Google ADs
Table of Contents
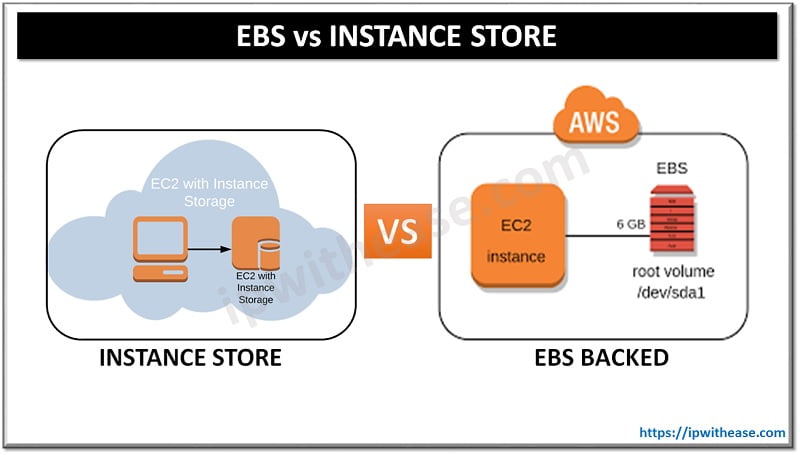
Amazon Web Services provides EC2 instances with two types of root device volumes –
- EBS-backed
- Instance store
Root device volume is basically where the Operating System is installed.
In this post we will understand the each one of these root device volumes & its pros & cons.
Google ADs
While creating your EC2 instance, the AMI type can be selected based on the following factors –
- Region
- Operating System
- Architecture (32 bit or 64 bit)
- Storage for Root Device Volume: Instance Store & EBS Backed
AWS Instance Store
- EC2 instances using instance store as root device volumes are called as Instance Store backed root device volumes. Instance store volume can be created from a template stored in the S3 bucket.
- An instance store provides temporary block-level storage for your instance. This is the disk that is physically attached to your host computer.
- Instance Store are sometimes also referred to as Ephemeral storage, that are suitable for buffer, cache, scratch data & other temporary contents.
- Data on an instance store volume persists only during the life of the associated instance; if an instance is stopped or terminated, any data on instance store volumes is lost.
- Since the instance stores aren’t persistent across reboots, they are sometimes also referred to as Ephemeral storage.
- Instance storage are the closest available memory to the instance, hence offer the lowest latency.
Instance store volumes are complicated and its best to gauge their limitations before planning to use them. Few limitations listed below are:
- In order to deliver very high random I/O performance, instance store volumes only run on solid state drives (SSD).
- Instance store backed Instances cannot be upgraded
- Taking a snapshot or AMI of an instance store volume is not as straightforward as taking snapshot of EBS volume.
- Data in the instance store can be lost if the underlying disk drive fails or if the instance stops, or if the instance terminates.
AWS EBS Backed Root Volumes
- An “EBS-backed” EC2 instance means that the root device for an EC2 instance launched from the AMI is an EBS volume created from an AWS EBS snapshot.
- AWS EBS is high performance block storage designed for use for EC2 instances handling throughput and transaction intensive workloads. These workloads may include relational, non-relational databases, containerized applications, file systems etc.
- EBS storage is storage on a remote network connected SAN or NAS (Network Attached Storage)
- Volume persists independently from the running life of an instance. After an EBS volume is attached to an instance, you can use it like any other physical hard drive.
- EBS volume can be detached from one instance and attached to another instance, supports encryption, and is also replicated across multiple availability zones to provide high availability & durability.
- Data on EBS stores persists over the reboots of the EC2 instances.
- EBS backed instances can help you save money as they can be turned off and when not being used
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Founder of AAR TECHNOSOLUTIONS, Rashmi is an evangelist for IT and technology. With more than 12 years in the IT ecosystem, she has been supporting multi domain functions across IT & consultancy services, in addition to Technical content making.
You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj