Table of Contents
Both VPC and VSS are used basically to support multi-chassis ether-channel that means we can create a port-channel whose one end is device A, however, another end is physically connected to 2 different physical switches which logically appears to be one switch.
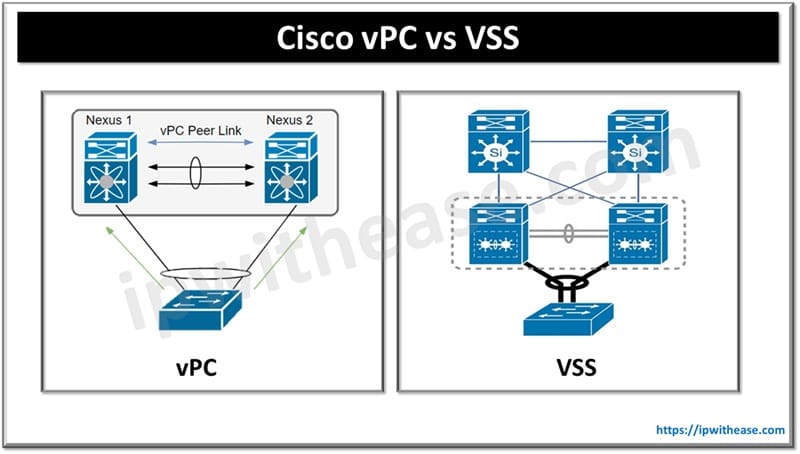
What is vPC (Virtual PortChannel)
Technology: Used in Cisco Nexus switches.
Function: Allows two Nexus switches to appear as a single switch for Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation (MLAG).
Control Plane: Each switch retains its own independent control plane.
Data Plane: Both switches forward traffic.
Peer Link: Used to synchronize MAC addresses, STP state, and other control plane information.
Pros
- No spanning-tree blocking on vPC links.
- Redundant and load-balanced connections.
- Each switch has an independent control plane, which enhances failure domain isolation.
Cons
- Requires Nexus switches.
- Configuration and troubleshooting can be complex.
- Some protocols may not be fully synchronized due to separate control planes.
What is VSS (Virtual Switching System)
Technology: Used in Cisco Catalyst switches.
Function: Merges two Catalyst switches into a single logical switch.
Control Plane: Only one active control plane; the second switch operates as a backup.
Data Plane: Both switches forward traffic.
Virtual Switch Link (VSL): Used to synchronize configuration and control plane information.
PROS
- Appears as a single switch to the network.
- Simplifies management and configuration.
- Eliminates spanning-tree blocked ports.
- Fully integrates control and data planes.
CONS
- If the active switch fails, failover occurs (with some downtime).
- More complex initial setup.
- Only supported on specific Catalyst series switches.
Comparison: vPC vs VSS
Similarities
Lets try to understand the similarities of features and functions that necessitate the need to understand the differential points before choosing one.
- Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation – Both vPC and VSS allow the aggregation of links across two physical switches, enabling a single logical connection to downstream devices.
- Elimination of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Loops – Both technologies create a loop-free topology, reducing reliance on STP and improving convergence times.
- Increased Redundancy & High Availability – They both enhance network resilience by ensuring that failure of one switch does not disrupt network connectivity.
- Single Logical Switch Appearance – Both present two physical switches as a single logical entity to connected devices, simplifying network design and operations.
- Faster Convergence – In case of a link or switch failure, both technologies provide fast recovery times, ensuring minimal disruption to traffic flow.
- Load Balancing & Efficient Traffic Distribution – Both vPC and VSS enable traffic load balancing across multiple links, improving bandwidth utilization and network performance.
- Simplified Network Management – Both reduce administrative complexity by consolidating switch management and reducing the number of control planes.
- Elimination of First Hop Redundancy Protocols (FHRPs) – In both technologies, connected devices see a single logical switch, eliminating the need for protocols like HSRP, VRRP, or GLBP between the two switches.
Differences
The Differentiation between both the feature set is tabled below –
| VPC | VSS |
|---|---|
| Feature specific to Nexus | Feature specific to catalyst 6500,4500 Series |
| Separate control plane for both switches. | 2 Switches merge to form 1 logical Switch with a single control plane. |
| Separate IP for each switch management and configuration. | Single IP for management and configuration of 1 Logical Unit (2 Physical Chassis) |
| HSRP is required. | First Hop Redundancy Protocol like HSRP not required. |
| Separate instance of STP, FHRP, IGP, BGP etc. will be required on each physical Switch of VPC. | Same instance of STP, FHRP, IGP, BGP etc. will be used on each physical Switch of VSS. |
| Both the switches are active and work individually. Only from VPC perspective are they elected primary and secondary. | Switches are always primary and secondary from all aspects. |
| Supports L2 Port Channels | Supports L3 Port Channels |
| Supports LACP | Supports PAGP and LACP |
| Control messages are carried by CFS over Peer Link and a Peer keep alive link is used to check heartbeats and detect dual-active condition | Control messages and Data frames flow between active and standby via VSL |
Download the comparison table vpc vs vss
Which One Should You Choose?
- Use vPC if you are deploying Cisco Nexus switches in a data center and need active-active forwarding.
- Use VSS if you are deploying Cisco Catalyst switches in a campus/LAN environment and prefer a single logical switch with a simpler control plane.
Continue Reading:
Nexus VPC Architecture and Components
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj