Table of Contents:
Hands-on experience is crucial for successfully learning networking concepts and protocols. Setting up a home lab allows aspirants to get practical experience configuring real Cisco equipment and topologies. This guide discusses recommended networking devices and accessories needed for a CCNA lab to help practice routing, switching and more. Lab testing is an essential part of CCNA course and certification preparation and to clear job interviews with confidence in skills.

Lab equipment You Need as CISCO CCNA Certified Expert
Below is the essential lab equipment for Cisco CCNA certified experts. Take a look:
Real Hardware Switches
Practice with physical switches is recommended to understand industrial workings. Having different models also helps learn new features. The following provide switch options:
Cisco Catalyst 2950T
This affordable layer 2 switch (~$30) supports basic switching without advanced features. However, it covers CCNA switching fundamentals like VLANs, trunking, etc. 8-port models are preferred for their quiet operation.
Cisco Catalyst 3550
As the 2950 lacks routing, this layer 3 switch enables inter-VLAN routing and router-on-a-stick configurations. At least one is needed in a CCNA lab.
Cisco Catalyst 2960/3560
These successors to 2950/3550 have additional capabilities but higher costs. Useful only if advanced features are planned for post-CCNA studies.
Avoid Cisco Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL due to lacking support for essential protocols. Stick to recommended switches above for an optimized CCNA lab.
Real Hardware Routers
For routers, Cisco 1841 and 2800 series are highly suitable:
Cisco 1841 router
This ‘end-of-sale’ router has two Fast Ethernet and two WIC module slots enabling use of different interfaces. The 1841 is affordable and its modular design facilitates practices.
Cisco 2800 series
Rack-mountable for organizing hardware, it runs Cisco IOS smoothly. However, these routers generate more noise and heat than 1800 series.
Avoid other router models lacking necessary interfaces/slots for CCNA tasks. Two 1841 routers and one 2800 series suit a balanced CCNA lab setup.
Flash Memory and RAM Requirements
CCNA labs must meet these hardware specifications:
Routers need minimum 64MB flash and 192MB RAM (1800 series) or 128MB flash and 512MB RAM (2800 series).
Incorrect memory sizes affect IOS compatibility and features support. Verify memory before router selection.
Network Cables
Cabling connects equipment’s in a lab topology:
- Cisco console cable (RS-232) for device management
- USB-to-serial converter dongle for multiple serial connections
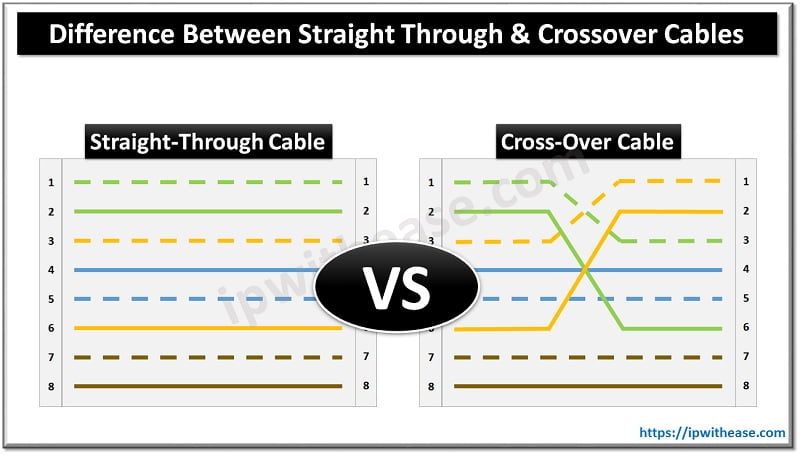
- Straight-through and crossover UTP cables for switched connections
- DB-9 or DB-25 serial cables for router WAN links
At least two each of console and serial cables are required. High-quality cables prevent operational glitches.
Software Emulators
For budget or space constraints, software emulations offer exposure to Cisco technologies:
GNS3
It runs router IOS images on a workstation. Although limited to router functions, GNS3 helps learn routing fundamentals.
Cisco VIRL
VIRL emulate both routers and switches on ESXi hypervisor. However, its resource intensive nature and licensing costs make it less suitable for entry-level CCNA labs compared to real hardware options.
Packet Tracer
As a teaching tool from Cisco, it simulates basic CCNA tasks without complex configurations. Good for beginners but real hardware eventually needed for advanced skills.
None replace hands-on practice on physical switches and routers. A combination of real and emulated devices optimally aids CCNA studies.
Related: GNS3 vs Eve-NG vs VIRL
Topology Design
Logical layout and connectivity of devices impacts learning:
- Three switches in a triangle (using multiple Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet ports) allow practicing Layer 2 protocols
- Two routers linked through WAN serial ports facilitate routing fundamentals
- Three router triangle (with redundant connectivity) enables redistribution and routing protocols experiments
Sample topologies discussed aid practicing network flows, configurations and troubleshooting – vital CCNA skills. Topology planning ensures lab functionality.
Related: Introduction to Network Topology & its Types
Device and Interface Numbering
Every switch/router has unique data and operational interface numbers. For example:
- Switch Fa0/0, Fa0/1 etc (Fast Ethernet ports)
- Router Se0/0, Se0/0/0 (Serial ports)
Knowing number conventions aids clear documentation and configurations. Interactive topology diagrams clearly depict interface mappings.
Putting It All Together
To summarize the essential CCNA lab requirements:
Switches:
- 2 x Cisco Catalyst 2950
- 1 x Cisco Catalyst 3550
Routers:
- 2 x Cisco 1841
- 1 x Cisco 2800 series
Accessories:
- Console cable, USB-to-serial adapter
- 4+ crossover and straight-through cables
- 2+ serial rollover cables
Software:
- GNS3 (optional)
This optimized combination delivers hands-on experience across CCNA topics at reasonable costs. Additional advanced devices can be added later as per career goals and evolving technologies.
Final Thoughts
A well-equipped CCNA lab is integral for networking skills development. This guide discussed choosing the right hardware switches, routers and accessories to replicate industrial environments. Combined with efficient topology design and configuration practices, it equips aspirants with practical abilities valued highly in interviews. Regular use enhances troubleshooting talent essential for professional success.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.