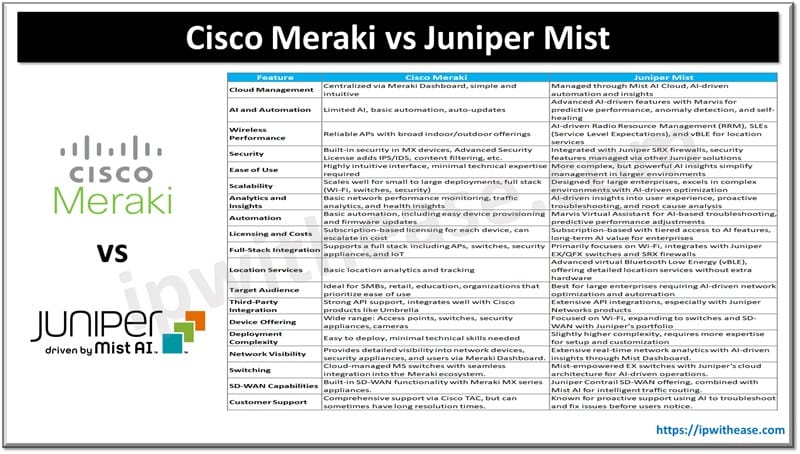
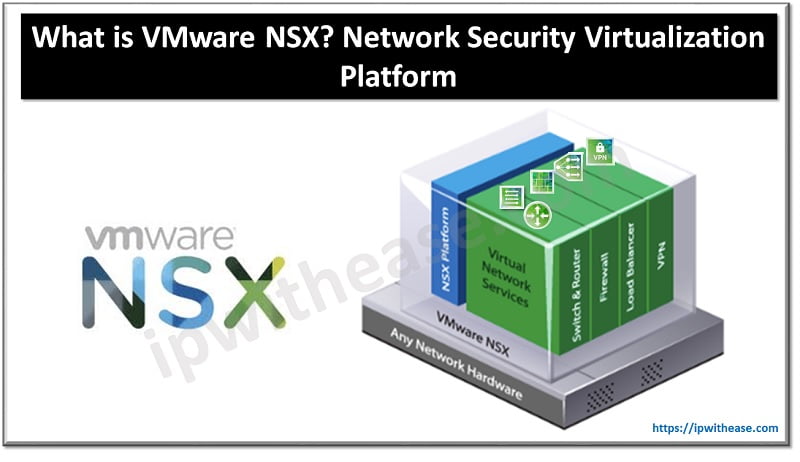
Table of Contents
Security has become a top priority as more businesses move to the cloud. However, although cloud services have inherent advantages like flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, they also open up new attack vectors.
For network engineers, ensuring the cloud is secure is no longer optional – it’s a necessity. In this post, we’ll review six essential tips to help you enhance cloud security and keep your organization’s data safe.

Mastering Cloud Security: 6 Essential Tips For Modern Network Engineers
Here are the six essential tips every network engineer should know:
1. Understand and Adhere to Compliance Standards
First, you cannot get by without knowing the compliance rules and standards applicable to your industry. Different networking sectors have different regulations when it comes to data security.
Common networking compliance frameworks include:
- GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation for protecting European citizens’ data.
- HIPAA: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act for healthcare information.
- PCI DSS: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard for credit card transactions.
Why does understanding and adhering to compliance standards matter?
Well, these regulations are in place to protect sensitive data, and if you don’t follow them, you could face serious legal and financial consequences.
What can you do? You can work closely with your compliance teams to ensure your cloud setup meets these standards. By doing so, you form a strong baseline for protecting cloud environments.
2. Stay on Top of Security Updates
As cloud environments become more complex, skill upgrades are essential to managing advanced security threats. Simply reacting to security threats isn’t enough; modern network engineers must proactively expand their knowledge.
Continuous learning is essential because it equips engineers to handle sophisticated security layers, like zero-trust models and AI-driven threat detection. To keep pace, many professionals turn to platforms which offers online courses for beginners and experienced engineers.
Modern engineering programs focus on real-world security skills and can help you stay current. You can also study to become an IT support specialist, build a solid networking foundation, and have a clear path to mastering critical IT skills.
Enrolling in more courses and taking more certifications will prepare you to manage evolving threats in cloud environments by staying updated with security patches and ongoing education.
3. Implement End-to-End Encryption
Encryption is one of the most fundamental elements of cloud security. As data moves between your on-premises infrastructure, cloud provider, and end-users, it must be encrypted to prevent interception and unauthorized access.
There are two primary forms of encryption to focus on:
- Data at Rest: Protecting data stored in the cloud (databases, file storage).
- Data in Transit: Encrypting data as it moves across the network using protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
Encrypting both ensures that even if someone intercepts your data, they can’t read or use it. Many cloud providers offer encryption tools, so adding this protective layer is now easier than ever.
4. Adopt the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
When it comes to giving users access, less is more. The Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) means employees should only have access to the necessary information and tools to do their jobs.
Why is this important? It’s important because the more people can access sensitive parts of your cloud system and data, the more vulnerable you are to security breaches.
To implement PoLP effectively:
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign permissions based on specific roles.
- Regularly review and adjust access levels.
- Keep administrative privileges limited to a few trusted individuals.
Controlling who has access to different data types minimizes the risk of unauthorized users causing damage.
5. Leverage Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone are no longer enough to secure user accounts, particularly when accessing sensitive cloud environments. MFA introduces an extra step to the login procedure by requiring users to verify their identity in multiple ways.
Think of it like this: even if someone guesses or steals your password, they’d still need another piece of information – like a code sent to your phone – to get in.
Standard MFA methods include:
- One-time passwords (OTPs) are usually sent via SMS or email.
- Hardware tokens or authentication apps.
- Biometric verification, like fingerprint or facial recognition.
Since MFA adds an extra layer of security to your cloud systems, it makes it harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
6. Proactive Cloud Monitoring and Incident Response
Monitoring your cloud environment is like having a security camera for your data. It allows you to spot suspicious activity and respond before any real and lasting damage happens. Setting up proactive monitoring tools is critical to catching potential threats early.
Here’s what you can do:
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) to flag unusual behaviors or unauthorized access attempts.
- Log management and analysis to track and audit user activity within the cloud infrastructure.
- Anomaly detection with AI-driven solutions can identify deviations from standard patterns, which might indicate a breach.
But don’t stop there; develop a comprehensive incident response plan. Remember to test this plan regularly to ensure it is current and effective.
Conclusion
Mastering cloud security requires a multifaceted approach that blends best practices with cutting-edge technology. By integrating these six essential strategies into daily practices, network engineers can build and maintain secure cloud infrastructures that support the needs of modern organizations.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.