Table of Contents
Hi viewers, in this post we will walk through detailed comparison of SNAT vs DNAT and when/where are they required in the network. While in case of SNAT, the destination IP address is saved not manipulated and the source IP address is changed. On the other hand, in case of DNAT, destination address is changed and the source IP address is not manipulated. But before we continue in detail, let’s understand NAT, SNAT and DNAT terminologies –
NAT is an abbreviation for Network Address Translation. NAT occurs when one of the IP addresses in an IP packet header is changed i.e. either Source IP address or Destination IP address.
What is SNAT?
SNAT is an abbreviation for Source Network Address Translation. It is typically used when an internal/private host needs to initiate a connection to an external/public host. The device performing NAT changes the private IP address of the source host to public IP address. It may also change the source port in the TCP/UDP headers.
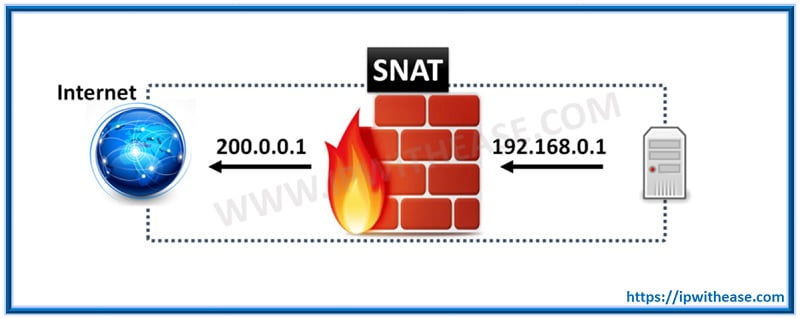
A typical scenario where we generally use SNAT is when we are required to change the private (i.e. RFC1918) address or port into a public address or port when the packets are leaving the network. In terms of order of operation on NAT device, SNAT feature comes to fore after the routing decision has been made. Moreover, when there are multiple hosts on the “inside” network who want to get to any host on the “outside” network, SNAT is used.
What is DNAT?
DNAT stands for Destination Network Address Translation. Destination NAT changes the destination address in the IP header of a packet. It may also change the destination port in the TCP/UDP headers. The typical usage of this is to redirect incoming packets with a destination of a public address/port to a private IP address/port inside your network.
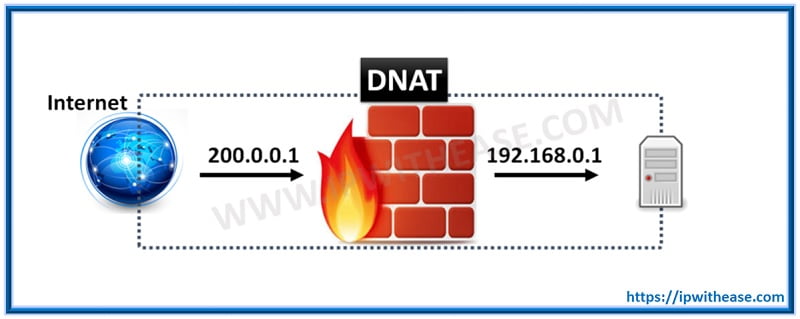
Destination NAT is performed on incoming packets, where the firewall translates a public destination address to a private address. DNAT is a 1-to-1, static translation with the option to perform port forwarding or port translation.
Users over Internet Accessing a Web Server hosted in a Data Center is a typical example where DNAT is used to hide the private Address of Web Server and NAT device translates the Public Destination IP reachable to Internet Users to Private IP address of Web Server.
Comparison: SNAT vs DNAT
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
| PARAMETERS | SNAT | DNAT |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation for | Source NAT | Destination NAT |
| Terminology | SNAT changes the private IP address of the source host to public IP address. It may also change the source port in the TCP/UDP headers. SNAT is typically used by internal users to access the Internet. | Destination NAT changes the destination address in IP header of a packet. It may also change the destination port in the TCP/UDP headers. DNAT is used when we need to redirect incoming packets with a destination of a public address/port to a private IP address/port inside your network. |
| Use Case | A client Inside LAN and behind Firewall wanted to browse Internet | A Website Hosted inside Data Center behind the Firewall and needs to be accessible to users over Internet |
| Address Change | SNAT changes the source address of packets passing through NAT device | DNAT changes the destination address of packets passing through the Router |
| Order of Operation | SNAT is performed after the routing decision is made. | DNAT is performed before the routing decision is made. |
| Communication Flow | When inside secured Network initiates communicates with outside world , SNAT happens | When outside insecured Network initiates communication with inside secured Network , DNAT happens |
| Single/Multiple hosts | SNAT allows multiple hosts on the “inside” network to get to any host on the “outside” network | DNAT allows any host on the “outside” network to get to a single host on the “inside” network |
Download the SNAT vs DNAT detailed comparison in PDF format.
Related FAQs
Q.1 How does SNAT work?
SNAT modifies the source IP address of outgoing packets from a private address to a public address. The return traffic is then sent back to the NAT device, which translates the public address back to the private address.
Q.2 Can SNAT affect inbound connections?
SNAT primarily affects outbound connections. For inbound connections, the corresponding DNAT (Destination NAT) would be used.
Q.3 How does DNAT work?
DNAT modifies the destination IP address of incoming packets to direct them to the appropriate device within a private network. The NAT device keeps track of the changes so that the response can be correctly routed back.
Q.4 Is DNAT the same as port forwarding?
Yes, SNAT and DNAT are often used together in scenarios where both the source and destination addresses need to be modified to facilitate communication between internal and external networks.
Q.5 Can SNAT and DNAT be used together?
Yes, SNAT and DNAT are often used together in scenarios where both the source and destination addresses need to be modified to facilitate communication between internal and external networks.
Q.6 What are the security implications of using SNAT and DNAT?
While NAT can help with security by hiding internal IP addresses, it should not be relied upon as the sole security measure. Proper firewall rules and other security measures should also be implemented.
Q.7 How does NAT affect protocols that embed IP address information in the payload?
Some protocols, such as FTP, SIP, or certain VPNs, embed IP address information within the payload. NAT devices must be configured to handle these protocols correctly, often requiring additional functionality like Application Layer Gateways (ALGs).
Q.8 What is a NAT table and how does it work?
A NAT table is used by a NAT device to keep track of active connections and their corresponding address translations. Each entry in the table maps an original IP address and port to a translated address and port.
Q.9 How does NAT traversal work?
NAT traversal techniques are used to establish and maintain connections through NAT devices. These techniques include STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT), TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT), and ICE (Interactive Connectivity Establishment).
If you want to learn more about NAT, then check our easy to understand Free NAT Cheatsheet in downloadable PDF Format explained with relevant Diagrams.
Related Video
For Better Understanding you can watch this video:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj


Good and concise explaination.