Table of Contents
In today’s article, we will cover hyperconvergence technology based Nutanix architecture, what are its components and their functioning, its features and use cases.
Emergence of Hyper Convergence Technology
Data center infrastructures designed around SAN storage type since the 90s have become a standard for power critical databases but as organizations’ growing dependence on technology has happened like cloud computing, traditional SAN based storage can’t keep up with the growing IT needs.
In the year 2009 a new concept of distributed computing came into existence with the concept of hyperconvergence technology. Nutanix was the first technology company to bring into the market HCI specific product in 2011 known as Complete cluster.
What is Nutanix?
Organizations are widely using public cloud services such as Amazon web services, Microsoft Azure and google cloud for deployment of critical IT applications onto cloud to run their businesses. Public cloud services are flexible and dynamic and enable organizations agility to adapt to changing requirements.
But despite all these capabilities cloud computing has its own challenges. Hyper converged infrastructure can come to rescue here with a combination of servers and storage into a distributed platform with intelligent software which creates flexible building blocks as replacement to legacy infrastructure consisting of numerous servers, storage networks, and storage arrays.
It combines locally attached storage devices and is powered by a distributed software layer. We will understand in the upcoming section about Nutanix architecture which is the first of its kind hyper converged solution and an HCI product.
Nutanix Architecture
Nutanix cloud architecture is based on hyper converged infrastructure, and the physical layer is quite different as compared to traditional architecture. Nutanix HCI converges data center stack including compute, storage, storage networking, virtualization thus replacing separate servers, storage, and SANs.
Each node in Nutanix cluster includes compute, memory, and storage. The Nutanix operating system Acropolis Operating System (AOS) software runs on each node pool storage across, and operating system functions are distributed across all nodes within the cluster to achieve performance, resiliency, and scalability.
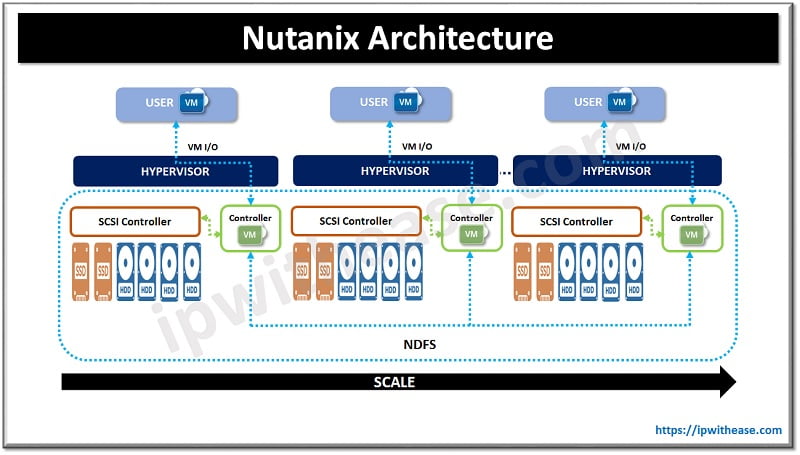
Typical Nutanix architecture includes three or more servers which will be implemented as a single Nutanix cluster. Each server contributes storage to the Nutanix cluster from their local disks on the server.
Hybrid cluster – The server provides a combination of solid-state disks (SSDs) for caching capability and hard disk drives (HDDs) for storage.
All flash cluster – The server provides solid-state disks (SSDs) for caching and storage both
Nutanix nodes run hypervisor and Nutanix controller VM (CVM). The CVM provides software intelligence to perform and is responsible for serving I/O to running VMs.
Types of Storage Configurations
Nutanix could have different type of storage configurations:
- Hybrid nodes with combined flash SSDs for performance and HDDs for capacity to storage
- All flash nodes having only traditional flash SSDs
- NVMe using NVMe SSDs
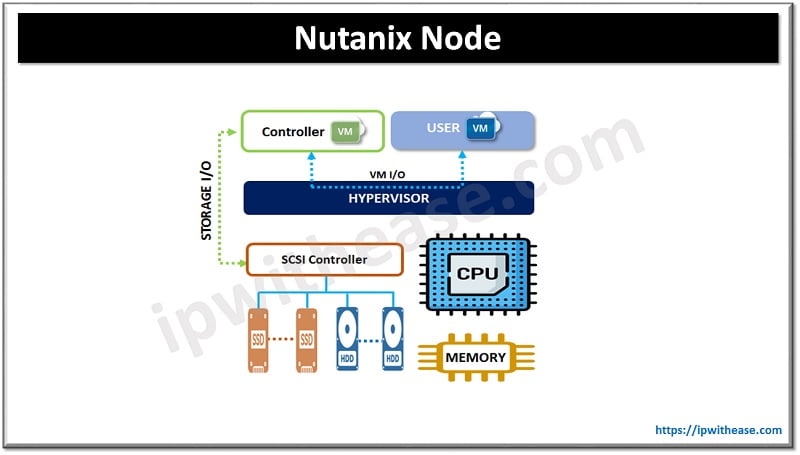
For data resiliency Nutanix uses replication factor (RF) having 2-3 data copies. RF enables block awareness and data copies are distributed across blocks for protection from failure of the entire block. Compression, deduplication, and eraser coding (EC-X) can be enabled on these. Intelligent tiering ensures data getting stored on VMs local nodes. Active data stored on fastest media for faster access.
Nutanix cluster comprises management cluster and workload cluster. Management clusters designed to run VMs to support data center management such as:
- Nutanix Prism Central
- VMware vCenter
- Active Directory Domain Controllers
- Other management workloads, such as DNS, DHCP, NTP, Syslog
Workload clusters reside in the virtual infrastructure workload domain and run tenant virtual machines. We can mix different kinds of compute clusters and provide separate compute pools depending on SLA requirements of availability and performance.
Storage clusters provide dedicated data services to tenants. Majorly deployed for specific use cases focusing on object, file, and block level storage
Edge/ROBO clusters are distinguishable from normal workload clusters by their size and limited external bandwidth.
Virtualization layer sits above physical layer, and it supports Microsoft Hyper V.
Features of Nutanix Clusters
- Multi-hypervisor support
- Implement and manage VM centric disaster recovery policies across multiple sites and data centres using multi-topology architecture
- Ability to mix diverse types of nodes into a single cluster to eliminate infrastructure silos in data centres
- Nutanix Data-at-Rest encryption satisfies regulatory requirements
- Encrypt all or selected partitions on persistent storage using strong encryption algorithm
Quick fact!
Nutanix market share in HCI market is 24.6% and 2nd largest after VMware.
Continue Reading
VxRail vs Nutanix: Hyper Converged Infrastructure
vSAN Operations Guide: Managing Fault Domains
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj