Introduction to Web 3.0
The Internet or World wide web as we call it has undergone multiple transformations since its inception. Started as a static information repository to dynamic and interconnected platforms as in his current form as of today. Initial days of static web which was referred as Web 1.0 and enabling user generated content era which was governed by web 2.0 as it was called. Both web 1.0 and web 2.0 were centralized models of the Internet or World wide web.
Today we look more in detail about Web 3.0 which is another transformation in the space of the Internet or World wide web, understanding its advantages and disadvantages, its characteristics etc.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is an extension of Internet or World wide web and it was introduced by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood in the year 2014. It is still in its early development stages and aims for a decentralized architecture. Like its predecessors Web 1.0 and 2.0 it is also a source of data and information for end users but improvised in terms of data security, privacy, and scalability. In Web 3.0 web content is expressed not only in natural language form but also in a form that can be understood and interpreted to be used by software agents or APIs to support find, share, and integrate information in an easier manner.
Web 3.0 is the backend of web or Internet it will entirely change the way we navigate, search, and use Internet.
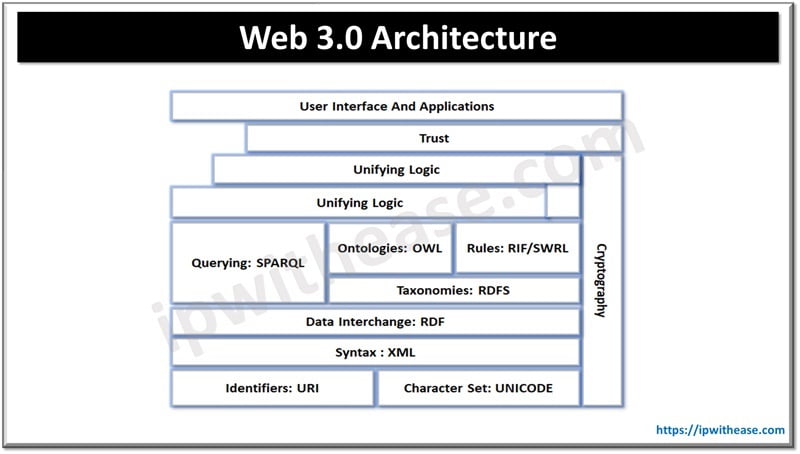
Web 3.0 is also known as decentralized or semantic web which aims to revolutionize Internet by enabling more user control, privacy, and interoperability features.
Features of Web 3.0
Let’s look at some of the features of web 3.0
- Decentralized model and blockchain technology – Decentralization is core of web 3.0 architecture instead of everything being centralized unlike web 1.0 and web 2.0. Blockchain technology is used to provide a secure and transparent framework to record and verify transactions. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, enhances trust, and enables peer-to-peer connections.
- Smart contracts in web 3.0 – blockchain technology powered smart contracts and self-executing having terms of agreement directly written in source code. Automation and enforcement of execution of agreements, elimination of the need of intermediaries and enhance trust and efficiency in transactions
- Data ownership and interoperability – emphasis is on interoperability, to allow different platforms and systems to communicate seamlessly and data sharing irrespective of underlying hardware.
- Decentralization of identities and data to empower users to have more control over their digital footprint is one of the key characteristic of web 3.0
- Artificial intelligence and web 3.0 – enhance web capabilities. AI algorithms to process and analyze huge data sets , enable personalized and context aware experience for end users. AI enabled Web 3.0 can adapt to individual preferences , provide targeted recommendations , and automate tasks leading to more intelligent and efficient online experience.
Pros and Cons of Web 3.0
PROS
- Increased ability to link information
- Effective ways to search information
- Better marketing approach
- Effective net surfing
- Easier communications
- Change in human interaction technique
CONS
- Less advanced devices will not be capable to handle web 3.0
- Web 1.0 and 2.0 sites will become quickly obsolete
- Migration challenges to move from web 2.0 to web 3.0
- User experience initially will not be good due to barrier of new technology and knowledge
- More expensive
Potential Risks of Web 3.0
With web 3.0 users have ease of access to information however anonymous and decentralized web models cannot handle harmful content, wealth inequality between normal and small investors, data inaccessibility due to higher costs associated with blockchain technology.
Some top Web 3.0 projects are Chainlink (Link), Filecoin (FIL), The Graph (GRT), Livepeer (LPT) , Akasha (AKT) etc.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj