What is PKI and why do we need it? How we are very much sure that data which we are sending to our colleague has not been tampered with and arrives safely? How do we know that no one is sniffing the network and downloading sensitive data? We should be having some security mechanism in place to deliver data safely and securely. This can be achieved by Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
What is PKI (Public Key Infrastructure)?
PKI uses two keys (asymmetric encryption) to encrypt and decrypt the data to increase security.
PKI is a framework/ guideline which different systems/ vendor/ technologies can interoperate and use to provide authentication and confidentiality in data transfer.
Let’s understand how public and private keys helps to secure the communication
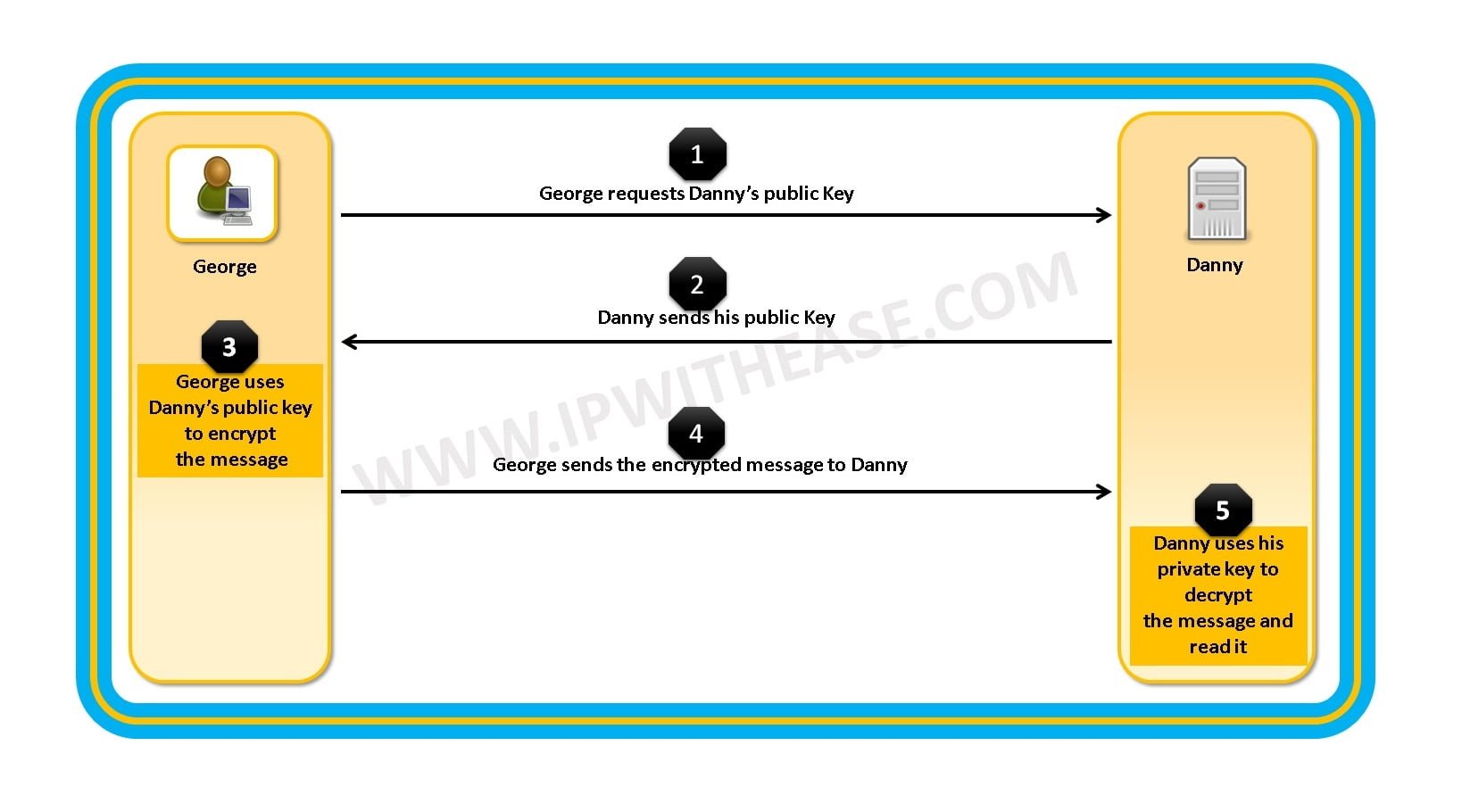
As shown in the diagram PKI (Asymmetric encryption) uses two keys instead of one, these keys are known as public and private keys. This increases security but at the cost of speed.
The keys are separate but mathematically related. The private key never leaves the original system whereas the public key, on the other hand, is distributed to other systems and does not have to be protected.
This way the sender uses the public key to encrypt the files and receiver decrypt the files using its private key.
Strength and Weakness of Asymmetric encryption –

Asymmetric Algorithms –
The most common asymmetric algorithms used are –
- Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Agreement: This algorithm does not rely on public and private keys for encryption. Instead, it uses a mathematical function that helps generate a shared secret between two parties.
- Rivest Shamir Adleman (RSA): An algorithm based on a series of modular multiplications that can be used for both encrypting and signing. You can control how secure this encryption is by using different key lengths. For instance you can use a 128 bit key or you can use a 256 bit key. Remember, longer keys (normally) result in a slower encryption and signing process but higher security.
- Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA): This algorithm uses a series of calculations based on a selected prime number and it is only used for digital signing. The maximum key size used to be 1024 bits but longer key sizes are now supported
Related- CEH Interview Question
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj