Table of Contents
Management of very large networks could be daunting, complex, and challenging for network administrators. Logical segregation of networks into smaller or medium chunks ease its manageability and reduce complexity.
Subnets were introduced in networks to reduce the complexity and management overhead, improved security, and agility. Subnet is a logical division of an IP based network which divides network into smaller and better manageable networks more efficiently, securely with optimized routing of data packets across the network segments.
As networks expand in size and complexity, the challenge of finding optimal routes to handle large volumes of data traffic becomes a bottleneck leading to congestion, delays, and jitter. Then their subnets come into the picture. Subnets are smaller networks within a larger network.
In this article we will learn more in detail about subnet, how subnetting functions and its advantages and disadvantages.
What is a Subnet?
Subnet is a logical segregation of an IP based network. It allows breaking down a larger network into a smaller and more manageable subnetwork having its own unique IP address range. It is a common practice in large enterprises to break down networks into subnets and this process is known as subnetting. Subnetting is widely used to segregate resources logically, to improve network performance, enforce security policies, and monitor network traffic.
Subnets allow creation of small traffic lanes instead of all devices trying to communicate over one large single lane leading to congestion.
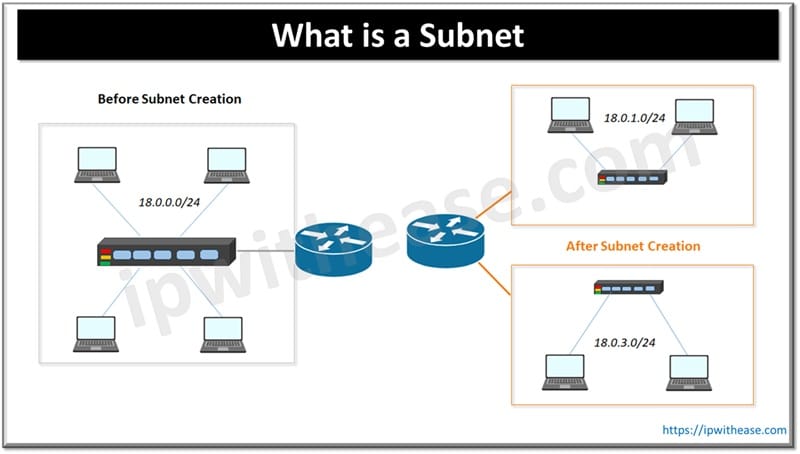
How does subnetting work?
Subnetting divides a single network into smaller networks. Any number of subnets can be created within the limits of IPv4 address space allocated to organizations. An IP address has two parts – network prefix or network ID and host ID. We will use a diagram to explain this.
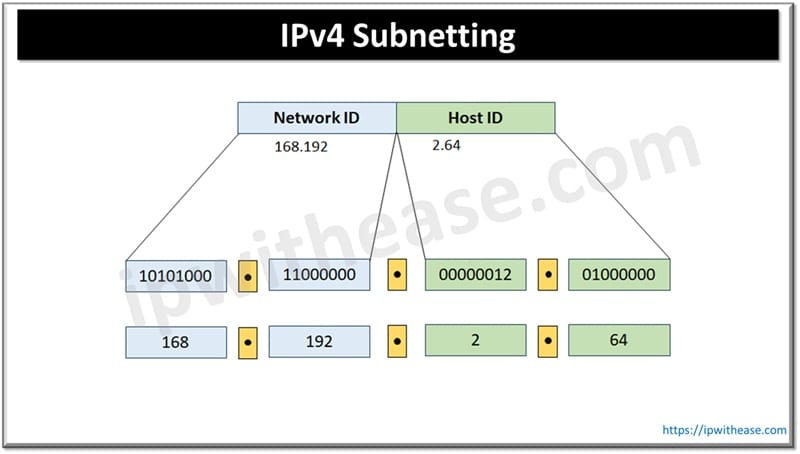
Related: What is IPv4 Subnetting?
To create a subnet, a subnet mask is required. In the subnet mask all network bits are replaced with ‘1’ and specific numbers of bits are allocated in host ID for a unique subnet generation. The subnet mask helps in routing data packets from the Internet to respective subnets. The subnet mask indicates a specific portion of address which is designated for use as subnet ID.
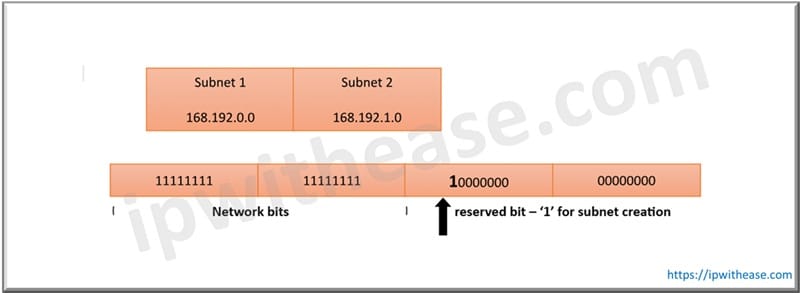
Post reserving a certain bit for subnet all remaining bits in host ID are set to ‘1’. Network ID remains unchanged.
Why is Subnetting required?
- Subnetting is required to control and manage excessive use of network IDs.
- Efficient distribution of network addresses into smaller chunks as per requirement of networks.
- Avoiding data breaches as with segregation better security policies and controls can be implemented.
- IP address wastage is controlled.
- In network channel seamless communication between each subnetwork due to traffic isolation and management.
Uses of Subnetting
- Creation of specific staffing structure to eliminate traffic and maintain order.
- Management of network efficiency with network expansions.
- Efficient routing and handling broadcast traffic with broadcast domains.
- Enhancing network security.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Subnetting
Advantages
- When a device sends a message in a network, it is received by all devices in that network. Subnets restrict the intranet work broadcast messages to specific subnet to minimize network congestion and eliminate network issues.
- Limiting network breaches with subnets as you can isolate compromised network easily.
- It eliminates wastage of network IP addresses and allows to allocate more or less IP addresses to each network segment depending on its need.
Disadvantages
- Router is required for different subnets to communicate with each other so additional hardware cost is introduced.
- Additional subnets result in high consumption of IP addresses as each subnet requires a unique broadcast address for each subnet.
- Increases network complexity and skilled network administrators are required to manage overhead of sub-netted network.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj