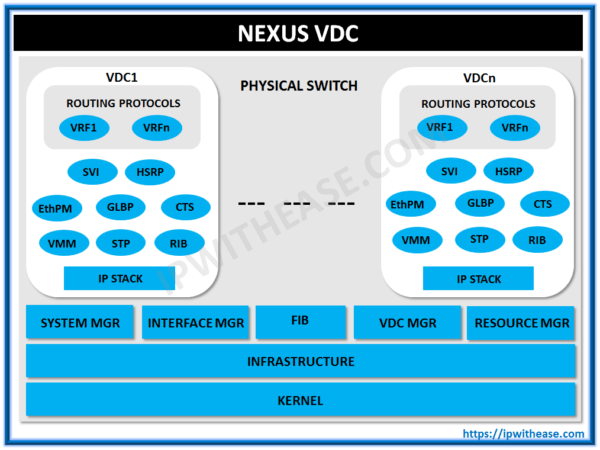
In the Datacenter environment, we have separate zones and placing physical devices for each zone isn’t feasible. Hence Cisco NEXUS delivered a solution (called VDC – Virtual Device Context) by giving the privilege of dividing a single physical Nexus switch into two or more logical switches that can act as independent switches and also have separate administration and operational capability.
Cisco VDCs also virtualize the control plane, such as the routing information base (RIB) and the routing protocols. VDC is supported on Nexus 7K platform.
Related- Nexus Interview Questions
Merits and Demerits of VDCs –
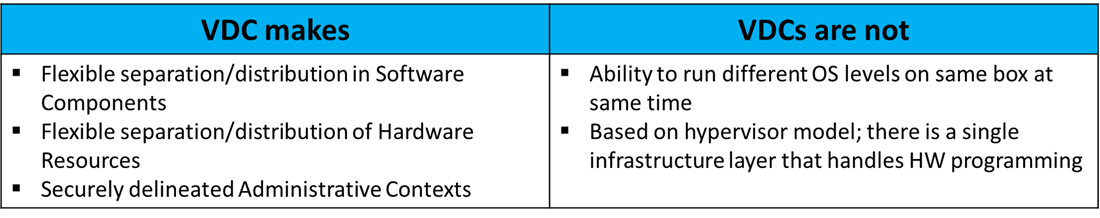
When we create a VDC certain resources are shared among VDCs while the other resources are dedicated to the VDC.
Types of Resources :
There are 3 types of resources basically:
- Global Resources: Resources that are allocated, set or configured globally for all VDCs for the master VDC are referred to as Global Resources i.e. boot image configuration, CoPP.
- Dedicated Resources: Resources that are allocated to a particular VDC are referred to as dedicated resources. Example L2, L3 ports, VLANs, IP address.
- Shared Resources: Some resources are shared between VDCs for example OOB Ethernet mgmt. port.
Types of Supervisor Model :
The number of cisco VDC that we can create on a Nexus switch depends on the supervisor model.
- SUP1 module: 3 non-default VDC & 1 default VDC or 4 non-default VDC and one admin VDC.
- SUP2 module: 4 non-default VDCs and 1 admin VDC.
- SUP2E module: 8 non-default VDC and 1 admin VDC.
VDC types Supported in Nexus:
- Default VDC
- Admin VDC
- Non –Default VDC
- Storage VDC
Related – VDC vs VRF
Related- Admin VDC vs Default VDC
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj