Table of Contents
Today we look more in detail about two virtualization concepts one related to virtualization of computing resources such as CPU, memory, disks, network cards and another is related to virtualization of network components such as firewalls, routers, switches, load balancers, VPN etc., their differences, advantages and so on.
Virtualization has drastically changed the way computing infrastructures are managed in today’s world. More and more organizations are moving towards adoption of virtualization technology and it is the backbone for cloud computing as well. Computing infrastructure virtualization such as CPU, memory, Disks etc. is already prevailing but organizations are now looking at a software defined approach towards virtualization of network components as well so as to decouple underlying hardware and bring in more interoperability and scalability across applications.
What is ESX
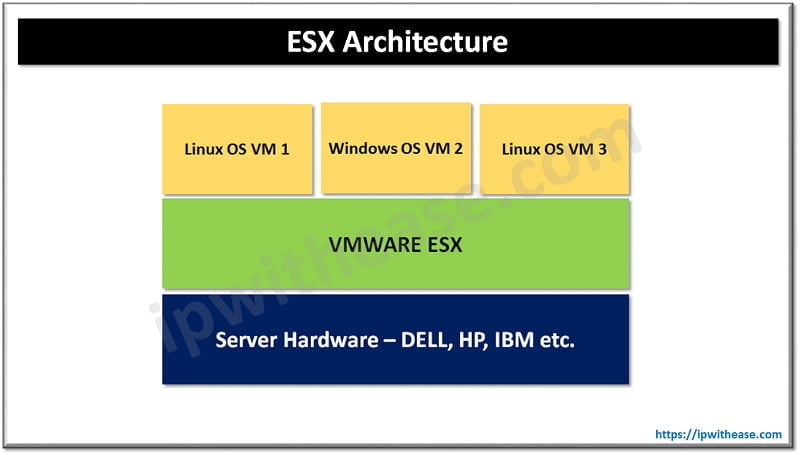
ESX server is an abbreviation for Elastic Sky X which is a virtualization tool developed by VMware. It is managed via a service console which is an operating system that manages the virtualization kernel (VMKernel). This is a bare metal hypervisor and this software can run directly on a physical server and it does not require any operating system to function. ESX can manage many virtual machines more efficiently.
VMKernel is Linux based and it tends to maximize the resources in the form of eliminating the need for an operating system to run this software. This server replicates resources of physical hardware into multiple virtual replicas and gives them to virtual machines for their use. The memory utilization is over provided hence memory limited of virtual machine can easily surpass the physical machine memory limitations.
Features of ESX
- OS independent thin architecture
- Superior consolidation and scalability
- Easy to manage with remote tools
- Reduces need for additional hardware, power and cooling
What is NSX
VMware NSX is a virtualization solution for virtual data centers and cloud environments. The NSX is a network hypervisor which is powered by virtual switches. The number of virtual switches outnumbered the number of physical switch ports. NSX leverages the concept of virtual switch and extends the capability of virtual networks. VMware NSX is made of several components as under :
- Layer 2 switch having flow-based marking , QoS and ACLs etc.
- Layer 3 router designed to do both EAST and WEST side routing
- Distributed firewall which run inside VMware kernel
- Load balancer to provide application load balancing in application
- Remote access with site-to-site VPN
- NSX API can integrate with number of different cloud management platforms
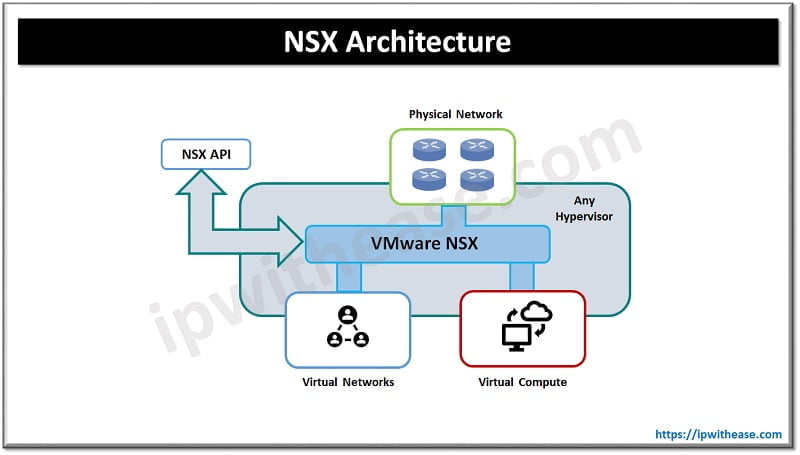
NSX works by encapsulating network traffic which is usually sent via physical switches and routers inside an encapsulation protocol like (STT, VXLAN and GRE). It helps to decouple networks from physical hardware, reproduce physical networks virtually by providing similar functions and services without the knowledge of underlying hardware, and it can integrate with cloud management applications for automation of network provisioning and management.
NSX gateway connects the virtual network to the physical network, each hypervisor is running a special VMware NSX virtual switch and NSX controllers which serve as management plane for all control. NSX is compatible with VMware vSphere, KVM, Xen , OpenStack, CloudStack and VMware vCloud automation center (vCAC) with vCloud Director (vCV).
Features of NSX
- Supports logical firewalling to secure multi-tier workloads
- Logical switching to offer isolation between workloads on different logical networks
- Application of security tags to any virtual machine and adding context about workload as needed
- Role based access control to regulate access to network resources within enterprise. Users can be assigned only one role
Comparison Table: ESX vs NSX
| FUNCTION | ESX | NSX |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtualization technology for server computing resources such as CPU, memory, disks , network adapters etc. | Virtualization technology for network resources both active and passive such as virtual switches, routers, load balancers, VPN, QoS, monitoring and security devices. |
| Purpose or aim | Overcome bottle neck associated with traditional IT computing, lower operating costs and ease of management, reduction in power consumption. | Overcome bottle neck associated with traditional network topologies , decoupling physical network hardware. |
| Working | ESXI hosts are hypervisors where VMware software is loaded. | NSX solutions are build to remove all manual configurations on switches and routers. |
| Features | Memory over commitment and deduplication, memory ballooning, network traffic shaping, network interface card teaming etc. | Offers routing with both logical distributer routers, L4-L7 load balancing , site to site and site to VPN capabilities, enables network administrator to provision and assign network and security services to applications etc. |
Continue Reading:
Difference between ESX and ESXi
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj