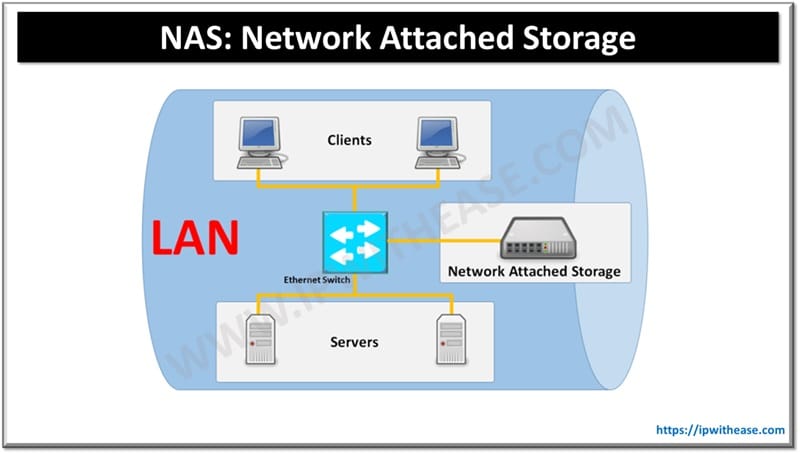
IT teams that rely on hardware IT infrastructure link their data storage processes to specific devices. However, conventional hardware might make extending, replacing, or updating proprietary technology difficult. This challenge is being solved by software defined storage (SDS), which has become the preferred alternative for many businesses and organizations.
SDS allows for preserving traditional operating practices and important software investments as storage hardware is upgraded, enlarged, and replaced. The contrast between contemporary software-defined storage ideas and hardware-based systems is stark.
Although the functions of each model are identical, the implementation differs, rendering the two models incompatible. Due to delays in data migrations, these incompatibilities may transform modest hardware improvements into massive operational overhauls, resulting in costly storage silos.
What Is Meant By Software Defined Storage?
Software-defined storage is data storage management that deliberately separates data storage management from physical hardware. Storage pools comprising many storage devices are created by software. These storage devices appear as a single unit, enhancing the current storage’s diversity, flexibility, and usefulness.
SDS does this by decoupling the storage-management software layer from the hardware. This frees management functions from every device under control. This storage enables businesses to overcome hardware issues by updating design and optimizing system investments.
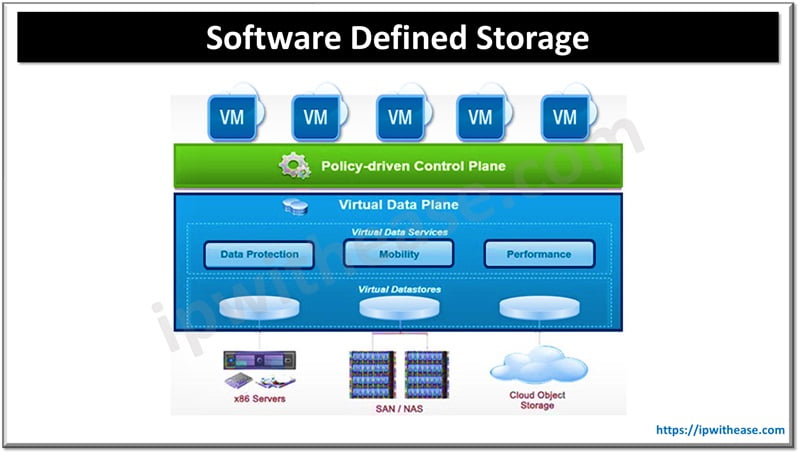
How Does Software Defined Storage Work?
As a software-based architecture, SDS eliminates codependency between your programs and the underlying hardware. It functions as a layer inside your IT infrastructure, running on commodity resources rather than brand-specific, pricey hardware. Disks and servers may be combined and matched without needing separate software. Similarly, application software may be upgraded or modified without requiring a complete storage hardware redesign.
SDS virtualizes storage request handling rather than storage itself. It may provide functionality like replication, automatic provisioning, deduplication, backup, and snapshots via virtualization.
Common Types of Software Defined Storage
Although categorizing SDS products might be complex owing to the absence of a standard definition, SDS operates on virtual machines and operating systems in a public cloud and on-premise servers. Here are some of the most prevalent SDS solutions on the market:
- Scale-out file storage: This SDS type solves traditional storage restrictions by producing scale-out files for file-based storage.
- Object, block, and file storage: This form of SDS storage stores data using dispersed servers and a single data system.
- Scale-out block storage clusters. This SDS has numerous server nodes that function as a unified block storage system to improve cache node coherence.
- Storage virtualization: This kind of SDS aggregates network-connected storage, hardware-based storage, and storage area networks to generate new storage pools.
- Hyper-Converged Infrastructure: This SDS combines storage, computation, networking, and virtualization resources in clustered servers. These solutions use server operating systems, virtual machines, hypervisor kernels, and containers.
Why Do Companies Need SDS?
Companies need software-defined storage for a variety of reasons. In this section, I will go over the significance of SDS in detail.
Flexibility
SDS allows businesses to choose the storage hardware that best meets their requirements, independent of the vendor. This enables businesses to avoid vendor lock-in and benefit from the most recent technological breakthroughs without overhauling their whole storage infrastructure. Furthermore, SDS allows firms to adjust their storage capacity up or down as required without affecting operations.
Cost Savings
SDS may assist businesses in lowering storage costs by utilizing commodity hardware and eliminating the requirement for pricey custom storage solutions. Furthermore, SDS allows enterprises to maximize storage consumption by pooling resources and using sophisticated data management methods such as compression and deduplication.
Simplified Management
SDS offers a consistent management interface for all storage resources, regardless of where or what kind they are. This decreases the difficulty of managing various storage systems and streamlines storage management. Furthermore, SDS allows businesses to automate typical storage chores such as data backups and replication, allowing IT professionals to concentrate on more strategic projects.
Improved Data Protection
Data replication, snapshots, and encryption are among SDS’s sophisticated data security capabilities. This enables businesses to secure the availability and integrity of their data in the case of hardware failures or other disturbances. Furthermore, SDS allows businesses to develop disaster recovery systems that are both cost-effective and simple to operate.
Enhanced Performance
Data replication, snapshots, and encryption are among SDS’s sophisticated data security capabilities. This enables businesses to secure the availability and integrity of their data in the case of hardware failures or other disturbances. Furthermore, SDS allows businesses to develop disaster recovery systems that are both cost-effective and simple to operate.
Improved Compliance
SDS allows businesses to improve storage performance using sophisticated caching methods and intelligent data placement. This guarantees that frequently requested data is kept on the quickest accessible storage medium, enhancing application speed and user experience. Furthermore, SDS allows businesses to use cutting-edge storage technologies like flash memory and NVMe, improving performance even further.
Future-proofing
Advanced data management capabilities, such as data retention rules and audit trails, are available in SDS. This assists businesses in meeting regulatory obligations for data privacy and security. Furthermore, SDS allows businesses to build granular access restrictions and encryption, protecting critical data from unwanted access.
Real-World Applications of SDS
SDS is a technology that abstracts and virtualizes storage resources to provide flexibility, scalability, and automation in storage infrastructure management. SDS has a variety of real-world applications in a variety of industries:
- Private Clouds: SDS is essential in private cloud deployments because it offers the flexibility and efficiency required for dynamic workloads.
- Data Analytics: SDS is used in big data and analytics applications to store, manage, and analyze massive volumes of data.
- Backup and Recovery: SDS streamlines backup and recovery operations, guaranteeing that data is safeguarded and recoverable in a failure.
- Virtualization: SDS streamlines backup and recovery operations, ensuring that data is protected and recoverable in the event of a failure.
- Hybrid Cloud: SDS connects on-premises and cloud storage, allowing hybrid cloud architectures for improved data mobility.
Conclusion
Software defined storage separates storage software from hardware, allowing enterprises to employ commodity technology while simply managing storage resources. It has various advantages, including enhanced agility, cheaper costs, and higher scalability. This makes it an inescapable progression for enterprises with big data needs trying to upgrade their data storage infrastructure.
By integrating software-defined storage solutions, you can establish a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective environment that suits the demands of your company. To guarantee a smooth transition to SDS, adhere to best practices for deployment and choose the appropriate SDS platform for your firm. By doing so, you’ll be well on your way to unlocking the full potential of software defined storage.
Continue Reading:
RAM VS ROM – Download Detailed Comparison Table
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.