Table of Contents
HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol), VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol), and GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol) are all protocols used for providing network redundancy and high availability in a local area network (LAN) environment. They operate at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model and are primarily used in scenarios where multiple routers are connected to the same LAN segment.
Most of the time while deciding over First hop redundancy protocol in a network, administrator and designers start looking on pros and cons of each of these protocols – Cisco proprietary HSRP / GLBP or Open Standard VRRP. Below differentiation of HSRP vs VRRP vs GLBP, will help understand the protocols better and how one protocol edges over the other.
Here’s a brief comparison of these protocols:
HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol)
- HSRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol.
- It allows for the creation of a virtual router, with multiple physical routers participating in an HSRP group.
- One router is elected as the active router, which handles traffic forwarding, while the others act as standby routers.
- The active router sends periodic hello messages to the standby routers to ensure their availability.
- In the event of the active router’s failure, one of the standby routers is elected as the new active router.
- HSRP supports IPv4 and IPv6.
VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol)
- VRRP is an open standard protocol.
- Similar to HSRP, VRRP allows for the creation of a virtual router, with multiple physical routers participating in a VRRP group.
- One router is elected as the master router, responsible for traffic forwarding, while the others act as backup routers.
- The master router sends periodic advertisements to the backup routers to maintain their availability.
- If the master router fails, another backup router takes over as the new master router.
- VRRP supports IPv4 and IPv6.
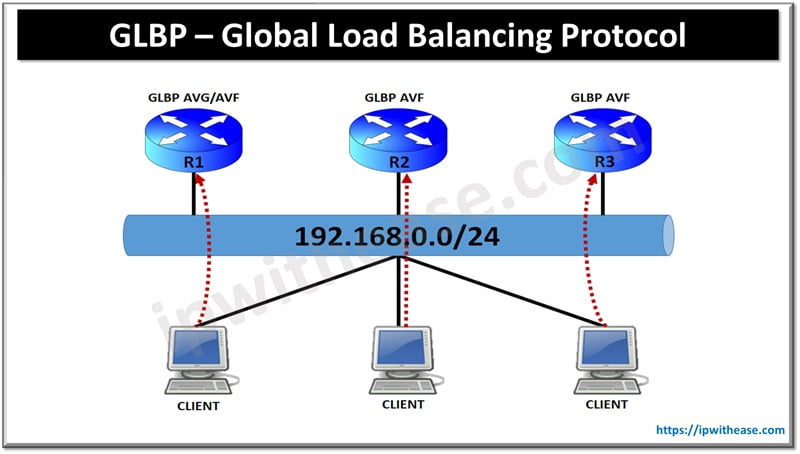
GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol)
- GLBP is a Cisco proprietary protocol.
- GLBP provides not only redundancy but also load balancing for outgoing traffic.
- Multiple routers participate in a GLBP group, with one router acting as the active virtual gateway and the others as backup virtual gateways.
- The active virtual gateway handles traffic forwarding and also assigns a virtual MAC address to each member router.
- Hosts on the LAN segment use the virtual gateway’s virtual IP address as their default gateway.
- GLBP distributes traffic among the backup virtual gateways using different load balancing methods.
- If the active virtual gateway fails, another backup virtual gateway takes over as the new active gateway.
- GLBP supports only IPv4.
Related- VRRP V2 vs V3
Comparison Table: HSRP vs VRRP vs GLBP
Below table summarizes the differences between the three type of protocols:
| Protocol Features | HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) | VRRP (Virtual Redundancy Router Protocol) | GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol) | |
| Router Role | 1 Active Router 1 Standby Router 1 or more listening Routers | 1 Master Router 1 or more backup routers | 1 AVG (Active Virtual Gateway) Up to 4 AVF (Active Virtual Forwarder) routers on the group passing traffic. | |
| Use Virtual IP Address | Can use real IP Address, if not, the one with highest priority become master. | Use Virtual IP Address | ||
| Scope | Cisco Proprietary | IEEE Standard | Cisco Proprietary | |
| Election | Active Router: 1- Highest Priority 2- Highest IP (tiebreaker) | Master Router: 1- Highest Priority 2- Highest IP (tiebreaker) | Active Virtual Gateway: 1- Highest Priority 2- Highest IP (tiebreaker) | |
| Optimization | Tracking | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Preempt | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Timer Adjustments | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Traffic Type | 224.0.0.2 – UDP 1985 (version1) 224.0.0.102 – UDP 1985 (version2) | 224.0.0.18 – UDP 112 | 224.0.0.102 – UDP 3222 | |
| Timers | Hello – 3 seconds | Advertisement – 1 second | Hello – 3 seconds | |
| (Hold) 10 seconds | (Master Down Interval)3* Advertisement + Skew time | (Hold) 10 seconds | ||
| (Skew Time)(256-priority)/256 | ||||
| Load Balancing Functionality | Multiple HSRP group per interface/SVI/routed int. | Multiple VRRP group per interface/SVI/routed int. | Load-balancing oriented – Weighted Algorithm 1. Host-dependent algorithm 2. Round-Robin algorithm (default) | |
| Requires appropriate distribution of Virtual GW IP per clients for optimal load-balancing. (Generally through DHCP) | Requires appropriate distribution of Virtual GW IP per clients for optimal load-balancing. (Generally through DHCP) | Clients are transparently updated with virtual MAC according to load-balancing algorithm through ARP requesting a unique virtual gateway. | ||
Download the comparison table: HSRP vs VRRP vs GLBP
Conclusion
HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP are all used to provide redundancy in a LAN environment. HSRP and VRRP create a virtual router with one active router and standby routers, while GLBP adds load balancing capabilities in addition to redundancy. HSRP and GLBP are Cisco proprietary protocols, while VRRP is an open standard protocol. The choice between these protocols depends on the specific requirements of the network and the equipment used.
Continue Reading
GLBP: Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj