Telnet is the protocol that allows a user to communicate with a remote device. It is used mostly by network administrators to remotely access and manage devices.
An administrator can access the device by telnetting to the IP address or hostname of a remote device.
To use telnet, a software (Telnet client) must be installed. On a remote device, a Telnet server must be installed and running. Telnet uses TCP port 23. Telnet was designed to work within a private network and not across a public network where threats can appear
SSH is the protocol used to remotely access and manage a device. SSH uses encryption, which means that all data transmitted over a network is secure from eavesdropping.
Like Telnet, a user accessing a remote device must have an SSH client installed. On a remote device, an SSH server must be installed and running. SSH uses TCP port 22 by default.
SSH offers security mechanisms that protect the users against anyone with malicious intent while Telnet has no security measures. The security issues of Telnet required a people to use SSH in order to protect network.
Enlisted below are the key similarities between SSH and Telnet –
- Both are network protocols which allow users to login to remote systems and execute commands on them.
- Access to command line of a remote host is similar in both protocols
- Both use TCP protocol
- Both work in Client-Server Model
- Both are terminal based protocols
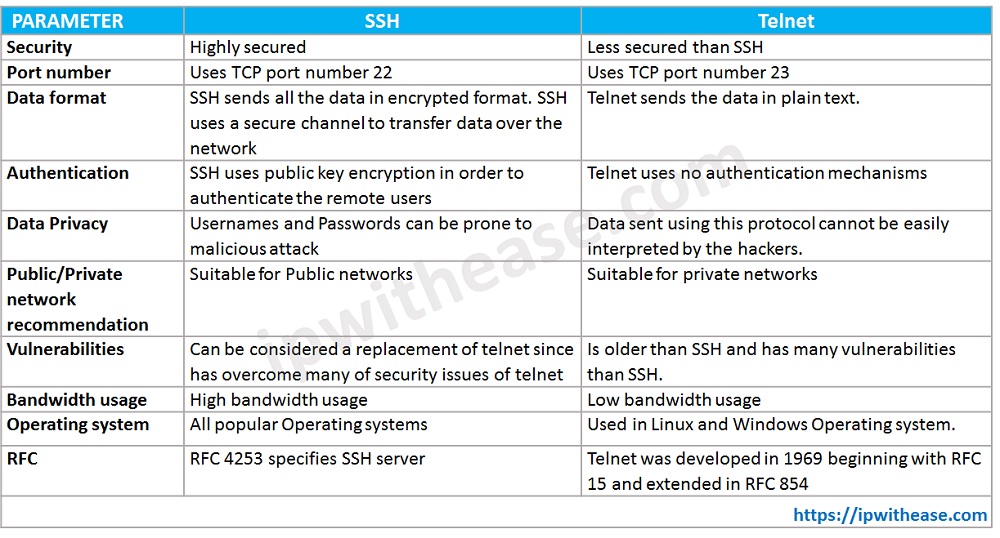
Below table elaborates the difference between both the protocols –
| PARAMETER | SSH | TELNET |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Highly secured | Less secured than SSH |
| Port number | Uses TCP port number 22 | Uses TCP port number 23 |
| Data format | SSH sends all the data in encrypted format. SSH uses a secure channel to transfer data over the network | Telnet sends the data in plain text. |
| Authentication | SSH uses public key encryption in order to authenticate the remote users | Telnet uses no authentication mechanisms |
| Data Privacy | Usernames and Passwords can be prone to malicious attack | Data sent using this protocol cannot be easily interpreted by the hackers. |
| Public/Private network recommendation | Suitable for Public networks | Suitable for private networks |
| Vulnerabilities | Can be considered a replacement of telnet since has overcome many of security issues of telnet | Is older than SSH and has many vulnerabilities than SSH. |
| Bandwidth usage | High bandwidth usage | Low bandwidth usage |
| Operating system | All popular Operating systems | Used in Linux and Windows Operating system. |
| RFC | RFC 4253 specifies SSH server | Telnet was developed in 1969 beginning with RFC 15 and extended in RFC 854 |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj