Table of Contents
Introduction to BFD
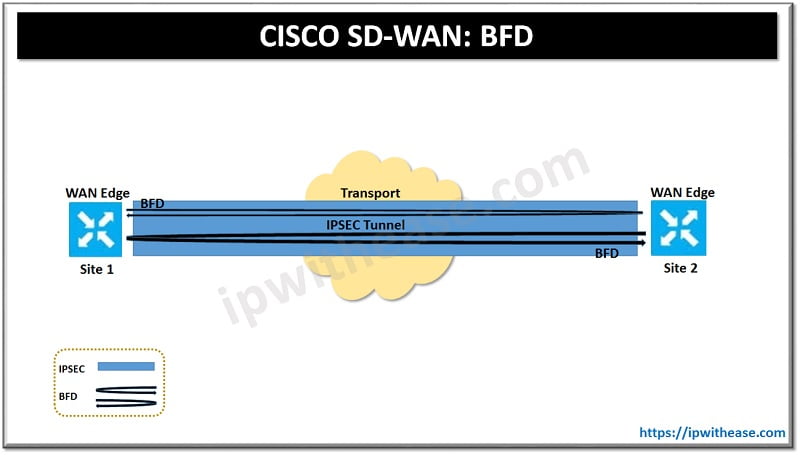
The Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) protocol is used to monitor the real-time condition of the underlying transport network. BFD packets are initiated by each router across every tunnel that is brought up as part of the SD-WAN fabric and serves two different purposes:
- Liveliness detection and
- Path quality monitoring.
BFD packets are echoed bi-directionally across each tunnel and, as such, active BFD neighbors are not formed across the SD-WAN fabric.
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection is a protocol that detects link failure as part of the Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) HA (high availability) solution, is enabled by default on all vEdge routers, and you cannot disable it. BFD runs between all routers in the topology.
BFD Parameters
Hello Interval
The Hello Interval specifies how frequently a BFD probe will be sent across a given tunnel. The default value for this timer is once per second, and the value is specified in milliseconds.
Range: 100 through 60000 milliseconds
Default: 1000 milliseconds (1 second)
Multiplier
The Multiplier value specifies how many consecutive BFD probes can be lost before declaring the tunnel to be down. This feature forms the basis of liveliness detection and is useful for detecting things such as indirect fiber cuts, where the physical interface remains in an “Up” state but no traffic can be sent across a link. In circumstances where the transport interface state changes from Up to Down, there is no need to wait for the multiplier to expire, as the tunnel is immediately set to Down and the corresponding routes are withdrawn.
Range: 1 through 60
Default: 7 (for hardware vEdge router), 20 (for vEdge Cloud virtual router)
Color
Color identifies a specific WAN transport provider. Color is equivalent for service provided by ISP. Choose the color of the transport media tunnel for data traffic moving between vEdge routers.
| Public Colors | Private Colors |
|---|---|
| public-internet | Mpls |
| biz-internet | metro-ethernet |
| 3g | private1 |
| Lte | private2 |
| Blue | private3 |
| Green | private4 |
| Red | private5 |
| Bronze | private6 |
| Silver | |
| Gold | |
| custom1 | |
| Custom2 | |
| Custom3 |
Default: default
MTU Discovery
MTU discovery can be enabled and disable depends on topology scenario. When MTU discovery is enabled, the path PMTU for the tunnel connection is checked periodically, about once per minute, and it is updated dynamically. When PMTU discovery is disabled, the tunnel MTU should be 1472 bytes, but the effective tunnel MTU is 1468 bytes.
Default: Enabled
Steps for Template configuration on GUI
Step 1. In vManage, select the Configuration > Templates screen.
Step 2. In the Device tab, click Create Template.
Step 3. Select the feature Template from drop down menu.
Step 4. Click on the type of device for which you are creating the template.
Step 5. Create a custom template for BFD > select the Factory_Default_BFD_Template and click on Create Template. The BFD template form is displayed. In template, top of the form contains fields for naming the template, and the bottom contains fields for defining BFD parameters. Click on the tab or the plus sign (+) to display additional fields.
Step 6. Fill the name of template in name field. The name can be up to the 128 characters and can contain only alpha numeric character.
Step 7. Fill the description field in template. The description can be up to the 2048 characters and can contain only alpha numeric character.
Commands for Configuration of BFD
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| bfd app-route multiplier number poll-interval milliseconds | Configure BFD for Application-Aware Routing |
| bfd color colorhello-interval milliseconds multiplier number pmtu-discovery | Configure BFD on Transport Tunnels |
Commands for Verification of BFD
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| show running-config policy | Shows the running configuration of policy configured on device. |
| show app-route sla-class | Shows the list of all SLA class configured with parameters |
| show app-route stats local-color mpls remote-system-ip X.X.X.X | Shows the statistics of loss, latency and jitter of all SLA class configured for particular remote peer. |
Conclusion
BFD uses these packets to detect the peer liveliness of the tunnel connection and to detect faults on the tunnel. BFD send Hello packet after interval of 1 sec and wait for multiplier value as 7 is default, if reply is not received tunnel declares as down.
Continue Reading
Cisco SD WAN Application Aware Routing
SD-WAN Fabric Bring Up in Cisco Viptela
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj