Table of Contents
A Management Port is an Ethernet interface used for out-of-band management, allowing remote access over the network. Whereas, a Console Port is a serial interface used for direct, local device access via a console cable, typically during initial setup or troubleshooting. Let’s explore the difference between the two ports in detail.
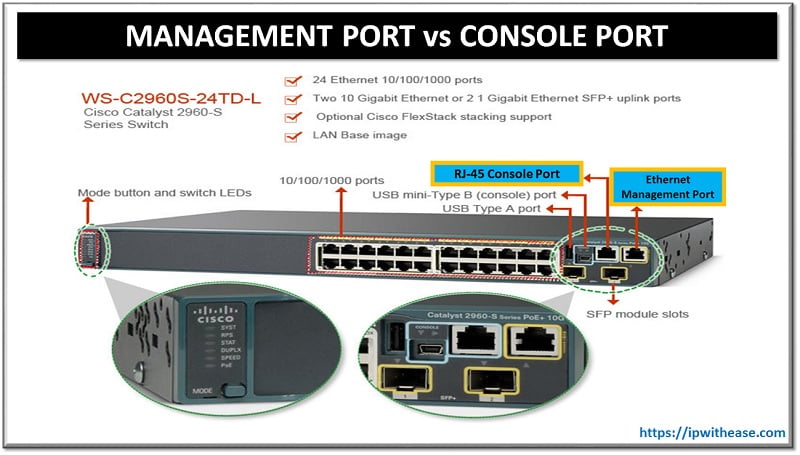
Management Port
Management Port is an Ethernet interface that provides out-of-band (OOB) access to a device over the network. It allows administrators to manage the device remotely, without relying on the main data plane.
Features
- Requires IP configuration
- Connects to a dedicated management VLAN or network
- Used for remote SSH, HTTPS, SNMP, etc.
- Often called “MGMT” or “OOB” port
Console Port
Console Port is a serial interface (usually RJ45 or USB) used to connect directly to a network device. It’s used during initial setup, recovery, or when network access is unavailable.
Features
- Requires a console cable and terminal software (like PuTTY)
- No IP needed it’s out-of-band and local
- Vital for first-time setups or password recovery
- Not dependent on network availability
Device management is essential in device provisioning, implementation, operations and configuration changes. Inband and out of band (OOB) are 2 management approaches administrators may consider. While OOB management operates on a “management plane” that is separate from the data plane used by data traffic on the device, in-band management traffic uses the same data plane as used by data traffic.
Hence OOB management can continue to function even during the event of data traffic congestion, device glitch or network attacks in addition to improved switch security.
Console port and dedicated Management port are 2 types of OOB management scenarios. Please note that Console and Management ports support non-transitive traffic and hence can’t be configured.
Related – In band and Out of Band Network Management
Difference: Console Port and Management Port
| PARAMETER | CONSOLE PORT | MANAGEMENT PORT |
|---|---|---|
| IP address Assignment | Can’t give IP address to console Port | IP address can be given to a management port |
| Communication Type | Asynchronous | Synchronous |
| Remote access via Telnet/SSH | No | Yes |
| Access required | Physical access to device required | IP reachability and TCP port 23 (for telnet) or TCP port 443 (for SSH) required or HTTP (80) |
| Segregation type | Physically separate connection | Generally a VRF based traffic segregation |
| Maximum Speed | 0.1 Mbps (115200 bps) | 1 Gbps |
| Connectivity Type | Serial , DB9 , RJ45 | RJ45 |
| Management type | Out of Band Management | Out of Band Management |
| Boot Sequence | Shows Boot sequence | Does not show boot sequence |
| SNMP, Logging on interface | No SNMP, syslog configurable on console interface | SNMP, syslog configurable on management interface |
| Application required | HyperTerminal | Telnet/SSH, Web GUI |
| Additional Features | The Console port supports these additional features: * Bit Rate 75, 110, 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 and 115200 bit/s | The Ethernet management port supports these features: * Express Setup (only in switch stacks) * Network Assistant * Telnet with passwords * TFTP * Secure Shell (SSH) * DHCP-based autoconfiguration * SMNP (only the ENTITY-MIB and the IF-MIB) * IP ping * Speed—10/100/1000 Mbps and auto negotiation * Loopback detection * Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) * DHCP relay agent * IPv4 access control lists (ACLs) |
Download the comparison table management port vs console port
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj



Than you