Table of Contents
What is MAC Address
In computer networking, MAC address as important as an IP address. Both work hand in hand for the delivery of information across network elements.
Now that we know that MAC (Media Access Control) is the key element in the networking world, let’s understand what a MAC address is, MAC address format, bits/ length, and its ingredients –
The MAC address is used by the Media Access Control sublayer of the Data-Link Layer (DLC) of telecommunication protocols.
Related – Control Plane vs Data Plane
Every NIC (also called LAN card) has a hardware address that’s known as a MAC, for Media Access Control. The MAC address is sometimes referred to as a networking hardware address, the burned-in address (BIA), or the physical address
A MAC address is given to a network adapter when it is manufactured. It is hardwired or hard-coded onto your computer’s network interface card (NIC) and is unique to it.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) translates an IP address into a MAC address. The ARP takes data from an IP address through an actual piece of computer hardware.
How many MAC Addresses can there be in the world?
The original IEEE 802 MAC address comes from the original Xerox Ethernet addressing scheme. This 48-bit address space contains potentially 281,474,976,710,656 possible MAC addresses. All three numbering systems use the same format and differ only in the length of the identifier.
MAC Address Format
Let’s try to understand the MAC address format with the help of the image given below.
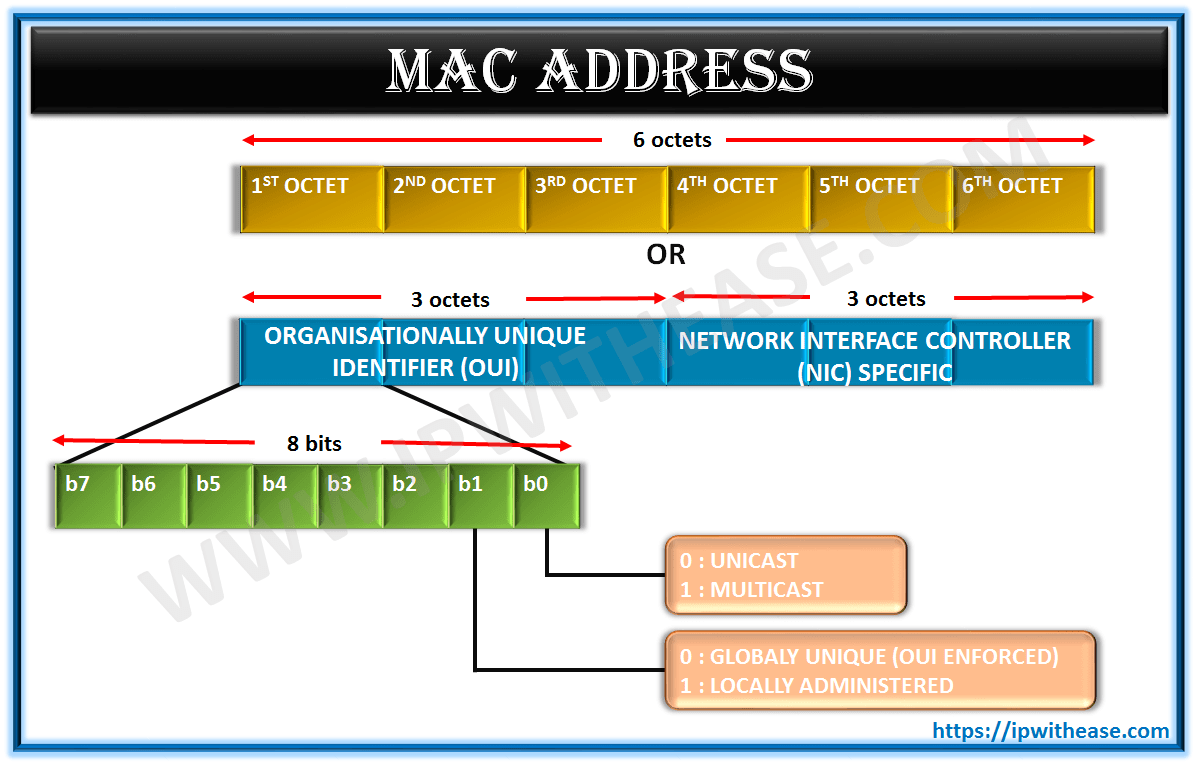
MAC Address Bits/ MAC Address Length
As shown in the above diagram, MAC addresses are 12-digit hexadecimal numbers (48 bits in length). By convention, MAC addresses are usually written in one of the following formats:
MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS or MMMM-MMSS-SSSS format
The first half (24 BITS) of a MAC address contains the ID number of the adapter manufacturer. These IDs are regulated by an Internet standards body (see sidebar). The second half (24 MORE BITS) of a MAC address represents the serial number assigned to the adapter by the manufacturer.
For example, consider a network adapter with the MAC address “00-A0-C9-01-23-45.” The OUI for the manufacture of this router is the first three octets—”00-A0-C9″ – In this case Intel corporation. Here are the OUI for other some well-known manufacturers.
Dell: 00-14-22
Nortel: 00-04-DC
Cisco: 00-40-96
Belkin: 00-30-BD
Finding a MAC Address
The table below summarizes options for finding a computer’s MAC address.
| Operating System | Method |
|---|---|
| Windows 95 and newer | winipcfg |
| Windows NT and newer | ipconfig/all |
| Linux and some UNIX | ifconfig -a |
| Macintosh with Open Transport | TCP/IP Control Panel – Info or User Mode/Advanced |
| Macintosh with Mac TCP | TCP/IP Control Panel – Ethernet Icon |
Related- Find Device MAC Address on Cisco Switch Port
MAC Address Usage
MAC addresses are used to send Ethernet frames between two stations in the same local area network. Each station has a unique MAC address that is used to identify who is the sender (source address) and who the receiver (destination address) is. But Ethernet frames can’t travel between networks. DHCP also usually relies on MAC addresses to manage the unique assignment of IP addresses to devices.
Related- How to find MAC Address of Access Point my PC is connected to
MAC Address vs IP Address
- MAC addressing works at the data link layer, IP addressing functions at the network layer (layer 3).
- The MAC address generally remains fixed and follows the network device, but the IP address changes as the network device move from one network to another.
- IP networks maintain a mapping (association) between the IP address of a device and its MAC address. This mapping is known as the ARP cache or ARP table. ARP, the Address Resolution Protocol, supports the logic for obtaining this mapping and keeping the cache up to date.
- DHCP also usually relies on MAC addresses to manage the unique assignment of IP addresses to devices.
- IP addresses are associated with TCP/IP MAC addresses are linked to the hardware of network adapters.
Continue Reading
How to Find IP Address And Network MAC Address
Static MAC Entry on the Switch
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj