Table of Contents
Network traffic flows help in building better understanding of traffic in computer networks at the transport layer. Measuring network traffic flow helps to understand and analyse how hosts are communicating, what are the traffic volumes, type of traffic etc. Identification of network connections is crucial to establish various security policies and analysis which plays a crucial role in security of digital assets and potential threats mitigation.
In today’s topic we will learn about 5-Tuple, its five components, working, features, example scenario and use cases.
About 5-Tuple
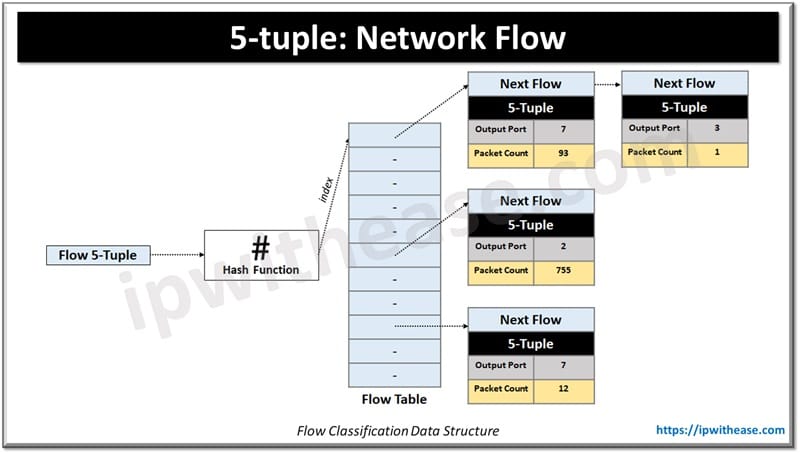
Network flow classification is used in the transport layer. Individual connection flows such as system maintenance state information specific to a flow such as number of bytes transmission by connection is the basis of the decision. A flow is identified using a 5-Tuple. The 5-Tuple term is associated with five base values which identify a network connection uniquely. These values typically include source and destination IP address, transport layer protocol in use, source and destination port number. 5-Tuple identifies UDP/TCP connections.
Each session will have a separate 5-Tuple – one for IPv4 and one for IPv6 When a UDP/TCP connection flows through a NAT64,. Unique identification of sessions can be done using an incoming / outgoing Tuple.
It provides a robust mechanism to identify and categorize network traffic. By encapsulation of essential connection parameters, the 5-Tuple enables analysis of the network effectively and efficiently and aids in identification of potential issues, threats and unauthorized activities over the network.
Components of the 5-Tuple
- Source IP Address: The IP address of the device initiating the communication.
- Example:
192.168.1.1
- Example:
- Destination IP Address: The IP address of the device intended to receive the communication.
- Example:
10.0.0.5
- Example:
- Source Port: The port number used by the source device to establish communication. Typically, this is a dynamically assigned ephemeral port (e.g., 49152–65535 for TCP/UDP).
- Destination Port: The port number on the destination device where the service or application is running.
- Example:
80(for HTTP),443(for HTTPS),22(for SSH).
- Example:
- Protocol: The transport protocol used for the communication.
- Common examples:
TCP,UDP,ICMP.
- Common examples:
How the 5-Tuple Works
- Packet Identification:
- Each network packet contains these five attributes in its headers (IP and transport layers).
- Network devices (e.g., firewalls, routers) inspect these attributes to identify and manage flows.
- Traffic Filtering: Firewalls and security appliances use the 5-tuple to create rules for allowing or blocking traffic. For instance:
- Allow:
Source IP: 192.168.1.1, Destination IP: 10.0.0.5, Protocol: TCP, Destination Port: 80. - Deny:
Source IP: 172.16.0.1, Destination Port: 22.
- Allow:
- Flow Tracking: Devices like load balancers and intrusion detection systems track flows using the 5-tuple to associate packets with specific sessions.
- QoS (Quality of Service): The 5- tuple is used to classify and prioritize traffic. For example, VoIP traffic (UDP, port 5060) might be given higher priority than file transfers.
- Connection Uniqueness: The combination of the 5-tuple values uniquely identifies a network session. This is essential for ensuring the correct routing and handling of packets in environments with multiple concurrent sessions.
Features of 5-Tuple
5-Tuple enables targeted analysis and enforces security measures. Let’s understand its key features:
- Network Analysis – 5- Tuple enables comprehensive analysis of a network, to allow administrators to gain insight into data flow across the network. This assists in identification of anomalous behaviour and potential security incidents.
- Access control policies – It enforces and manages access policies within networks. Organizations can implement stringent controls using 5 -Tuple access controls.
- Threat detection and prevention – Proactive detection and prevention of breaches can be done more efficiently with 5- Tuple. Analysis of network connections with 5 -Tuple parameters help to identify and neutralize network threats
- Security policies enforcement – Its parameters are used to establish a robust security policies enforcement to ensure proactive and resilient network infrastructure. Alignment of security policies to 5 -Tuple help to mitigate potential threats
- Regular auditing and updates – 5- Tuple based parameters aided with regular auditing and updates ensures alignment of security measures with evolving threats and operational requirements for overall security resiliency.
Example Scenario
Imagine a user on a computer at 192.168.1.100 opens a web browser to visit 203.0.113.10 over HTTP:
- Source IP:
192.168.1.100 - Destination IP:
203.0.113.10 - Source Port:
52345(randomly chosen by the OS) - Destination Port:
80 - Protocol:
TCP
This 5-tuple uniquely identifies the web session and is used by network devices to allow the traffic or apply policies.
Applications
- Firewalls: To define access control rules.
- Load Balancers: To distribute traffic to different servers.
- IDS/IPS: To detect and prevent malicious activities.
- QoS: To manage traffic priorities.
- Network Monitoring: For analyzing specific traffic flows.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj