Table of Contents
Configure Cisco Router as DNS Server
Domain Name Servers (DNS) are the Internet’s equivalent of a phone book. They maintain a directory of FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Names) and translate them to Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
This is necessary because domain names are easy for people to remember and hence end systems access websites based on IP addresses.
In scenarios where local DNS server cannot be used, corporate customers need to be fully dependent on 3rd parties like ISP or some public DNS Server.
This arrangement will have a lot of overhead and dependencies. Cisco routers have the ability to integrate DNS functionality and provide the local DNS service which gives more control to the customer.
Let’s understand below how the DNS service on the local Cisco Router can be performed in simple steps:
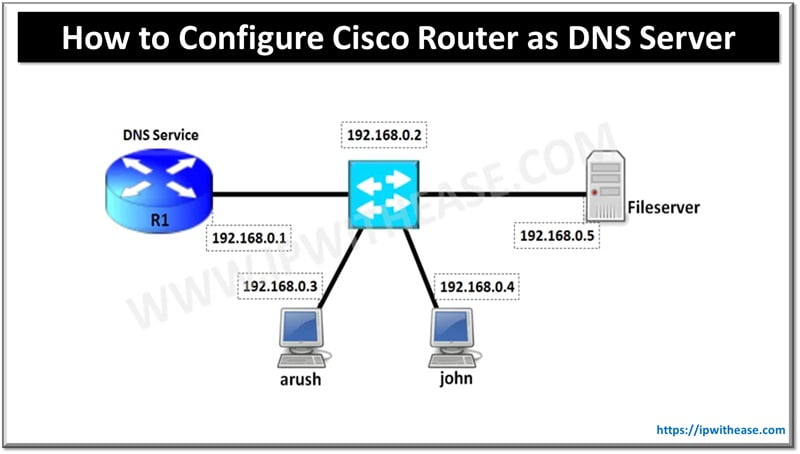
Below is the reference diagram where Cisco Router R1 (192.168.0.1) will be configured with DNS Service. Also, we have 2 workstations arush and john with IPs 192.168.0.3 and 192.168.0.4 respectively. The fileserver is given the IP 192.168.0.5.
Step 1
Enable DNS service and domain lookup on the router –
R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# ip dns server
R1(config)# ip domain-lookupStep 2
Configure the router with a public name-server. The DNS request from inside users will be sent to Router which will further send the query to DNS servers over the Internet. The IP address of the Destination is served back to the requesting workstation.
R1(config)# ip name-server 4.2.2.2Step 3
Configure the DNS server with the hostnames of your local network. In this case, when any other PC wants to ping “arush”(workstation) , the router will resolve its netbios name to the appropriate IP address. Same in the case of “filerserver”.
R1(config)# ip host fileserver 192.168.0.5
R1(config)# ip host arush 192.168.0.3Step 4
R1# ping arush
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/6 ms
--------------------------------------------------------------------
R1# ping fileserver
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.5, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/6 msStep 5
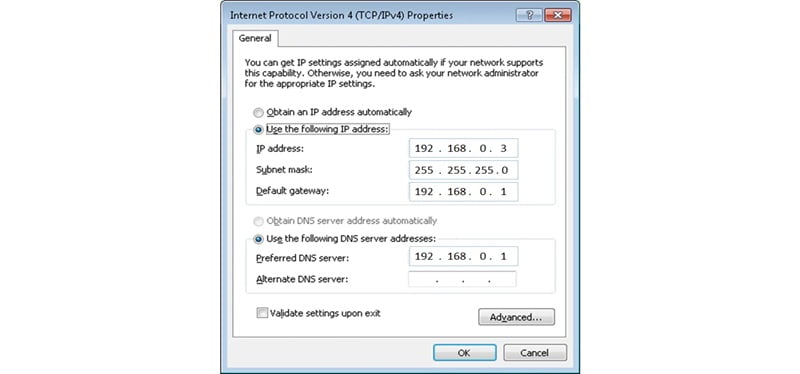
We configure the workstations and file servers to use router’s IP address as the DNS server as below –
Related- Cisco IP Host
FAQs on Cisco Router as DNS Server
Question: What is Cisco DNS?
Answer: The Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database in which you can map hostnames to IP addresses through the DNS protocol from a DNS server. Cisco IOS image builds a cache table of hostname-to-address mappings. This cache memory speeds up the process of converting names to addresses.
If your network devices require connectivity with devices in networks for which you do not control name assignment, you can assign device names via Cisco DNS that uniquely identify your devices with in the entire internetwork.
Question: How do I make my Cisco router a DNS server?
Answer: A Cisco IOS device provides DNS service to clients. CISCO Router acts as both a Cache name server and as an Authoritative name server for local hosts. When CISCO Router as a Cache name server, the device points DNS queries toward name servers that resolve network name into IP address. Cache name server caches the DNS queries so that it can answer requests quickly without having to query Authoritative servers for each transaction.
When CISCO router configured as an authoritative NS (Name Server) for local host, the device will listen on port number 53 for DNS queries and then response DNS queries using cached entries in its own host table. An authoritative NS (Name Server) usually issues zone transfers or responds to zone transfer requests from other authoritative NS (Name Server) for the same zone. Cisco IOS DNS server not able to perform zone transfers. Below are the commands used to configure router as a DNS server and mapping of hostname to IP address.
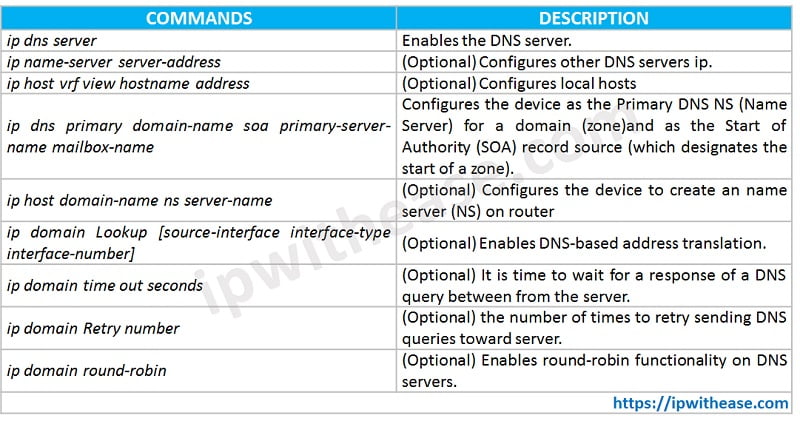
Question: What should I put for DNS server?
Answer: DNS server is responsible to translate domain names into IP addresses like nslookup www.google.com to 172.217.167.196. In DNS server IP assignment to host we have multiple options like there are public DNS services like OpenDNS and Google DNS and DNS Server of your ISP itself.
Question: What is a reason to enable (configure) DNS service on a router or switch?
Answer: Configuring DNS on a CISCO router/switch allows for easy administration from the console. It enables DNS resolution from the console. External source resolution is not allowed unless you have configured the hostnames on the DNS server.
Question: Can I use 8.8 8.8 DNS?
Answer: Yes, Google DNS is a public DNS service that is provided by Google with the aim to make the Internet and the DNS system faster, safer, secure, and more reliable for all Internet users. Google’s global DNS servers is available for anyone to use. Some ISP’s are now even preferring to assign Google’s Global DNS servers rather than use and maintain their own servers.
Question: What is Google Public DNS?
Answer: Google Public DNS is a free global Domain Name System (DNS) resolution service that can be used as an alternative to your current DNS provider and it is available to everyone and everywhere.
Question: What is OpenDNS?
Answer: OpenDNS is an American company providing DNS resolution services with features such as:
Features:
- Phishing Protection
- Content Filtering
- DNS lookup
- Cloud Computing Security
- Delivers faster more reliable home internet.
- Easy to set up.
Advantages of using OpenDNS:
OpenDNS offers DNS service that is faster and reliable. With OpenDNS, you will quickly reach out to destination and never experience the outages that occur with the DNS service provided by an ISP. OpenDNS servers store the IP addresses and hostnames of millions of websites in their cache so it would take less time to resolve user’s requests. When user request for an IP of a website that has been previously requested by another OpenDNS user, in that case DNS will cache the entry in host table and reply will be very quick. OpenDNS also has feature to block phishing sites and prevent virus and malware infections.
Disadvantages of using OpenDNS:
OpenDNS routes all traffic via the OpenDNS. They are providing all DNS host resolutions, OpenDNS records full information about Internet browsing history of user.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

I am here to share my knowledge and experience in the field of networking with the goal being – “The more you share, the more you learn.”
I am a biotechnologist by qualification and a Network Enthusiast by interest. I developed interest in networking being in the company of a passionate Network Professional, my husband.
I am a strong believer of the fact that “learning is a constant process of discovering yourself.”
– Rashmi Bhardwaj (Author/Editor)