Many Network administrators at times get tangled in the conceptual difference of Load Balancing and Load Sharing. Prima facie, both may be thought of as one of the same things, as they both serve the purpose of load distribution. However as we drill down, the terms tend to differ.
What is Load Balancing?
Load balancing refers to the process of distributing network traffic evenly among a pool of resources that are responsible for supporting an application. A load balancer is like a traffic director who manages the flow of requests from clients to servers. It ensures that the requests are distributed across all servers efficiently to optimize speed and capacity utilization. The load balancer also prevents any server from being overloaded, which could negatively impact performance. In case of a server failure, the load balancer redirects the requests to the remaining online servers.
What is Load Sharing?
The goal of load balancing tools is to establish a dispersed system in which requests are uniformly divided among several servers. Load sharing, on the other hand, involves directing some of the traffic to one server and the rest to other servers. The loads don’t have to be identical, but they should be arranged in a manner that doesn’t overload the system as a whole.
So let’s differentiate how both Load Balancing and Load Sharing concepts differ from each other and where are they used.
Load Balancing vs Load Sharing
- Load balancing is more of a dynamic technique of distributing the load across 2 or more links while Load Sharing works by statically splitting the traffic types and then distributing the load across multiple links. Though we understand that dynamic load distribution will be more efficient on equal load distribution.
- While Load Balancing utilizes round-robin or maximum connections etc. to distribute traffic, Load sharing 1st splits the traffic based on source or destination IP/Mac address etc. and then distributes traffic across links.
- IGP protocols are the best example of load balancing traffic across 2 or more links, GLBP is another good example.
- eBGP is the best answer which uses Load Sharing mechanism for incoming traffic by utilizing AS- Path attribute.
Related – F5 Big-IP Load Balancing Methods
Comparison Table: Load Balancing vs Load Sharing
Below table gives a simple comparison of both the concepts of Load Balancing and Load Sharing –
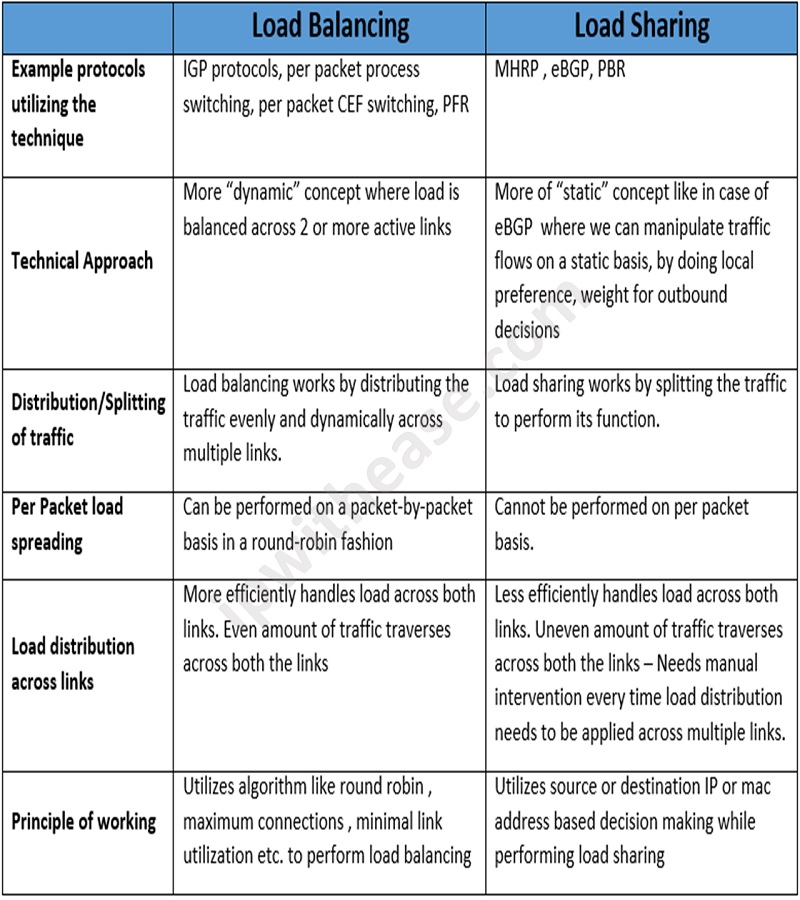
Download the comparison table: Load Balancing vs Load Sharing
Which One Is Right for You?
When it comes to choosing between load balancing and load sharing, it depends on your specific requirements and the characteristics of your application or system.
To choose between load balancing and load sharing, consider the following factors:
- Workload Characteristics: Analyze the workload of your application or system. If the workload is consistently high and requires high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability, load balancing might be more appropriate. On the other hand, if the workload can be divided into different categories or priorities, load sharing can be a viable option.
- Resource Utilization: Evaluate how efficiently you want to utilize your resources. Load balancing aims for equal distribution, ensuring optimal utilization of resources. If your resources have similar capabilities and capacity, load balancing can help you achieve efficient resource utilization. Load sharing, on the other hand, allows you to allocate workload based on resource capabilities or predefined rules, which can be useful if you have resources with varying capacities.
- System Complexity: Consider the complexity and overhead associated with each approach. Load balancing often requires dedicated load balancer hardware or software, which can introduce additional complexity and cost. Load sharing can be achieved through simpler methods such as round-robin or priority-based routing, which may be easier to implement.
- Application Requirements: Understand the specific requirements of your application or system. If your application requires fault tolerance, high availability, and the ability to handle sudden increases in traffic, load balancing can help distribute the load and prevent single points of failure. If your application has different types of tasks or priorities that can be allocated to specific resources, load sharing can be a suitable choice.
In many cases, load balancing and load sharing can complement each other. You may use load balancing to distribute traffic across multiple servers or resources and then implement load sharing within each individual server or resource to divide the workload efficiently.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your specific needs, the characteristics of your application or system, and the available resources. Consider evaluating your requirements against the factors mentioned above to make an informed decision.
Continue Reading:
Load Balancing Interview Questions
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj