Table of Contents
Online businesses embarking on different digital transformations have led cloud computing services to become an important trend. These days, we’re all busy building, creating, and storing data in the cloud. Cloud services enable the use of software, applications, platforms, and infrastructures to develop an organization’s activity. Cloud service models or cloud computing service models can be categorized into three parts – IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service), and SaaS (Software-as-a-Service).
Each term refers to a resource available to users as an on-demand model. These services are typically built using a pay-per-use system, meaning users don’t have to invest much to set up and maintain IT infrastructure.
Let’s learn more about IaaS and how it differs from PaaS and SaaS.
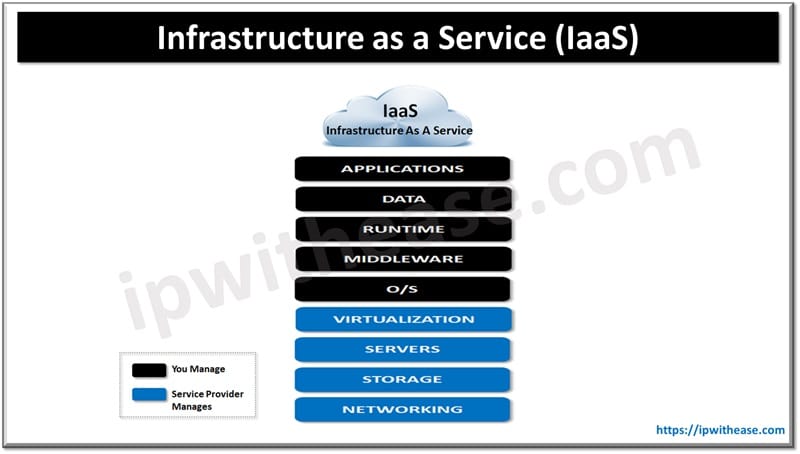
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud-based service that delivers virtualized resources – servers, storage, and networking, to businesses via the Internet. With IaaS service, organizations can build and manage servers, networks, operating systems, and data storage without buying or maintaining their own physical infrastructure. IaaS providers manage and maintain the underlying infrastructure and cater to multiple users on a single piece of hardware.
IaaS offers excellent flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice among businesses of all sizes.
IaaS leverages hyperscale cloud infrastructure provided by the major cloud providers – Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to provide vast computing, networking resources, and storage. Hyperscale cloud platforms are the backbone of IaaS, offering on-demand resources, scalability, flexibility, and capability to support millions of users simultaneously.
Related: What is Infrastructure as a Code (IaC)
Benefits of IaaS
- High performance and low latency: IaaS providers operate data centers in multiple geographies, and their customers can locate apps and services closer to users to minimize latency and maximize performance.
- Higher availability: With IaaS, a business can easily create redundant servers and even create them in other geographies to ensure availability during local power outages or physical disasters.
- Higher security: With a high level of security on site, at data centers, organizations can take advantage of more advanced security and protection than if they hosted the cloud infrastructure in-house.
- Improved responsiveness: Customers can get resources in minutes, test new ideas quickly, and roll them out to more users.
- Access to best technologies: Cloud providers compete by providing their users with the latest technologies. IaaS customers can take advantage of these technologies much earlier and at a lower cost than they can implement them on-premises.
Another key benefit of IaaS is its ability to scale rapidly in hyperscale cloud environments. These platforms provide unlimited capacity, allowing businesses to manage even the largest workloads easily. IaaS can grow dynamically as demand increases, providing more resources instantly while maintaining cost efficiency and global availability.
When to use IaaS
- Startups and small companies prefer IaaS to save money, time, and resources on hardware and software procurement.
- Larger companies running high-performance applications prefer IaaS because they want to have complete control over their applications and infrastructure.
- Companies experiencing rapid growth prefer IaaS because of its scalability, allowing them to adjust their computing resources easily as their needs evolve.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
Let’s see how different they are from each other:
| IaaS | PaaS | SaaS | |
| Used by | It is used by skilled developers (network architects) to develop unique applications | Mid-level developers use it to build applications | It is used by the end users |
| User controls | Operating system, runtime, and application data | Application data | Users have no control |
| Scalability | It is highly scalable and flexible | It is highly scalable to suit different businesses according to resources | It is highly scalable to suit small, mid, and enterprise-level businesses |
| Technical understanding | It requires technical knowledge | Basic knowledge is required for the initial setup | No technical knowledge is required as the provider handles everything |
| Computing model | It provides virtualized computing resources over the internet | It delivers tools required for the development of applications | It hosts software to make it available to clients |
Conclusion
IaaS is the go-to solution for businesses looking for a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective infrastructure. Thanks to hyperscale cloud platforms, IaaS offers virtually unlimited resources, and global reach, making it the ideal choice for rapidly growing organizations.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.