Networking requirements keep growing each year. Today’s network requires high speed, low latency, and high scalability along with secure isolation of network segments. Virtualization in data centres have increased demands on physical network infrastructure resulting in traditional networks not able to cope up with demands of applications. Network virtualization is used to abstract from underlying physical networks.
Today we look more in detail about VXLAN and VRF Lite technologies, differences between both of them, their advantages and use cases and so on.
About VXLAN
Virtual extensible local area network (VXLAN) is an encapsulation protocol which offers tunnelling of layer 2 (L2) connections over an underlying layer 3 ay network is physical infrastructure used by an overlay network. Physical hardware, cables and network protocols are underlay physical network components. Border gateway protocol (BGP), and Open shortest path first (OSPF) are widely used protocols for L3 routing. Overlay network examples are virtual private networks (VPNs), IPsec tunnels, and peer to peer networks. VXLAN is defined in RFC 7348.
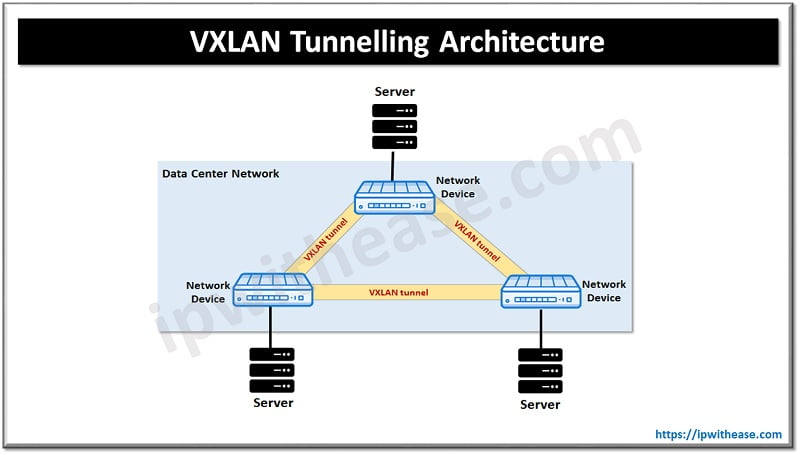
This standardization was created in collaboration with vendors like Cisco, VMware, and Arista but this standard is not vendor locked. VXLAN allows creation of highly scalable logical networks with support for multi-tenant broadcast domains and spans boundaries of physical networks. Decoupling of virtual networks from physical networks simplifies management of large and complex networks. With VXLAN the overlay network can be redesigned without reconfiguring the underlay network. It is possible to use two or more underlay L3 network to deploy virtual overlay L2 network domain.
Features of VXLAN
- Maximum number of virtual networks supported by VXLAN is more than 16 million
- Highly scalable networks and high number of L2 domains
- Support for multicast, multi-tenancy, and network segmentation
- Centralized network management after deployment and configuration
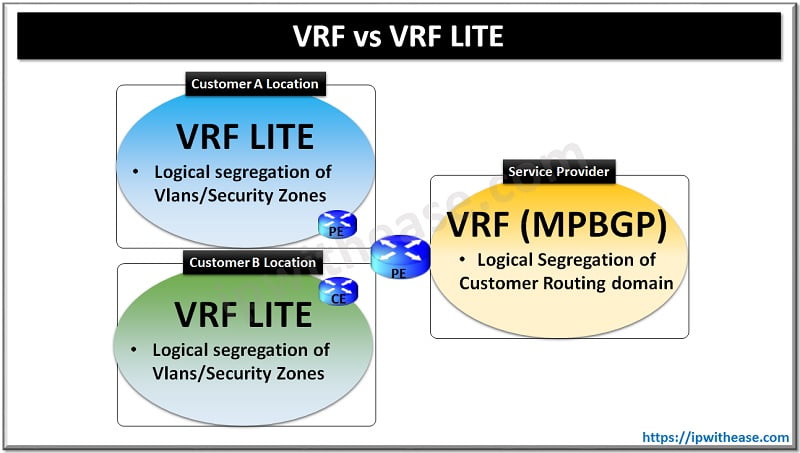
About VRF Lite
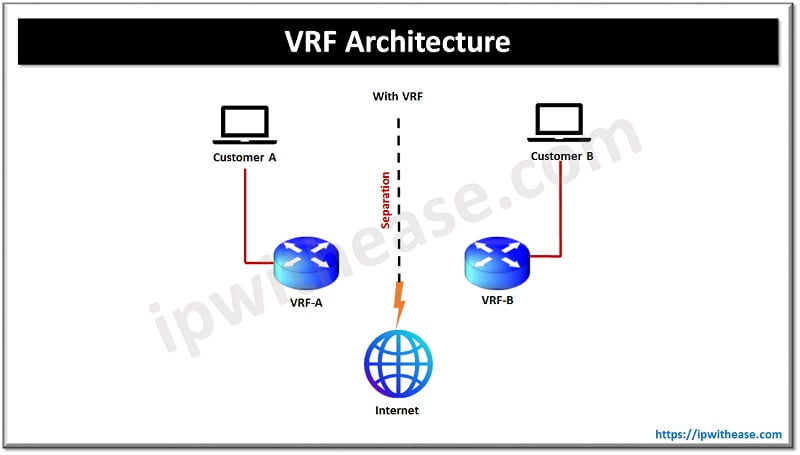
VRF is VPN routing and forwarding or virtual routing and forwarding. A router by default uses a global routing table containing information of all directly connected networks and prefixes which it learned via static and dynamic routing protocols. VRFs are like VLANs for routers and we can use multiple virtual routing tables instead of one global routing table.
