Table of Contents
Classful and Classless Routing are two routing protocols that differ the way they handle subnet masks. Classful routing does not include subnet mask info and relies on default IP address classes. Classless routing, on the other hand, includes subnet mask info, allowing VLSM and more efficient IP address usage.
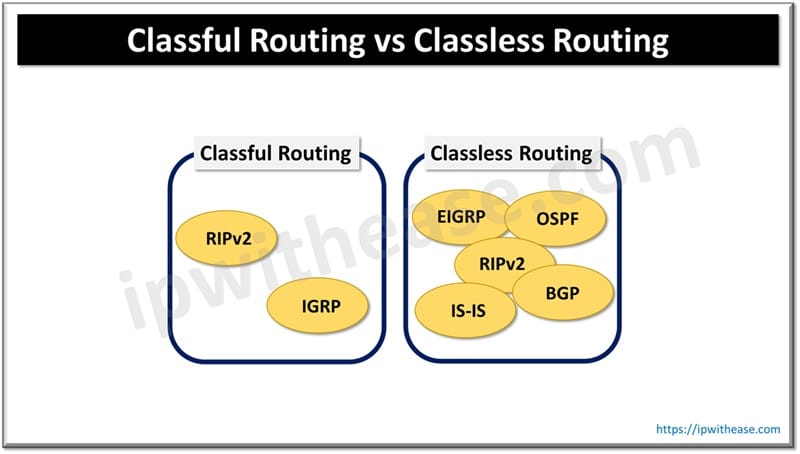
What is Classful Routing?
Classful Routing protocols do not send subnet mask information when a route update is sent out. All devices in the network must use the same subnet mask E.g.: RIP v1
Features
- Does not send subnet mask info in updates.
- Assumes default subnet masks based on IP address class.
- Doesn’t support Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM).
- Examples: RIP v1, IGRP
Pros
- Simple to configure in small networks.
- Fewer routing table entries due to class aggregation.
Cons
- Wastes IP addresses.
- Inflexible in complex or large networks.
What is Classless Routing?
Classless Routing is performed by protocols that send subnet mask information in the routing updates. Classless routing allows VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking) E.g.: RIP V2, EIGRP, & OSPF.
Features
- Includes subnet mask info in updates.
- Supports VLSM and CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing).
- Allows more efficient use of IP space.
- Examples: RIP v2, EIGRP, OSPF, BGP
Pros
- Efficient IP address usage.
- Better for large, hierarchical networks.
- Allows for route summarization and more flexible design.
Cons
- Slightly more complex to configure.
Comparison: Classful vs Classless Routing
Below table clearly differentiates both Classful and Classless Routing :
| PARAMETER | Classful Routing | Classlesss Routing |
|---|---|---|
| VLSM Support | Not Supported | Supported |
| Subnet Mask in updates | Does not include Subnet mask in routing updates | Includes Subnet mask in routing updates |
| Major Subnet | Subnets are not advertised to a different major subnet | Subnets are advertised to a different major subnet |
| Discontiguous Subnets | Discontiguous Subnets are not visible to each other | Discontiguous Subnets are visible to each other |
| Example Protocols | RIPv1 | RIP v2, EIGRP, OSPF and BGP |
| Exchange of Routing updates | Exchange Routing updates at regular intervals | Exchange Routing updates only when changes occur in network topology |
| Hello messages | Do not use Hello messages | Uses Hello messages for neighbor state check |
| Bandwidth Consumption | Consumes more network bandwidth | Consumes less network bandwidth |
| Address | Addresses have 3 parts: •Network •Subnet •Host | Addresses have 2 parts: •Subnet or prefix •Host |
Download the comparison table: Classful vs Classless Routing

Why Classless routing is used in Modern Networks?
Modern networks demand flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. Thus Classless routing dominates today’s infrastructure, offering better support for subnetting, summarization, and efficient IP space management.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj