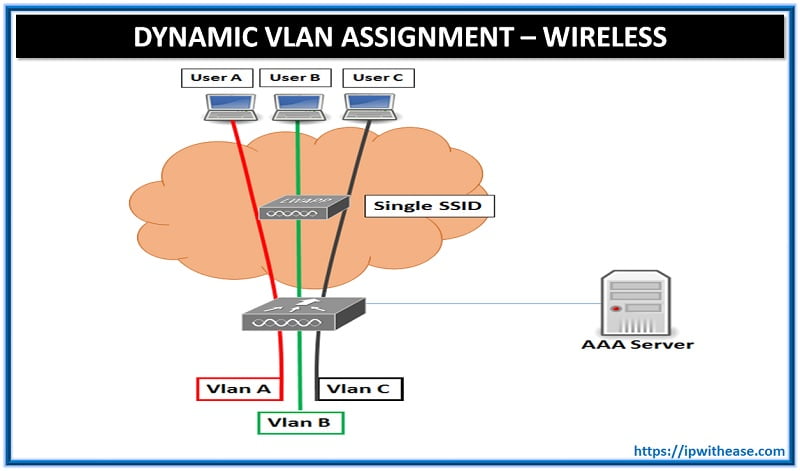
Dynamic VLAN Assignment
Objective: To dynamically Assign Wireless User to VLAN based on user credentials. This type of setup is called “Dynamic VLAN Assignment”
Description: Dynamic VLAN assignment is one such feature that places a wireless user into a specific VLAN based on the credentials supplied by the user. This task of assigning users to a specific VLAN is handled by a RADIUS authentication server, such as Cisco Secure ACS. This can be used, for example, to allow the wireless host to remain on the same VLAN as it moves within a campus network.
Related- Cisco ACS vs ISE Comparison
Therefore, when a client attempts to associate to a LAP registered with a controller, the LAP passes the credentials of the user to the RADIUS server for validation. Once the authentication is successful, the RADIUS server passes certain Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) attributes to the user. These RADIUS attributes decide the VLAN ID that should be assigned to the wireless client. The SSID (WLAN, in terms of WLC) of the client does not matter because the user is always assigned to this predetermined VLAN ID.
WLC Configuration
This configuration requires these steps:
- Configure the WLC with the Details of the Authentication Server
- Configure the Dynamic Interfaces (VLANs)
- Configure the WLANs (SSID)
Configure the WLC with the Details of the Authentication Server
It is necessary to configure the WLC so it can communicate with the RADIUS server to authenticate the clients, and also for any other transactions.
Complete these steps:
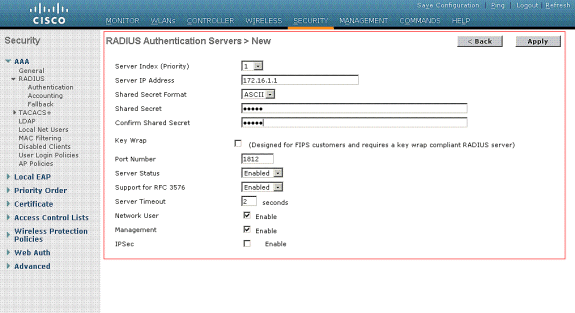
- From the controller GUI, click Security.
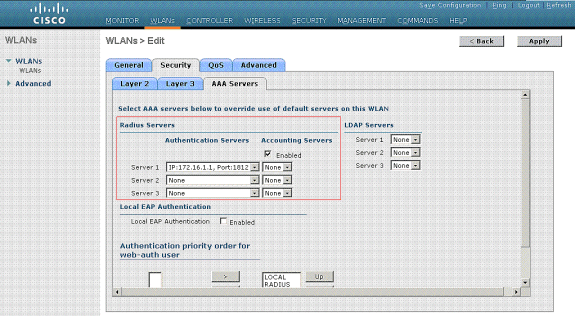
- Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server and the Shared Secret key used between the RADIUS server and the WLC.
This Shared Secret key should be the same as the one configured in the RADIUS server under Network Configuration > AAA Clients > Add Entry. Here is an example window from the WLC:
Configure the Dynamic VLAN (Interfaces)
This procedure explains how to configure dynamic interfaces on the WLC. As explained earlier in this document, the VLAN ID specified under the Tunnel-Private-Group ID attribute of the RADIUS server must also exist in the WLC.
In the example, the user1 is specified with the Tunnel-Private-Group ID of 10 (VLAN =10) on the RADIUS server.
You can see the same dynamic interface (VLAN=10) configured in the WLC in this example. From the controller GUI, under the Controller > Interfaces window, the dynamic interface is configured.
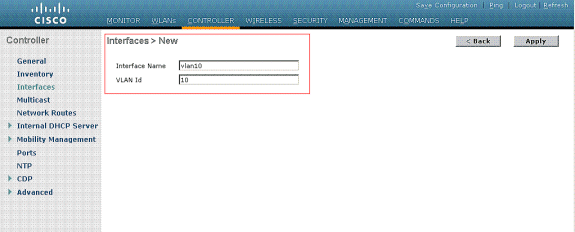
- Click Apply on this window.
This takes you to the Edit window of this dynamic interface (VLAN 10 here).
Enter the IP Address and default Gateway of this dynamic interface
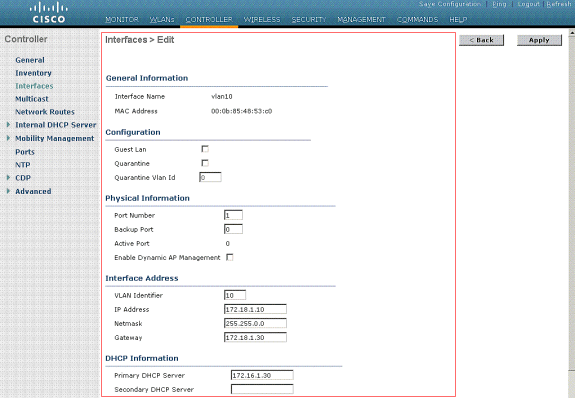
Note: Because this document uses an internal DHCP server on the controller, the primary DHCP server field of this window points to the Management Interface of the WLC itself. You can also use an external DHCP server, a router, or the RADIUS server itself as a DHCP server to the wireless clients. In such cases, the primary DHCP server field points to the IP address of that device used as the DHCP server. Refer to your DHCP server documentation for more information.
- Click Apply.
Now you are configured with a dynamic interface in your WLC. Similarly, you can configure several dynamic interfaces in your WLC. However, remember that the same VLAN ID must also exist in the RADIUS server for that particular VLAN to be assigned to the client.
Configure the WLANs (SSID)
This procedure explains how to configure the WLANs in the WLC.
Complete these steps:
- From the controller GUI, choose WLANs > New in order to create a new WLAN.
The New WLANs window is displayed.
- Enter the WLAN ID and WLAN SSID information.
You can enter any name to be the WLAN SSID. This example uses VLAN10 as the WLAN SSID.

- Click Apply in order to go to the Edit window of the WLAN SSID10.
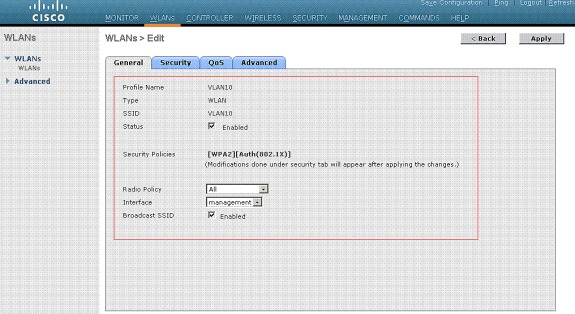
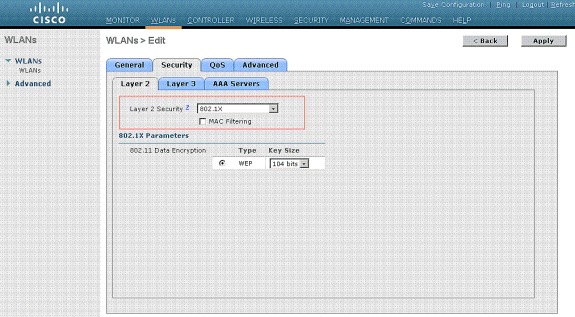
Normally, in a wireless LAN controller, each WLAN is mapped to a specific VLAN (SSID) so that a particular user that belongs to that WLAN is put into the specific VLAN mapped. This mapping is normally done under the Interface Name field of the WLAN SSID window.
In the example provided, it is the job of the RADIUS server to assign a wireless client to a specific VLAN upon successful authentication. The WLANs need not be mapped to a specific dynamic interface on the WLC. Or, even though the WLAN to dynamic interface mapping is done on the WLC, the RADIUS server overrides this mapping and assigns the user that comes through that WLAN to the VLAN specified under the user Tunnel-Group-Private-ID field in the RADIUS server.
- Check the Allow AAA Override check box in order to override the WLC configurations by the RADIUS server.
- Enable the Allow AAA Override in the controller for each WLAN (SSID) configured.
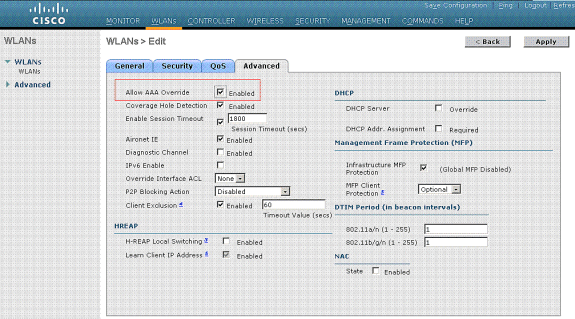
When AAA Override is enabled, and a client has AAA and controller WLAN authentication parameters that conflict, client authentication is performed by the AAA (RADIUS) server. As part of this authentication, the operating system moves clients to a VLAN returned by the AAA server. This is predefined in the controller interface configuration.
For instance, if the corporate WLAN primarily uses a Management Interface assigned to VLAN 2, and if the AAA Override returns a redirect to VLAN 100, the operating system redirects all client transmissions to VLAN 100 even if the physical port to which VLAN 100 is assigned. When AAA Override is disabled, all client authentication defaults to the controller authentication parameter settings, and authentication is only performed by the AAA server if the controller WLAN does not contain any client-specific authentication parameters.
Continue Reading:
CONFIGURE INTERFACES ON WIRELESS CONTROLLER 5508
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj