Table of Contents
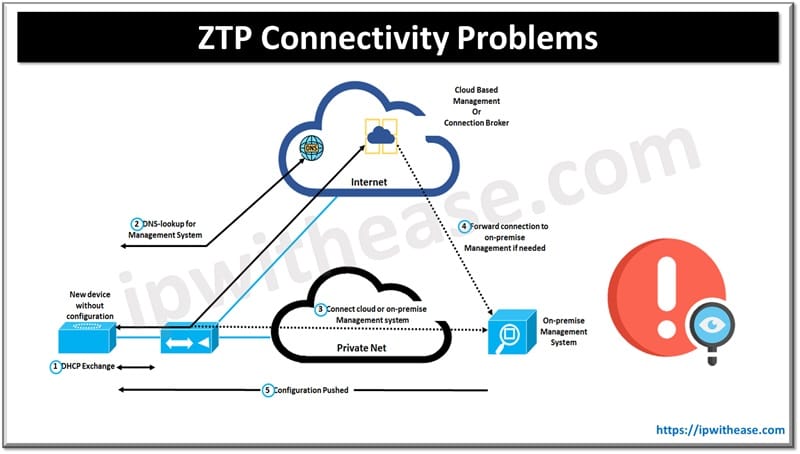
Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) relies heavily on network connectivity to automate device onboarding and configuration, but ZTP connectivity issues can halt the entire process. Here’s an in-depth outline for a blog post tackling these issues:
ZTP Connectivity Dependencies
ZTP depends on several network protocols to facilitate automated device onboarding and configuration:
- DHCP: DHCP assigns IP addresses and network settings to devices automatically. In ZTP, DHCP is crucial for providing the device with an IP address, default gateway, and other network details, so it can communicate on the network and locate configuration servers.
- DNS: DNS translates domain names to IP addresses. For ZTP, DNS is used to resolve the domain names of configuration servers or other necessary resources, enabling devices to find the correct server for downloading configuration files or firmware.
- TFTP/HTTP: TFTP and HTTP are used to transfer configuration files or firmware updates from the ZTP server to the device. TFTP is lightweight and commonly used in network booting because it requires minimal configuration, while HTTP is also popular due to its broader compatibility and flexibility in data transfer.
These protocols work together in ZTP to provide network connectivity, direct the device to the right configuration resources, and facilitate the download of necessary files, enabling automated provisioning. Reliable network connectivity is essential for successful ZTP deployment because the entire process hinges on a device’s ability to communicate with network services and servers to retrieve configuration data. It ensures that each step in the ZTP process, IP assignment, server discovery, file transfer, and secure communication; occurs seamlessly, enabling automated and efficient device provisioning.
Common Connectivity Issues in ZTP
- DHCP Configuration Problems: Misconfigurations in the DHCP server or in how devices request IP addresses.
- DNS Resolution Failures: Issues in translating domain names, impacting device reachability to configuration servers.
- Firewall and ACL Blocks: Network security measures like firewalls or access control lists can inadvertently block essential ZTP traffic.
- Latency and Packet Loss: Excessive latency or packet loss may prevent the device from receiving configuration files or firmware updates.
- MTU Size Mismatches: Mismatched MTU sizes can cause fragmentation, leading to failure in ZTP file transfers.
Diagnosis & Fixes for ZTP Connectivity Issues
DHCP Troubleshooting
Diagnosis:
>>Verify DHCP server configuration and DHCP relay settings.
>>Use packet capture to confirm that DHCP requests and responses are working.
Solutions:
>>Correct any misconfigurations in DHCP settings, such as option codes and IP ranges.DNS Troubleshooting
Diagnosis:
>>Check DNS server configuration and ensure the device has the correct DNS IP address.
>>Use tools like nslookup or dig to confirm DNS resolution.
Solutions:
>>Ensure ZTP servers are correctly registered in DNS and update as necessary.Firewall and ACL Analysis
Diagnosis:
>>Examine firewall rules and ACLs that could be blocking essential ZTP traffic.
>>Create temporary rules allowing ZTP traffic and check for connectivity improvements.
Solutions:
>>Add ZTP-specific policies allowing necessary ports and protocols.Testing for Latency and Packet Loss
Diagnosis:
>>Use ping or traceroute to analyze network latency and identify any high-loss routes.
Solutions:
>>Adjust network routing or prioritize ZTP traffic if possible to reduce latency.Verifying MTU Size
Diagnosis:
>>Use path MTU discovery tools to detect mismatches and adjust accordingly on network interfaces.
Solutions:
>>Set consistent MTU sizes across devices and network links to avoid fragmentation.Best Practices for Preventing Connectivity Issues in ZTP
- Network Documentation: Keep up-to-date network topology and configuration records.
- Automated Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to detect and alert on DHCP, DNS, or other connectivity issues.
- Regular Network Audits: Periodically audit network configurations to identify and rectify potential ZTP roadblocks.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj