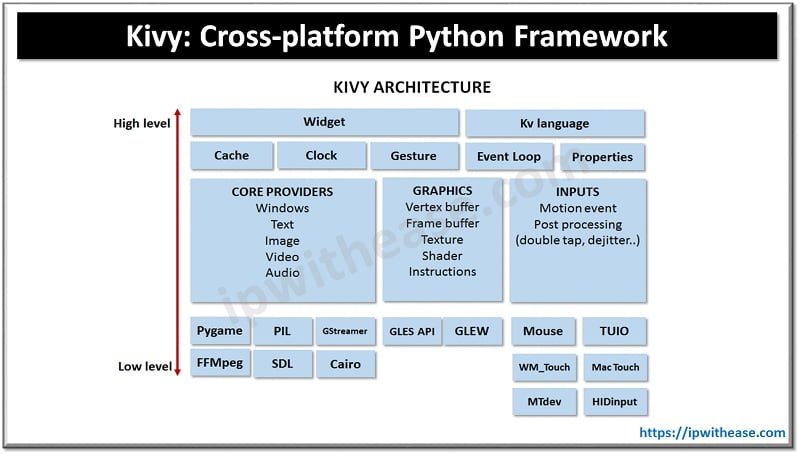
DNS:
Domain Name System or DNS is the service that makes use of DNS servers for resolving human-readable names into IP addresses. Similar to the way in which name is mapped to phone number by directory or phone books, the host name is mapped by DNS server to IP address. This is done since in comparison to IP address, remembering the name is easy. Before DNS development, management of host file was needed since it contains IP address along with their names respectively. However, with the addition of several computers to internet over time, the management of updated hosts file copies became difficult in all the computers. This has shown the way to develop DNS athwart the world.
Working of DNS proceeds with the exchange of messages between the machines of client and servers. The host name of destination is passed by the application of client to DNS process so as to get the IP address.
The physical networks make use of hardware addresses while in the internet, IP addresses are used. Domain names are the symbolic addresses that are used by users or in applications. The IP addresses are converted to MAC address by ARP/RARP protocols and vice versa of this is also true. Translation between IP address and domain name is done by DNS.
It serves as the distributed database, implementation of which takes place in name servers hierarchy. The division of domain name is done in label, top level domain and host name. It is important for every organization to approach the central authority for the purpose of obtaining TLD.
Multicast DNS:
mDNS is also involved in the resolution of domain names to the IP addresses, similar to DNS. Unlike the conventional DNS, the operation of mDNS is up to the level of local network since the operation of DNS takes place at global level. In the Zeroconf network, it works in the combination of the protocol DNS-SD. There is no need of manual operation in the network of zero configurations. Also, the dependence of zeroconf network is not on DHCP server or DNS server for operation.
Clients are allowed by DNS-SD for discovering service instances named list and type of service. Query message of standard DNS is used for the purposes of resolving the services to hostnames. Specification of mDNS protocol is there in RFC 6762 while that of DNS-SD is done in RFC 6763. mDNS has several implementations such as Windows, Avahi, Bonjor etc.
At the local level of link works the multicast DNS and therefore routing is not required for reaching to the nodes. No router forwards the mDNS packet. Local is the only single domain of top level defined by IETF for scope of link local. Reservation of this is done for the name of link local that is used in the network of mDNS. Any device is allowed by this for generating domain name of link local in forms like single-dns-label.local.
Moreover, users themselves can also make use of the hierarchical name like d.printing.local or c.printing.local etc. for this purpose. The treatment received by .local domain is similar to that by any different domain appearing in the list of DNS search but the significance that it get remains local only. If .local comes at the end of the domain name, it reflects that mDNS protocol should process this message.
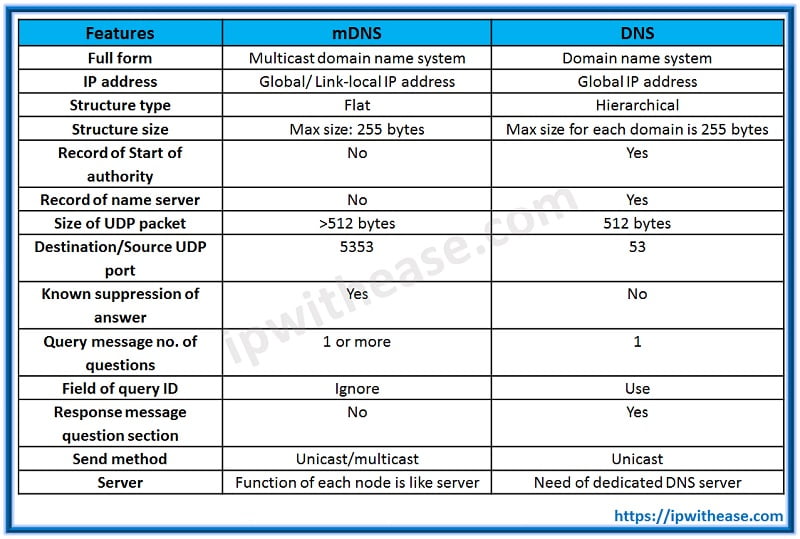
Difference between DNS and mDNS:
Following is the difference between mDNS and DNS in tabular format:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj