Table of Contents
Macvlan and IPvlan are both network drivers, used mainly for connections on different Virtual Machine’s interfaces and network types. Let us understand both the terms in detail and then compare “Macvlan and IPvlan”.
What is MacVLAN?
MacVLAN helps the user to configure sub-interfaces (also known as slave devices) of a parent physical Ethernet interface (also known as upper device) with its own unique MAC address and as a result with its own IP address. Applications, Virtual Machines and containers can now be grouped to a specific sub-interface, in order to connect directly to the physical network using their own MAC and IP addresses.
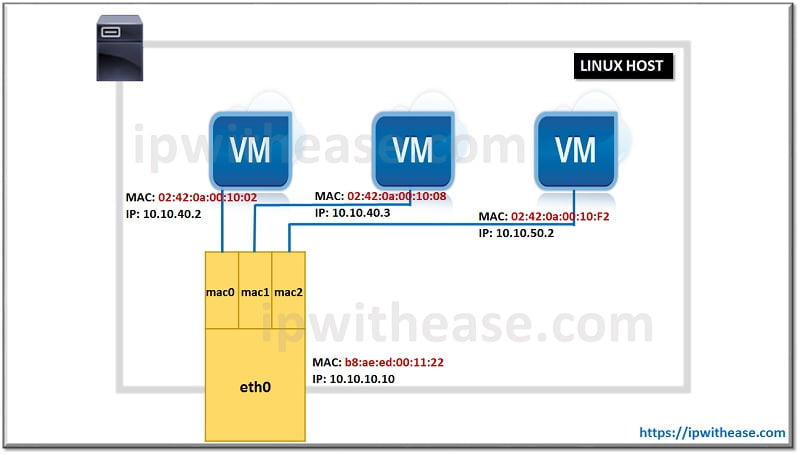
From experience, Macvlan technology proved to be almost an ideal solution to connect natively Virtual Machines and containers to a physical network but with some drawbacks:
- First of all, the host as a switch is connected regarding a policy that sets a limitation to the number of different MAC addresses allowed on the physical port. Although, the user should cooperate with the network administrator to change this policy. Unfortunately, many times this might not be possible (or a quick PoC should be set up).
- In addition, most NICs have a limitation on the number of MAC addresses they support natively. Sometimes exceeding that specific limit may affect the system’s performance.
- Finally, according to IEEE 802.11 protocol specifications, multiple MAC addresses on a single client are not allowed. Therefore, Macvlan sub-interfaces will be blocked by the user’s wireless interface driver or AP.
What is IPvlan?
IPvlan is very similar to MacVLAN technology with one important difference and that is – IPvlan does not assign unique MAC addresses to created sub-interfaces. All the sub-interfaces share parent’s interface MAC address by using unique IP addresses.
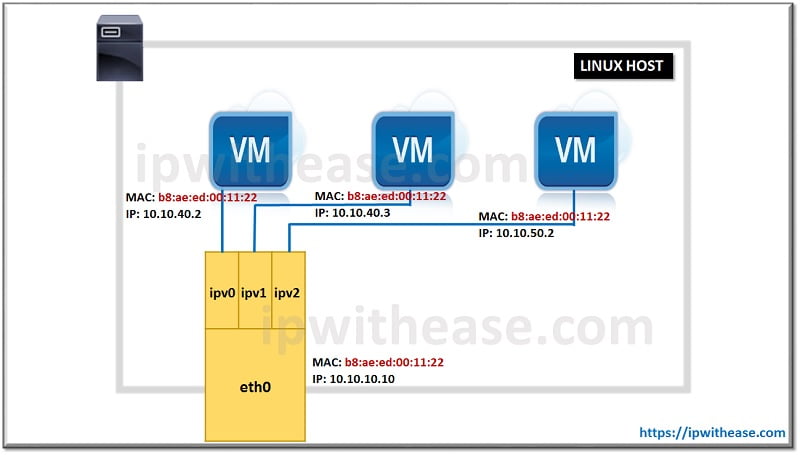
Due to the fact that most Virtual Machines or containers usually on a single parent interface make use of the same MAC address, it results in some drawbacks of implementing IPvlan technology:
- Firstly, all the shared MAC addresses can affect DHCP services. In case the user’s Virtual Machines or containers use DHCP, in order to acquire network settings. Then the user should be aware that he has to use a unique Client ID in the DHCP request and make sure that DHCP server assigns IP addresses according to Client ID and not client’s MAC address.
- Finally, auto-configured EUI-64 IPv6 type addresses are based on MAC type addresses. Therefore, all the Virtual Machines or containers that share the same parent interface, will auto generate the same IPv6 address. We advise the user to make sure that all the Virtual Machines or containers use static IPv6 addresses or IPv6 privacy addresses with SLAAC disabled.
MacVLAN vs IPvlan
As a general rule, IPvlan should be used in scenarios where some switches restrict the maximum number of mac addresses per physical port because of the port security setup. MacVLAN needs to be used in projects where a common DHCP server is used, because the DHCP server would need a unique mac address which IPvlan does not have.
MacVLAN is easy to set up, on the other hand IPvlan is not as easy as advanced router configuration is required.
Comparison Table
Below table summarizes the points of differences between the two:
| PARAMETER | MacVLAN | IPvlan |
|---|---|---|
| Network Interface Compatibility | Common DHCP Server | Limited Mac Address |
| Hardware Performance | Low CPU, Normal Network Utilization | High CPU, Low Network Utilization |
| Security | Meets 802.11 standards | Unknown |
| Implementation | Easy to Set-Up | Needs Advanced Router Configuration |
Download the comparison table: MacVLAN vs IPvlan
Use Cases
| Use Case | Recommended Driver |
|---|---|
| Physical network wants to see containers as separate devices | macvlan |
| Limited MAC address support (e.g. Wi-Fi, cloud) | ipvlan |
| Need more control over routing (L3-based networking) | ipvlan in L3 mode |
| Performance-critical apps | ipvlan |
| Legacy environments with MAC filtering | macvlan |
Continue Reading
What is MacVLAN? Detailed Explanation
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj