Table of Contents
SDN, Software Defined Networking is the latest architecture that is used for cost-effective, adaptable and easily manageable applications. Here, you are given spate forwarding functions and the networking controls.
It helps you to directly enable the control of the application and the network services. There is a protocol known as OpenFlow, the same is used to build SDN solutions and is considered as the fundamental element.
SDN Architecture
Moving on to the next part, that is SDN architecture. There are many benefits of SDN architecture and the reason why people prefers it. Before going to the architecture, let’s see some of the core benefits that you will get here.
- Directly Programmable: You can directly program the network control as forwarding functions are decoupled here.
- Centrally Managed: You can directly get the global view of SDN. Network intelligence will help you to do that as it is centralized in the SDN controllers.
- Easy to configure: You can quickly configure and manage all the network programs and the application.
These are various benefits that you will get when you are working with SDN.
Now, let us continue with the architecture. The architecture is complex yet when you divide it into several parts, you will get to know about the architecture easily and it will be interesting for you.
For the start, there are three main layers in the architecture, inside of which there are many component presents. The three main layers that you will see are
- Application Layer
- Control Layer
- Infrastructure Layer
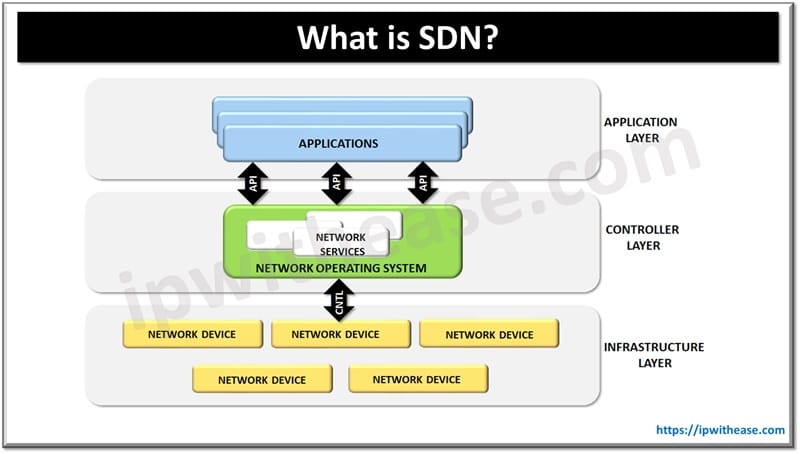
These three layers are also known as the Three Stacks of SDN. This is because all the functions and the controls are splitting into these three layers. These splitting of data forwarding functions and the controls is also known as Disaggregation. The name is simply derived because it is not integrated as a single unit. All the mentioned three layers have different functionality and usage. We will each of them in deep.
SDN Application Layer
SDN Application Layer is basically the main layer using which the SD communicates with the programs. It uses the resources from the SDN controller (second layer) using various APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). All the data is collected from the controller via the northbound interface (NBI) and structured well in the application. It includes all the applications such as analysis and management of the applications in addition to large business applications that are mostly used in the data centers.
So, basically the application layer has one application logic and there are several NBI Drivers present. In some cases, there is just one NBI driver but it might be more than one. It can further communicate with higher-level NBIs using the NBI agents.
SDN Controller (Control layer)
The middle layer of the SDN has two main tasks. One of them is to transfer and communicate with the application layer using the APIs and the next task is to receive the instructions from the networking devices present in the last layer.
The controller receives the information from the hardware and sends it to the application layer after extracting the information. Here, when the information is received from the hardware, an abstract view is formed before it gets transferred to the application layer. This is the main task of the layer.
In the SDN controller, there is a CDPI driver present along with the NBI agent and the SDN Control logic. The controller is also known as the control plane. CDPI stands for Control to Data-Plane Interface.
SDN Datapath (Infrastructure layer)
The infrastructure layer is also known as datapath. It connects all the networking devices with the controlling layers. The main purpose of this layer is to forward the data and control data processing.
The hardware devices are directly connected in this layer. The data is then processed from the hardware and sent it to the further level, that is the control layer. The datapath consists of all the network elements.
The element present over here are CDPI Agent and there is forwarding engine as well as you will also find the processing functions over here. All of these are used to communicate with the SDN control plane interface which is also known as CDPI.
Applications of SDN
If you re wondering for what all purposes SDN is used, here are some of the applications where SDN is widely used.
SDMN
SDMN also is known as Software-defined mobile networking is the design approach for mobile networks. Here, the protocol specific features are used to efficiently used the hardware and also the core network and radio access are used more effectively.
SD-WAN
Just like WAN is used for the regular network, one can also use the SDN for wide area Network. The advantages of using SDN in the wide area network include the reduction of cost and leased lines are also commercially available. One can easily control the hardware separately from the other central controller using the SD-WAN.
SDLAN
SD LAN also is known as Software-defined Networking is used in the local area. The main reason why people used SDN for the LAN is because of the visibility and control. Not to mention, you get more security when using the SDN instead of regular networks. Moreover, you can use a cloud management system or even wireless connectivity for the LAN eliminating the need of a physical controller.
Webscale with SDN
The first architectures using SDN were built by the tech giants namely Google and Amazon. The main aim of these companies was to make scalable data center using the open source. Therefore, they used the combination of the open source and also commodity hardware along with the central controller.
The SDN is very much useful here as it provides a complete abstract view of the entire network. One can easily get to know about the network and get the information in real time. This information includes network activity, analytics, etc.
Moreover, there are many other uses of SDN but it is mostly used in these purposes.
Continue Reading:
Introduction to Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela)
Related Video
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj