Table of Contents
Introduction to EIGRP
As we know, EIGRP i.e. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol is a routing protocol that specify how routers or data switches communicate with each other. It is referred to as a Transport Layer Protocol as it runs on top of the IP. Unlike application layer protocols (Telnet, BGP etc.), EIGRP has its own reliability mechanism.
EIGRP uses 5 packet types in communication with its neighbours. The routing information carried by the packets is sent reliably by means of a sequence number. The sequence number is assigned to each reliable packet (i.e. Update, Query, and Reply) and a clear-cut acknowledgment is required for that sequence number.
EIGRP uses Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) to exchange packets between the neighbors in a reliable and ordered manner.
In this article, we will discuss the packet types of EIGRP.
EIGRP Packet Types
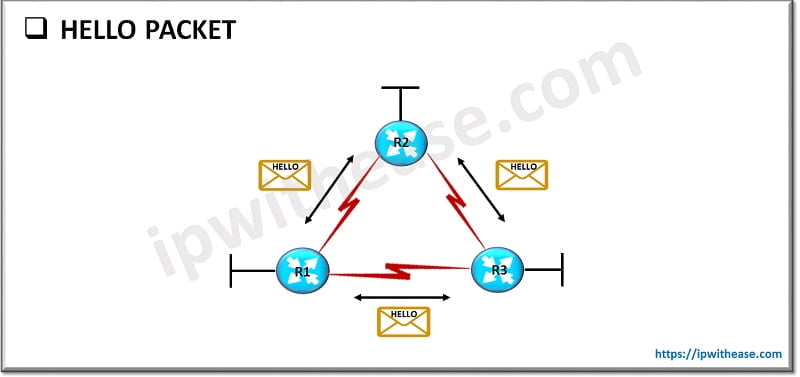
Hello Packet
EIGRP uses hello packets in the discovery of neighbors. They are multicast to 224.0.0.10. By default, EIGRP sends hello packets every 5 seconds (60 seconds on WAN links with 1.544 Mbps speeds or less). Important features of Hello Packet are:
- Opcode 5
- Neighbor discovery
- It is always multicast.
- The periodical timer is 5 seconds. Hold down timer is 15 seconds.
Acknowledgment (ACK) Packet
An acknowledgment packet acknowledges the reception of an update packet. It is a hello packet with no data. EIGRP sends acknowledgment packets to the unicast address of the sender of the update packet. Important features of ACK Packet are:
- Opcode 5
- Used to acknowledge the receipt of EIGRP packets (Update, Query and Reply)
- It is always a Unicast
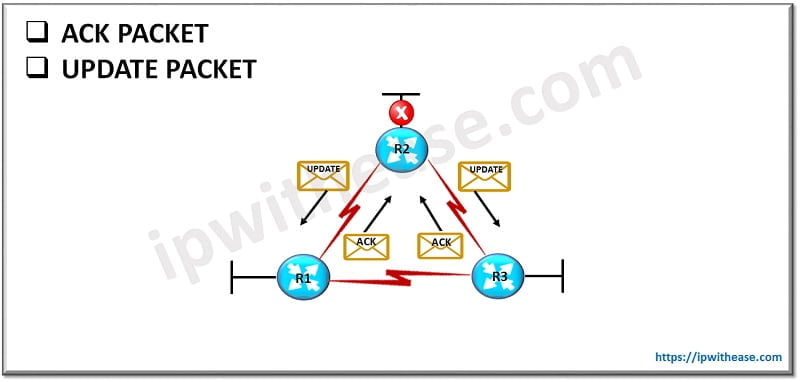
Update Packet
Update packets contain routing information for destinations. EIGRP unicasts update packets to newly discovered neighbors; otherwise, it multicasts update packets to 224.0.0.10 when a link or metric changes. Update packets are acknowledged to ensure reliable transmission. Important features of Update Packet are:
- Opcode 1
- Used to convey/propagate EIGRP routing updates
- Can be Unicast or Multicast
- Sequence Number & Acknowledgement Number
- Uses RTP
Query Packet
EIGRP sends query packets to find feasible successors to a destination. Query packets are always multicast. Important features of Query Packet are:
- Opcode 3
- Used to get specific information from neighbour router
- Can be Unicast or Multicast
- Uses RTP
- Sequence & Acknowledge numbers
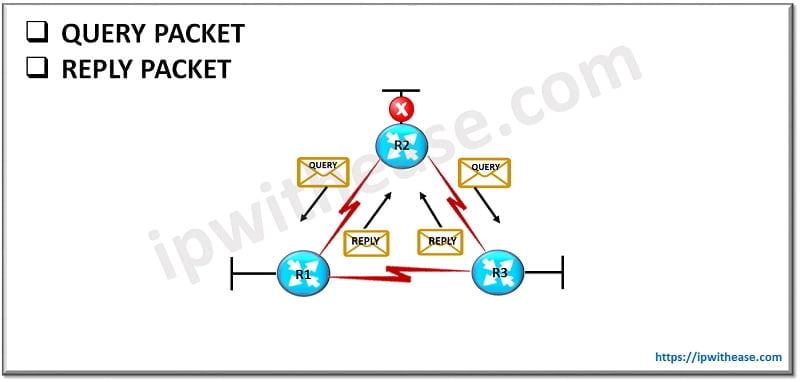
Reply Packet
EIGRP sends reply packets to respond to query packets. Reply packets provide a feasible successor to the sender of the query. Reply packets are unicast to the sender of the query packet. Important features of Reply Packet are:
- Opcode 4
- Used to respond to a query
- It is always a Unicast
- Use RTP
Comparison Table: EIGRP Packet Types
Below table summarizes the important points of differentiation between the 5 types of packets:

Download the Comparison table: EIGRP Packet types
Continue Reading:
EIGRP vs OSPF : Know the difference
Are You Preparing for Interview:
If preparing for your next interview, please go through the list of Top 100 EIGRP Interview questions.
Watch Related Video:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj