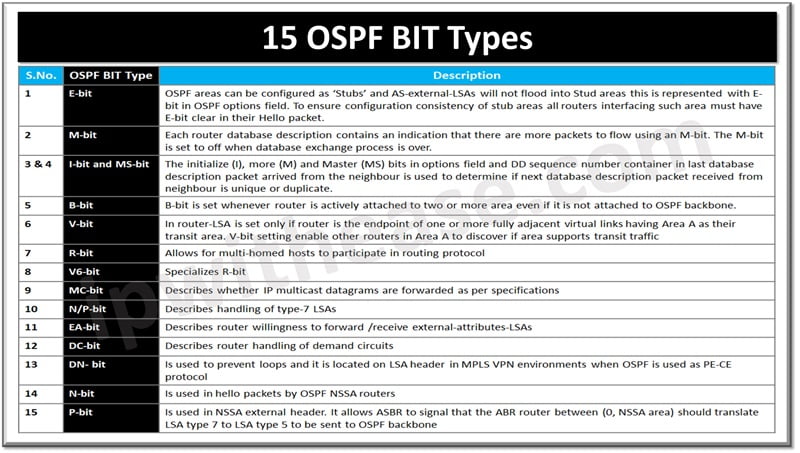
Table of Contents
About Templates
Configuration of device is maintained in a template that supports automatic rollback and deploy over devices in network without network administrator headache to configure each device.
Why we need Cisco SD-WAN Templates?
We need configuration templates to solve the issues including version control, human error, and scaling considerations when deploying to a large number of devices. It can also be automatic rollback if any issue occurred. SD-WAN solution simplifies onboarding and provisioning of a device with support mechanisms such as PNP and ZTP to automatically bring the device online and into the fabric.
Planning to Configure Template
- Hostnames
- Site ID
- Chassis Serial number of the device
- System IP
- Organization name
- Identify the number of interfaces active and assign IP address
- Define circuit transport type (Color)
Types of Cisco SD-WAN Templates
There are two types of configuration templates.
Device Template
Device templates are specific to vEdge Model. Device template is a group of a feature templates and can only be applied to specific device types. Multiple device templates for the same model of hardware, depending on the device’s location, connectivity options, or what role it is playing in the network. A device template can’t be shared across different device types.
Feature Template
Feature template can be used across multiple different device types of vEdge model. Feature templates provide the option to define variables for configuration parameters like System, VPN, Interface, OSPF, SNMP, AAA, Policy etc.
Groups of a Device Template
- Basic Information: This includes parameters such as System, Logging, AAA, BFD, and OMP feature templates.
- Transport and Management VPN: This includes configuration of VPN 0 and VPN 512.
- Service VPN: This includes BGP, OSPF, and interface parameters to be configured.
- Additional Templates: This includes a local policy, security policies, SNMP configuration templates.
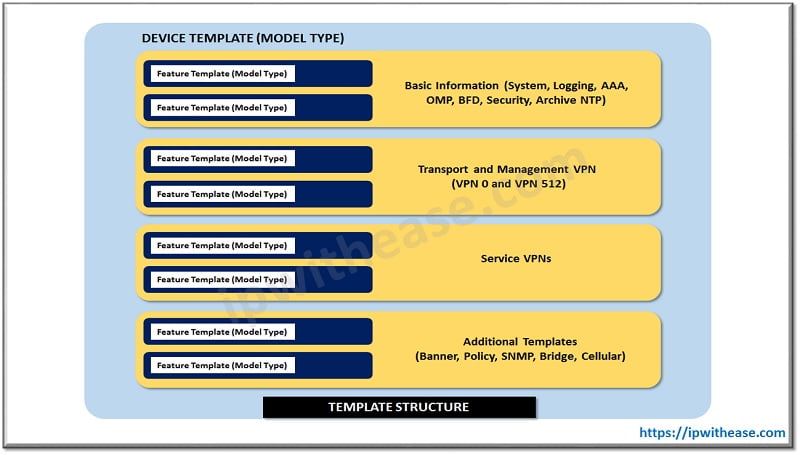
Values can be defined in a template
- Default: Factory default value. Default values cannot be changed.
- Global: This value will be same in configuration option globally applied to all devices utilizing this template.
- Device Specific: This value is specific to device with interface names. The values to these variables are set when the device template is attached to a specific device.
Options of Feature Template that can be configured
- System: Configure basic system information such as System IP, Site ID, and Hostname, organization name.
- Logging – Configure logging to a remote logging server to collect logs.
- AAA: Specify the authentication method and configure Radius, TACACs, or local authentication.
- BFD: BFD configure the timers and app-route multipliers for each transport or color. BFD timers are used for App-Aware Routing.
- OMP: timer configuration Change graceful restart timers or control redistribution from other routing protocols into OMP.
- Security: Change IPsec security settings such as anti-replay, authentication, and encryption.
- Archive (optional) – Archive the running configuration with in a specific defined time onto a file server.
- NTP (optional) – Configure the NTP server and authentication if required.
- VPN: Define a service VPN, routing protocol and redistribution, or static routing.
- BGP: BGP configuration in a VPN or VRF.
- OSPF: Configuration of OSPF in a VPN or VRF.
- VPN Interface: Define an interface that is part of a service VPN or VRF. Configuration parameters like IP Address, QoS, ACLs, and NAT.
- VPN interface bridge (optional): Configure layer 3 parameters of a bridge interface, like IPv4 address, DHCP helper, ACLs, VRRP, MTU, and TCP MSS.
- DHCP server (optional): Configure DHCP server characteristics
- Banner (optional): Configure the login banner or message-of-the-day banner (MOTD).
- Policy (optional): Attach a localized policy.
- SNMP (optional): Configure SNMP parameters, like SNMP string and location, SNMP version, views, and communities, and trap groups.
- Bridge (optional): Define layer 2 characteristics of a bridge, like the VLAN ID, MAC address aging, maximum MAC addresses, and physical interfaces for the bridge.
- Routing protocol templates: BGP or OSPF, and VPN interface templates are configured under a VPN.
Conclusion
Cisco SD-WAN Templates are used to configure devices in network very quickly and efficiently without human error. It helps auto provisioning of device by pushing configuration in device anywhere in organization network remotely.
Continue Reading:
Cisco Viptela ZTP (Zero Touch Provisioning)
OMP Path Selection Checklist in Viptela
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj