Introduction to SDN
As already discussed in our last blog, SDN, Software Defined Networking is the latest architecture that helps you to directly enable the control of the application and the network services.
In this article, we will discuss the business benefits of SDN technology and its advantages in the ever-changing and demanding ecosystem.
List of SDN Benefits
The list of 7 SDN benefits ( Software Defined Networking) is described below –
Ease of Management
A single management console with better visibility into network resources simplifies planning, and the setting up of networks — real and virtual. Configurational faults will also tend to trickle down with onset of SDN technology in IT infrastructure.
Cost Reduction – (CAPEX and OPEX cost optimization)
The programmable nature of SDN architecture makes it easier to design, deploy, manage and scale the networks. The ability to automate provisioning introduces agility to networks and reduces human resource requirements, resulting in lower operating expenditures.
Adopting SDN allows IT administrators to use less expensive hardware for greater effect since new devices essentially become “white box” switches with all the intelligence centered at the SDN controller.
Efficient utilization of network resources
One of the biggest drawbacks of traditional networking architectures is that the applications running at Layer7 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model have little or no visibility into resources available at the network layer. Hence, the resource requirements was hardly precise and network elements were chronically over-provisioned.
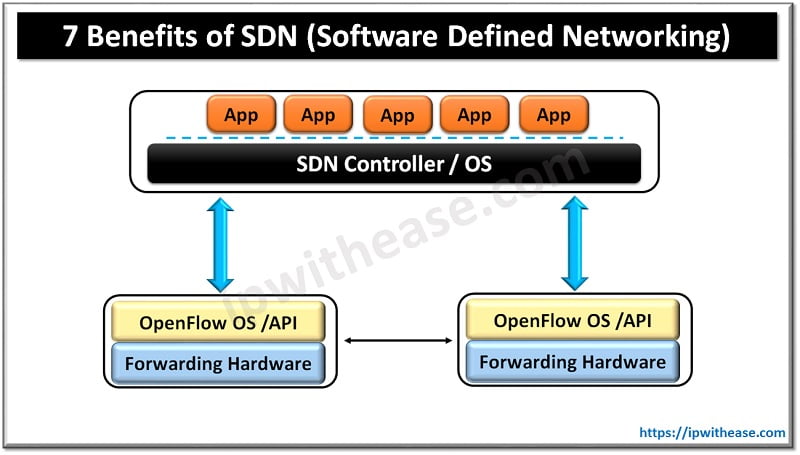
In SDN architecture, the centralized controller can see into the resource requirements of the applications and able to match the resource requirements against the resource availability, resulting in efficient utilization of networking hardware.
Centralized Network Processing
In traditional network architecture, the intelligence (i.e. algorithms to construct efficient paths are embedded within the network elements – routers, switches, etc.) and decision-making are distributed across the network. This eliminated a single point of failure problem but caused the network elements to become bloated with complexity and layers upon layers of protocols.
In the SDN architecture the decision making intelligence is at the centralized controller, which greatly reduces the complexity of network elements. By abstracting the control and data planes, SDN can accelerate service delivery and provide more agility in provisioning both virtual and physical network devices from a central location.
Enhanced Security
Virtualization has made network management more challenging. With virtual machines coming and going as part of physical systems, it’s more difficult to consistently apply firewall and content filtering polices. When you add in complexities such as securing BYOD devices, the security problem is compounded. The SDN Controller provides a central point of control to distribute security and policy information consistently throughout the enterprise.
Centralizing security control into one entity, like the SDN Controller, has the disadvantage of creating a central point of attack, but SDN can effectively be used to manage security throughout the enterprise if it is implemented securely and properly.
Improved Content Delivery and Network Performance
SDN is designed to shape and control data traffic. This means SDN can implement quality of services (QoS) for VOIP and multimedia communications. Network responsiveness is improved by SDN to ensure a flawless user experience.
Reduced Downtime
Since SDN helps in virtualizing most of the physical networking devices, it becomes easy to perform an upgrade for one piece rather than needing to do it for several devices. SDN also supports snapshotting the configuration, which helps you quickly recover from any failures caused by the upgrades.
Continue Reading:
SDN vs SD-WAN: Understand the difference
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

I am here to share my knowledge and experience in the field of networking with the goal being – “The more you share, the more you learn.”
I am a biotechnologist by qualification and a Network Enthusiast by interest. I developed interest in networking being in the company of a passionate Network Professional, my husband.
I am a strong believer of the fact that “learning is a constant process of discovering yourself.”
– Rashmi Bhardwaj (Author/Editor)