There are a lot of steps that make up an App Development Process. Depending on how developers approach app projects, these steps may differ from one another. However, one step that all developers should perform is testing the apps before market launch.
If you’re an app developer who wants to put out a valuable mobile application in the market, including testing procedures is highly necessary. Your goal is not only to optimize the app use before it hits various platforms. Many companies should adhere to standards and compliance for UI, functionality, and usability. Hence, many services cater to mobile testing procedures.
Mobile Application Testing
Here are some of the steps for the mobile application testing process. It’s best to familiarize these steps before you launch an application for mobile devices. Use these steps as a guide to ensure that apps are in the most optimal state before putting them out for mobile users.
STEP 1: Prepare for mobile testing
The first step is to prepare for the mobile testing procedure of the application. Developers should know the details and the nitty-gritty aspects of the device to ensure no wasted time in the testing. The preparation stage also caters to the planning and covering of the app prerequisites. Developing teams must know the application inside and out. As a developer, ask yourself the following questions:
- What does the app do?
- Is the app native, hybrid, or web?
- What are the targeted devices for the apps?
- How compatible is the application with selected networks?
- Is the app supposed to interact with other applications?
- Do all the features work well?
- What mix of emulated and automated testing is necessary to test the app?
There may be a lot of questions that cover the basics of the app. However, this step aims to plan to select necessary testing procedures for the targeted app usage. Sometimes, testing budgets may not be very high, so only specific tests have more priority than others, depending on the application.
STEP 2: Select the most relevant test procedures
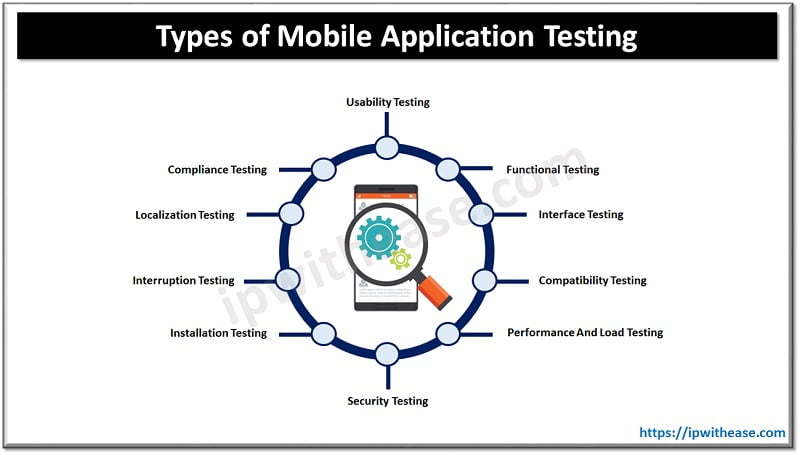
There is more than one type of mobile testing procedure. Another critical point of selecting the tests is knowing when to perform the tests. Selecting the relevant tests affects the test case and scripts that are part of the test performance. These are the most common tests for mobile applications:
- ︎Usability testing
- Functional testing
- Interface Testing
- Compatibility testing
- Performance and load testing
- Security testing
- Installation testing
- Interruption testing
- Localization testing
- Compliance testing
Other test types are relevant to cover the overall performance of an application. At this stage, it’s best to decide which tests to automate and which tests to do manually.
STEP 3: Formulate test case and test script
All tests have a different succession of steps. The test case covers the steps for each test type you will perform on the application. Think of it as listing out what each feature of the application should do. Test cases and test scripts indicate the “how it works” of the application and features, and “what is the expected result?”
The difference between a test case and a test script is this: the test case covers manual testing, while test scripts are for automated testing.
TIP: Automated testing works best for repetitive and predictable outcomes and needs little to no active monitoring for the steps. Manual testing covers the more dimensional side of the application, i.e., user experience and app feedback.
STEP 4: Run the selected tests for the application
Once the test case and test scripts are done, it’s time to perform the selected test types of the application. It’s up to the team of developers how to run and schedule the tests of the application. While some tests require several trials and errors, it’s still a good idea to keep testing and revising apps for any error and glitch.
Big companies often have in-house teams responsible for the mobile app testing procedure of ongoing applications. Others outsource and sign-up services of testing companies available to assess the applications.
STEP 5: Review the test results
Testers should document and compile the test results for necessary changes and feedback. Once there are documented problems within the app, it’s best to eliminate these errors and revise them. Then, when errors are fixed and adjusted, teams rerun tests to verify improvements.
Conclusion
The mobile app testing procedures for any application are not a one-size-fits-all process. Each app works differently, and the only way to assure that a high-quality app is out in the market is to prepare the applications in the best version possible.
Teams and companies spend thousands on developing applications for mobile devices. It would be a more expensive cost not to test apps and find out these apps don’t bring value to mobile users.
While consumer and mobile user inputs and insights help refine the apps, the foundation of the apps should be in the most glitch-free version possible. The last thing any developer wants is to have an application that only “half-works” and shuts down seconds after a mobile phone user opens the application.
Continue Reading:
Mobile Operating System and its Types
What is GSM? Mobile Technology
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.