Table of Contents
Adversarial AI attacks are malicious techniques which manipulate machine learning models by feeding in incorrect and unintended behaviour. As AI is being adopted to enhance cybersecurity measures across industry by unlocking faster threat detection, automated incident responses and analytical capabilities its widespread adoption is challenged by cyber criminals.
Cyber criminals are finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in AI systems and launching sophisticated attacks with manipulation of AI algorithms, bypassing conventional security protocols. These threats challenge the cyber security landscape and force cyber professionals to rethink their defense strategy.
In this article we will learn more in detail about Adversarial AI, how attackers exploit AI.
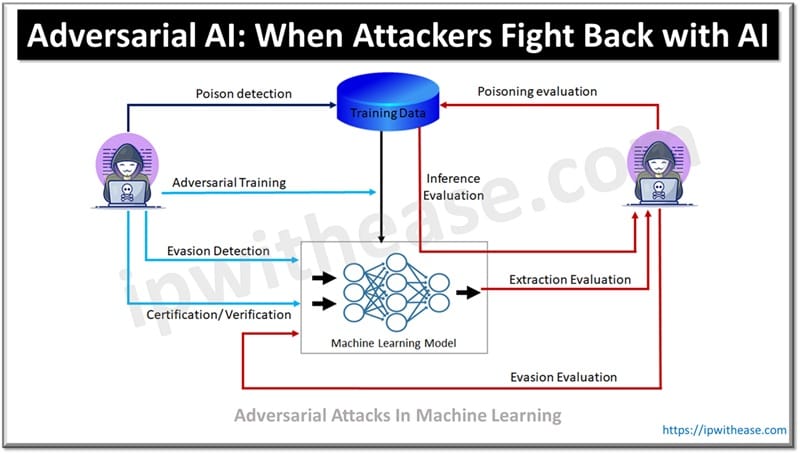
What is Adversarial AI
Adversarial attacks manipulate ML input data to mislead AI models. It tries to deceive the machine learning model by providing false inputs. Malicious data is mistaken as valid data which can affect the model, classifier and interfere with the model to generate predictions. A targeted attack modifies data to avoid detection and present itself as legitimate source.
How Attackers Exploit AI
Cybercriminals keep on looking for innovative ways to exploit AI vulnerabilities. Let’s look at some types of attacks which cybercriminals launch by exploiting AI.
Data Poisoning Attack
AI training data corruption which impacts decisions or outcome of model. By injecting malicious information into AI model attackers impact AI model behavior in adverse manner leading to manipulated output. A poisoned model incorrectly classifies a malware which would lead systems exposed to critical threats. Manipulated data trains AI to approve harmful and offensive content which undermines user security and safety. Data poisoning is difficult to detect in large and complex data sets.
Model Inversion Attacks
When model inversion attacks happen it exploits AI model output to disclose sensitive information about training data sets. These attacks leverage patterns and relationships in AI models and reconstruct personal or sensitive data which was not supposed to be exposed. Such as facial recognition systems, attackers might use model output and perform reverse engineering on image. In healthcare, attackers can extract private medical records of patients by analysis of classification and predictions made by AI systems. Publically accessible AI systems are more susceptible here as through APIs and open platform attackers can query models repeatedly to undercover hidden patterns.
Adversarial Machine Learning
It involves creation of intentional deceptive inputs to exploit AI system weaknesses. These inputs are subtle and seem inconsequential to confuse AI into making incorrect predictions or classification which are used for malicious purposes. For example, an image alteration by adding unnoticeable noise can lead to AI image recognition mistaken for someone else’s identity.
Malicious AI BOT and Automated Attacks
Malicious AI BOT and Automated Attacks enable cybercriminals to scale and automate operations with unprecedented speed. AI driven bot can execute a series of attacks such as credential surfing, phishing attacks and brute-force attacks. AI bots can learn and adapt in real time and bypass basic defences and can simulate human behavior. They can mimic user actions and infiltrate systems. For example, in credential surfing attack bots can test thousands of stolen credentials across platforms with unmatched speed. They can also be used for mass data scraping, harvesting sensitive information to launch further attacks or sell data on dark web.
Deep Fake for Social Engineering
Advanced AI algorithms are leveraged to create a hyper-realistic fake image, videos, audio. Cybercriminals can impersonate almost anyone close to individuals and enable manipulating users into harmful actions such as financial transactions or disclosure of sensitive information. CEO fraud is a common example of AI based Deep fake fraud in social engineering. An employee receives an authenticated audio, video or text message requesting purchase of Apple cards, wire transfer etc.
Weaponization using deep fakes harms reputation, spreads misinformation and impacts people’s trust in credible institutions.
AI Powered Phishing
AI Powered Phishing is an AI based new technique used by cyber criminals to deceive their victims and trick them into clicking a malicious link, or opening a fake website. Using AI cyber criminals can craft near genuine phishing messages. These attacks often use AI scrapping from social media profiles, professional networking websites, email patterns and web browsing habits. The harvested data let cyber criminals create tailored and more personal messages of recipient interest.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj