Table of Contents
Threat hunting is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, providing organizations with an additional layer of protection against cyber threats. In this blog post, we’ll take a detailed look at threat hunting and explore the types, benefits, and tools available to help organizations identify and mitigate risks.
We’ll also discuss the differences between threat hunting and threat intelligence and how organizations can use threat hunting to improve their security.
What is Threat Hunting?
Threat hunting is a proactive approach to security that involves actively searching for signs of malicious activity or vulnerabilities in a network. It is an important part of a comprehensive cyber defense strategy, as it can identify unknown threats that may have gone undetected by traditional security measures.
It is different from traditional security monitoring, which relies on predetermined rules and signatures to detect malicious activity. With threat hunting, security teams are able to use their knowledge and expertise to search for threats that may be difficult to detect with automated tools.
The goal of Cyber threat hunting is to identify and mitigate risks before they can cause damage. By using threat hunting, organizations can quickly detect and respond to malicious activity, minimizing the potential damage and preventing future incidents.
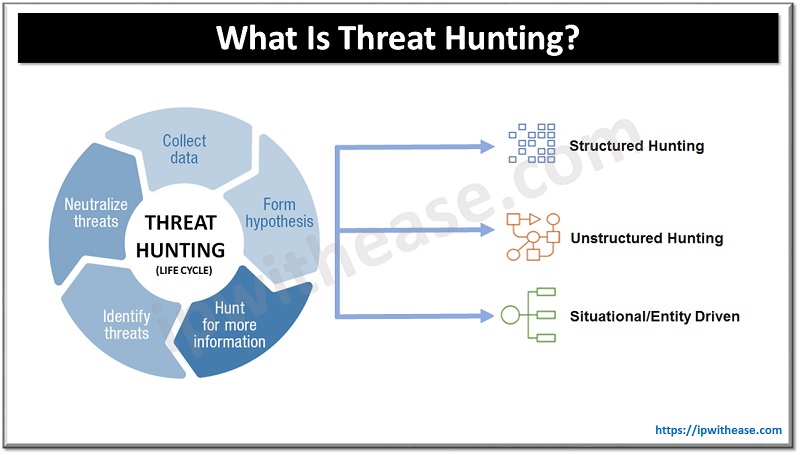
Types of Threat Hunting
Based on the type of working, there are two main categories:
- Manual Hunting – involves manually inspecting a network for signs of malicious activity. This requires a great deal of knowledge and expertise, as manual hunting relies on the security team’s ability to recognize and respond to potential threats.
- Automated Hunting – involves using a specialized data security platform to scan a network for signs of malicious activity. These tools can be used to detect threats that may have gone unnoticed by manual hunting.
Regardless of the type of threat hunting used, it is important for organizations to have a comprehensive security strategy in place that includes both manual and automated hunting.
Based on a trigger/security data, there are three types:
- Structured hunting – When conducting a structured hunt, the hunter relies on an Indicator of Attack (IoA) and the Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs) of the attacker. The hunter’s efforts are targeted towards the TTPs of the threat actors, allowing them to detect threats before any harm can be done to the environment. The hunt is made easier with the help of the MITRE Adversary Tactics Techniques and Common Knowledge (ATT&CK) framework, which includes both PRE-ATT&CK and enterprise frameworks.
- Unstructured hunting – Upon detection of an indicator of compromise (IoC), an unstructured investigation is launched. This sign typically directs the hunter to look for pre- and post-Detection patterns. By following this method, the hunter can analyze the data that has been kept as far back as the permissible limits and other prior incidents.
- Situational or entity driven – A hypothesis based on the situation develops from an internal risk evaluation or a trends and vulnerabilities examination that is specific to a business’s IT system. Entity-oriented insights are sourced from crowd-sourced attack info that, when analyzed, demonstrate the newest tactics and procedures of the current cyber-attacks. Subsequently, a threat hunter can look for these restricted activities within the environment.
Benefits of Threat Hunting
It provides organizations with a number of benefits:
- Ability to detect and respond to threats before they can cause significant damage.
- By actively searching for signs of malicious activity, organizations can quickly identify and mitigate risks before they become a major problem.
- It can also provide organizations with valuable insight into their security posture.
- By viewing the results of threat hunting, organizations can get an understanding of their security weaknesses and create a plan to address them.
- It can help organizations stay ahead of the curve when it comes to cyber threats. By actively searching for threats, organizations can stay one step ahead of malicious actors and prevent future incidents.
Threat Hunting Tools
There are a number of tools available to organizations that want to implement threat hunting. These tools range from open-source tools to commercial solutions. Open-source tools are typically free to use, but may require additional expertise to use effectively. Commercial solutions are typically more expensive but provide a greater level of support and features.
Some of the most popular tools include:
- Mozilla Open Source Security – A suite of security tools that can help organizations detect and respond to threats.
- CrowdStrike Falcon – A cloud-based security platform that provides organizations with threat intelligence, endpoint visibility, and automated threat hunting capabilities.
- Splunk Enterprise Security – A comprehensive security platform that provides organizations with threat hunting, incident response, and compliance capabilities.
Difference Between Threat Hunting & Threat Intelligence
- Both are important aspects of a comprehensive security strategy, but they are not the same. Threat hunting involves actively searching for signs of malicious activity or vulnerabilities in a network, while threat intelligence involves gathering and analyzing intelligence on potential threats.
- Threat hunting is a proactive approach to security, while threat intelligence is a reactive approach. Threat hunting is used to identify and mitigate risks before they can cause damage, while threat intelligence is used to monitor and respond to threats after they have been identified.
How to Use Threat Hunting to Improve Security
Organizations can use threat hunting to improve their security posture in a number of ways. Here are a few tips to get started:
- Develop a comprehensive security strategy that includes both manual and automated hunting.
- Leverage threat intelligence sources to identify potential threats and prioritize threat hunting activities.
- Use a variety of threat hunting tools to detect and respond to threats quickly.
- Invest in training and education to ensure that security teams are prepared to identify and respond to threats.
- Test and refine security strategies to ensure that they are effective and up-to-date.
By leveraging threat hunting and threat intelligence, organizations can improve their security posture and reduce their risk of a cyberattack.
Conclusion
Threat hunting is an important part of a comprehensive security strategy, providing organizations with an additional layer of protection against cyber threats. By leveraging threat hunting and threat intelligence, organizations can improve their security posture and reduce their risk of a cyberattack.
As organizations continue to face an ever-evolving threat landscape, threat hunting and threat intelligence will become increasingly important. By taking a proactive approach to security, organizations can ensure that they are better prepared to identify and respond to threats quickly.
Continue Reading
Understanding the TCP SYN Flood Attack: What It Is & How to Protect Yourself?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj