What is MPLS?
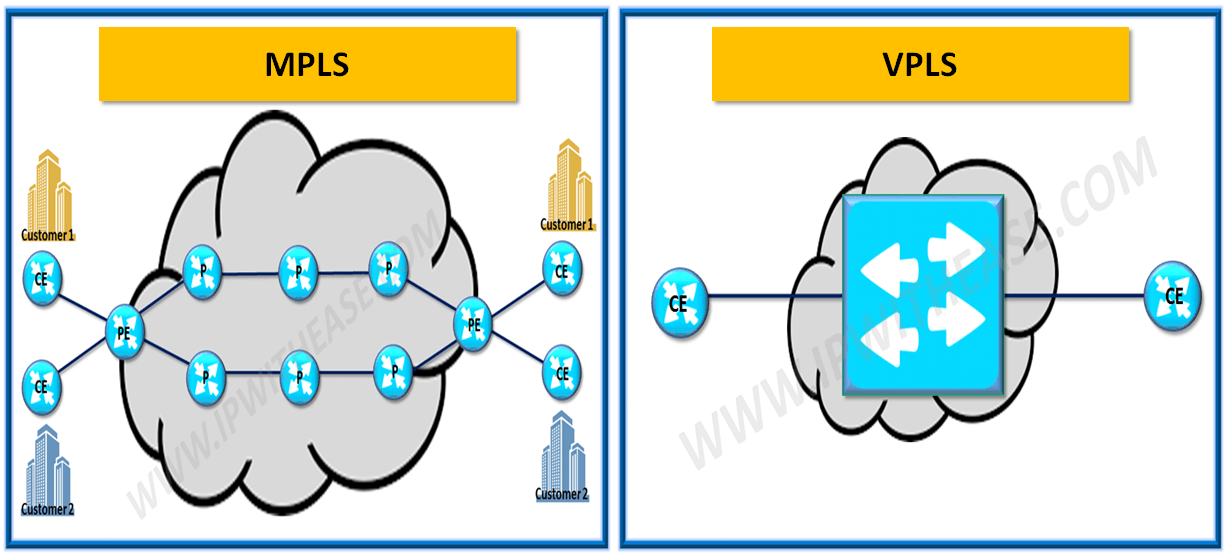
MPLS (abbreviation for Multiprotocol Label Switching) enables a service provider to provide an economical and flexible VPN across a shared network infrastructure.
MPLS sends data along the most efficient routes using labels. It directs data from one network node to the next based on labels rather than long network addresses and therefore avoiding complex lookups.
Related – 75 MPLS Interview Questions
What is VPLS?
VPLS (Abbreviation for Virtual Private LAN Service) is a service that uses MPLS to securely and seamlessly connect multiple LANs over the Internet, making them appear as if they were all on the same LAN.
VPLS extends a Layer 2 network across geographically dispersed sites using shared network infrastructure. VPLS creates a virtualized Ethernet switch at the provider’s edge to link remote sites.
While both MPLS and VPLS supporting point to multipoint connectivity across diverse customer locations, still they have contrasting characteristics.
In the case of MPLS, the provider participates and is fully aware of customer location routes including LAN, VPLS, in contrast, works as Layer 2 technology, and does not participate or control customer site routes. This arrangement where VPLS isn’t aware of customer side network routes makes it a preferred choice when it comes to financial customers or customers requiring highly secured WAN connectivity.
VPLS also becomes useful in scenarios where non-IP traffic needs to be transported over WAN towards other customer remote locations/offices.
However, VPLS pays the price in terms of scalability. Due to the VPLS principle of working as Layer 2 medium, hence Ethernet broadcasts are sent over WAN links and therefore consume bandwidth which reduces scalability.
Comparison Table : MPLS vs VPLS
Below table enumerates the difference between VPLS and MPLS –
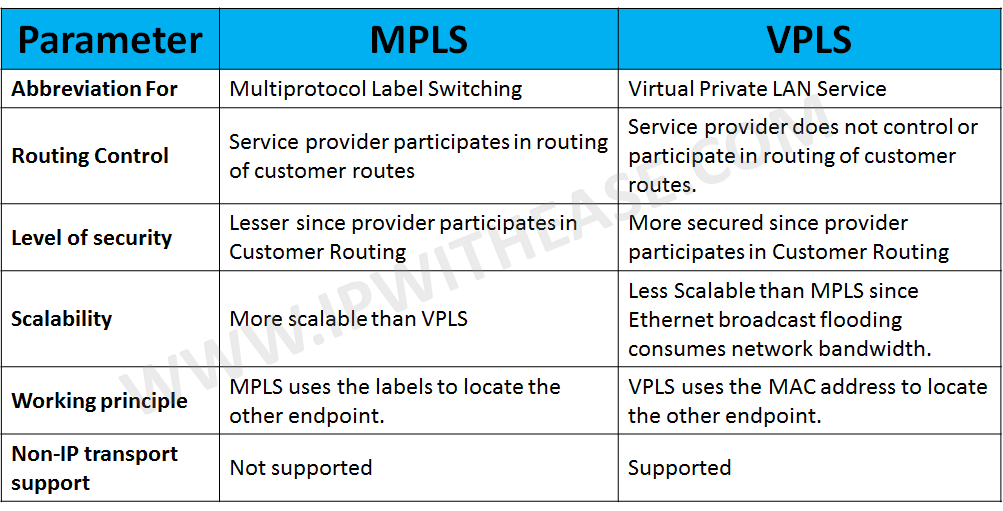
| PARAMETER | MPLS | VPLS |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation For | Multiprotocol Label Switching | Virtual Private LAN Service |
| Routing Control | Service provider participates in routing of customer routes. | Service provider does not participate in routing of customer routes. |
| Level of Security | Lesser since provider participates in customer routing. | More secured since provider does not participate in customer routing. |
| Scalability | More scalable than VPLS | Less scalable than MPLS since Ethernet broadcast flooding consumes network bandwidth. |
| Working Principle | MPLS uses the labels to locate the other endpoint | VPLS uses the MAC address to locate the other endpoint |
| Non- IP transport support | Not Supported | Supported |
![]()
Download the comparison table here.
Continue Reading:
MPLS vs Internet – Difference between MPLS and Internet
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj