Introduction to eBGP
eBGP is a flavour of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) used for communication between different autonomous systems (AS). eBGP functions as the protocol responsible for interconnection of networks from different organizations or the Internet. eBGP is used and implemented at the edge or border router that provides interconnectivity for two or more autonomous system.
In this post, we will discuss on how to troubleshoot indirectly connected eBGP Neighbors.
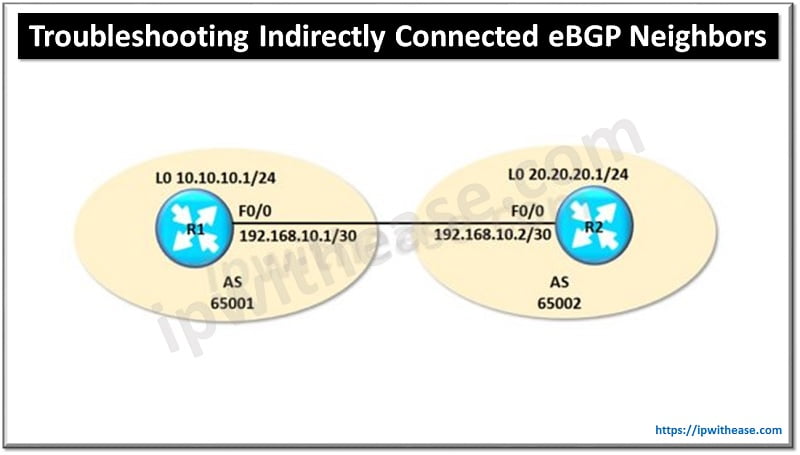
Example Scenario: Indirectly connected eBGP neighbors
As show in above diagram, two Routers need to form eBGP session through Loopback Interfaces.
Now, let’s verify the configuration;
R1
Router bgp 65001
bgp log-neighbor-changes
Neighbor 20.20.20.1 remote-as 65002
R2
Router bgp 65002
bgp log-neighbor-changes
Neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 65001
Next, we issue command “show ip bgp summary” to verify BGP memory usage, BGP neighbors and the state of communication.
BGP router identifier 10.10.10.1, local AS number 65001
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
20.20.20.1 4 65002 0 0 1 0 0 never Idle
BGP router identifier 20.20.20.1, local AS number 65002
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.10.10.1 4 65001 0 0 1 0 0 never Idle
As per output of both Routers, state is showing “idle”. So, it could be due to one of following reason –
- Do we have route for indirectly connected neighbor Interface IP which we are going to use for neighbor session?
- By default, eBGP router uses TTL value 1, which means eBGP neighbors should be directly connected, but in our case neighbors are Non-Directly connected, so we need to change TTL values by using “ebgp-multihop” command.
- By default, BGP router use outgoing Interface IP address to make TCP session, so if we are going to use any other interface (like: In our example is Loopback 0) instead for outgoing interface to make neighbor relationship, then we need to specify Interface by using of Command “update-source”.
-To display all TCP transactions start of session, session errors use command “debug ip tcp transactions”
- Check if any ACL is blocking TCP port 179.
Related: What is eBGP Multihop In BGP?
So let’s first verify route for Neighbor loopback Interface IP on both routers –
C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 10.10.10.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 20.20.20.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
As per output, both routers only know directly connected Interface, and both don’t have route for Neighbor Loopback.
Step1:
Set static route or either we can use Dynamic routing for loopback Interface reachability.
Router2(config)#ip route 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.10.1
Let’s verify loopback interfaces reachability;
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 20.20.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.10.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 2/4/6 ms
As per output, now both routers have loopback interface reachability.
Step2:
Increase eBGP TTL value, because Neighbors are not using directly connected interface IP.
Router1(config-router)#neighbor 20.20.20.1 ebgp-multihop 2
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.1 ebgp-multihop 2
We have set ebgp-multihop 2, let debug;
May 1 13:26:20.837: Reserved port 0 in Transport Port Agent for TCP IP type 0
May 1 13:26:20.837: TCP: connection attempt to port 179
May 1 13:26:20.837: TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 2895227812
May 1 13:26:20.837: TCP: sent RST to 192.168.10.2:51878 from 10.10.10.1:179
May 1 13:26:20.839: Released port 0 in Transport Port Agent for TCP IP type 0 delay 240000
May 1 13:26:20.839: TCP0: state was LISTEN -> CLOSED [0 -> UNKNOWN(0)]
May 1 13:26:20.905: TCB 0xA2A3E5E0 destroyed
As per output, we can see Router2 is send TCP session using source IP of its own outgoing interface F0/0, so now we need change it.
Step3:
Lets change eBGP source interface to make TCP session.
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.10.10.1 update-source loopback 0
Now we can see BGP session is up;
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 20.20.20.1 Up
Router2#
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.10.1 Up
Step4:
Check if any ACL is blocking TCP port 179 and if so, disable the ACL or include statement to allow TCP port 179 traffic.
Continue Reading:
Troubleshooting directly connected eBGP neighbors
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj