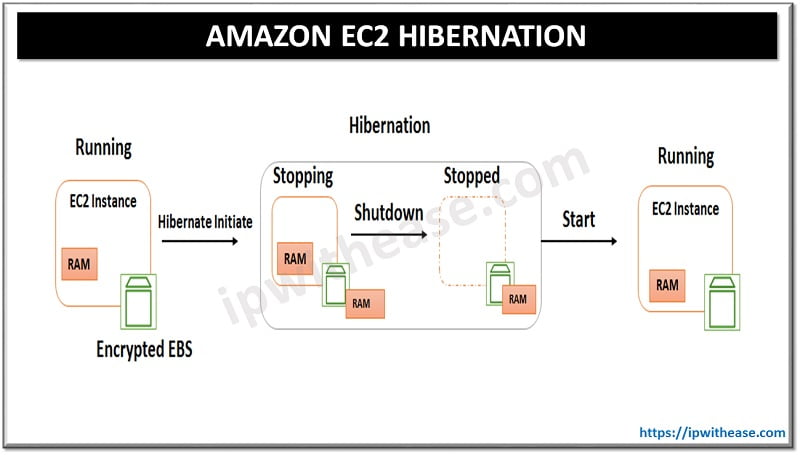
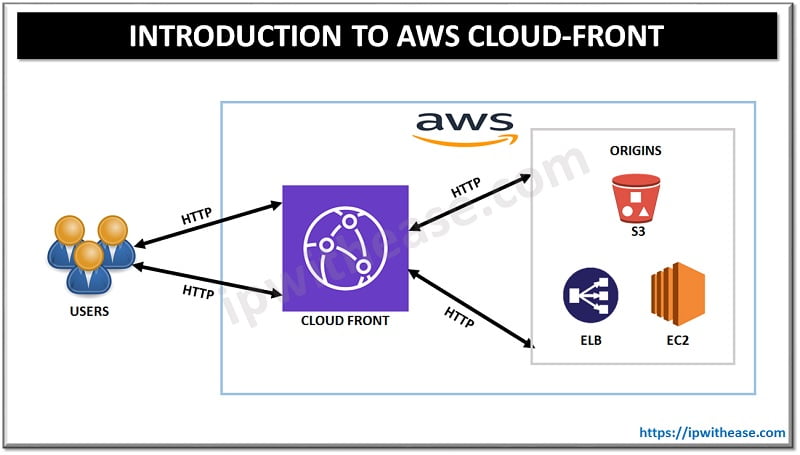
Table of Contents
We are living in an era of advanced technology and digitization. Now, almost each and every company stores its data in digital form. The increase in technology and online dependence has consequently led to rising cybercrimes that further increase the vulnerability of both devices and data. As a result, it has become crucial for companies to take action to secure their confidential information and data.
Cyber security is often the first thing that comes to our mind when we talk about cyber attacks. But nowadays, the majority of companies store their data in the cloud which makes it essential to recognize the importance of cloud computing.
This article will briefly explain what Cloud Computing and Cyber security are.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the term used to describe the delivery of hosted services over the internet. There are 3 main categories into which these services fall. They are Saas, PaaS, and IaaS. The aim of cloud computing is to offer simple use and scalable access to IT services and computing resources. It mainly focuses on networking, data management, storage, services, and devices.
The hardware and software elements are necessary for a cloud computing model’s effective execution. This is included in cloud infrastructure. Other names for cloud computing include utility computing and on-demand computing. The word “cloud computing” was inspired by the cloud symbol, which is widely used in flowcharts and diagrams to represent the internet.
Types of Cloud Services
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The on-demand paradigm for pre-configured virtualized data center computing resources is made possible by infrastructure as a service (IaaS). It includes network, storage, and operating systems. It’s crucial to think about how virtual machines are provisioned, managed, and turned down because this may require automating the production of virtual machines at scale.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) gives companies access to tools and other computing infrastructure, allowing them to concentrate on developing and running online applications and services. Development, operations, and DevOps teams are predominantly supported by PaaS systems. Here, risk management relies heavily on the maintenance and setting of self-service entitlements and rights.
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) consists of programs that are hosted by a third party and typically made available as software services via a client-side web browser. SaaS removes the need to install and maintain apps on end-user devices, yet any employee may still browse the web and download files. In order to monitor the types of SaaS applications accessed, usage, and cost, effective visibility, and access controls are necessary.
Cloud Deployments Types
How a company delivers its cloud service may reflect how it manages and safeguards its business demands and assets.
- Public Cloud
A third-party IaaS cloud provider manages a public cloud. The delivery of servers, storage, and other digital resources occurs across the internet. A customer simply requires a web browser to access services and manage accounts because the provider covers all infrastructure and bandwidth costs.
- Private Cloud
In a private cloud, networking, cloud computing services, and infrastructure are all run by a single company that is not connected to any other businesses or open platforms. One of two methods can be used to manage a private cloud: either the company’s data center is situated on-site, or a third-party vendor is compensated to host everything on a private instance.
- Hybrid cloud
It mixes on-premises storage with either private or public clouds. Security in a hybrid cloud is a joint obligation between the enterprise and the cloud service provider.
Examples of Cloud Computing
Email: It is utilized for both personal and professional tasks. But the dominant communication mechanism has completely switched from being downloaded and stored to being cloud-based. That holds true for all gadgets, including desktop computers and smartphones.
Credit/debit cards: They are becoming more and more popular as a means of payment for in-person transactions. Because every bank’s and credit card company’s database is connected to the cloud, credit and debit cards are more widely available and convenient than before. And that’s particularly true for new payment services like PayPal and Venmo.
Importance of Cloud Computing
- It protects against security breaches.
- It aids in overseeing remote work
- It facilitates crisis recovery.
- It also aids in following rules.
- It eliminates weak links and increases access levels.
What is Cyber Security?
It is the collection of tools, regulations, and security measures used to defend computer networks and devices from cyber attacks and other network intrusions that could cause interruptions in regular operations or the disclosure of sensitive data.
Among the important security that cyber security safeguards are:
- Operating system Hardening
- Protection of Password
- Firewall
- Encryption of file
Different features are available in cyber security to defend computer networks and devices against potential network threats. On the server side, it offers protection against malware, viruses, and other threats. However, it is unable to view or decrypt encrypted data sent from a user to a cloud platform.
Types of Cyber security
- Network Security: It is the act of safeguarding the digital network from cyber attacks, hackers, or other intruders, including harmful software containing malicious files, especially crucial when dealing with quantum data loading.
- Application Security: Here the objective is to keep systems & devices of the organization safe from any unseemingly harm. If an application is compromised, the data it is designed to protect may become accessible. Long before a program or device is put to use, effective security begins during the design phase.
- Information Security: Privacy & Data Integrity are protected here while any transfer or storage of data happens.
- Operational Security: It includes the choices & processes utilized for the management and safety of various data assets. This covers the rules governing where and how data may be shared, as well as the rights that users have when logging onto a network.
- Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity: This aspect deals with the way a company or business reacts when any cyber-security attack happens, or in other situations that lead to the loss of secured data or hindrance in operations. It details the process the organization uses to recover its operations and information so that regular business activities can resume. Business continuity serves as the organization’s fallback when certain resources are unavailable.
- End-user Education: It deals with the most erratic aspect of cyber security: people. Anyone who disobeys good security practices runs the risk of unwittingly introducing a virus into an otherwise protected system. Users must be instructed to remove suspicious email attachments, stay away from putting in unidentified USB devices, and other important lessons in order for a company to be secure.
Importance of Cyber security
- Protection against threats from external
- Safeguards against threats from internal
- Respect for the law
- Increased output
- Savings and added value
- Brand reputation and trust
Examples of Cyber Security
- Encryption: Encrypting data while it is in use, transit, and storage.
- Authentication: Securely identifying individuals and digital things
- Authorization: Establishing and putting into practice privileges for computing resources
- Network Security: Using methods like a network perimeter, one may secure networks
With the possibility of cybercrime increasing, the question of when data loss may happen has become more pressing. Make a commitment to regularly auditing your cloud computing data and implementing the necessary cyber security measures. By adopting a few preventative measures now, you can prevent future business disruptions.
This has also increased the unprecedented demand for Cloud Computing experts. You can clear the exam if you thoroughly know about the cloud computing course syllabus and prepare well for it from a reputed institute. The job opportunities are tremendous.
Continue Reading:
Network Vulnerabilities and the OSI Model
What is Cloud based Disaster Recovery, and Why do you need it?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.