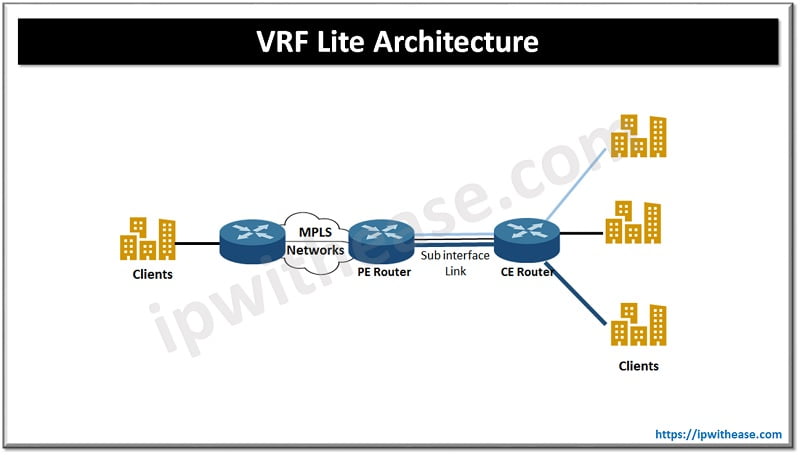
VRFs are commonly deployed for MPLS networks but when we use VRFs without MPLS then it is referred to as VRF Lite. VRF lite is used to isolate customer networks as it allows multiple secure customer routing domains to co-exist in one physical device simultaneously while staying completely isolated from each other.
Features of VRF Lite
- Enables virtual creation of multiple route instances on single physical device
- Simultaneously management of multiple routing tables
- Used for MP BGP and MPLS deployments
- Multiple VPNs for customers can use overlapping IP addresses without any conflicts
Comparison Table: VXLAN vs VRF Lite
Below table summarizes the difference between the two:
Function | VXLAN | VRF Lite |
| Definition | It is an encapsulation protocol which provides data center connection using tunnelling and extends a layer 2 segment across layer 3 network infrastructure. | It is a feature which enables overlapping of IP addresses among the VPNs. |
| Purpose | Encapsulates the MAC in UDP and supports scalability up to 16 million VXLAN segments. | Allows to store multiple instances of routing tables to coexist with same router and at same time it is ideal when multiple customers share same router (logically segregated and independent). |
| RFC standard | Formal internet standard specified in RFC 7348 and it is application layer protocol based on UDP. | VRF lite interfaces are layer 3 interfaces. |
| Used in | Used by all major providers such as Cisco, EVPN, VMware etc. | Data centres and campus LAN environments. |
| Protocols supported | VXLAN uses UDP for encapsulation. | VRF lite supports OSPF, BGP and RIP routing protocols. |
| Encryption | Traffic over internet is unencrypted and securing VXLANs require using SSH tunnel. | Traffic is automatically segregated and eliminate need for encryption and authentication. |
Download the comparison table: VXLAN vs VRF Lite
Continue Reading:
VRF vs VRF LITE : Detailed Comparison
What is VRF? VRF Complete Guide
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj