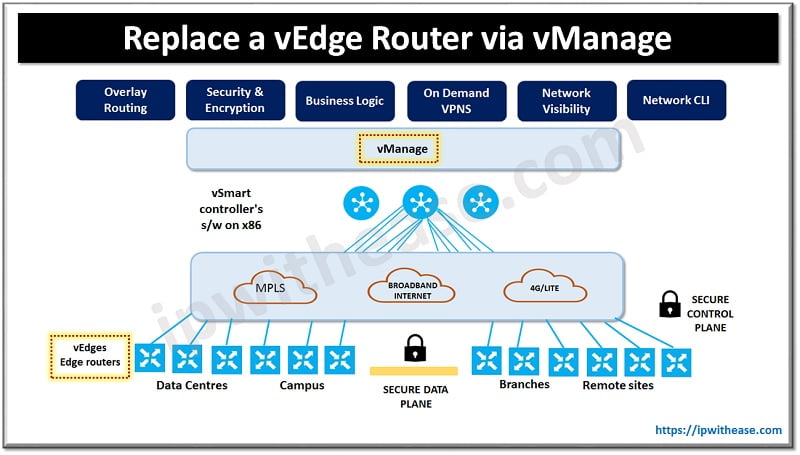
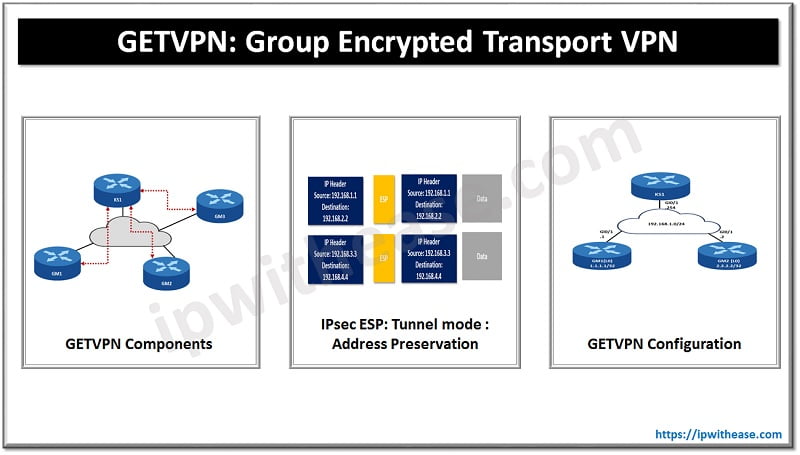
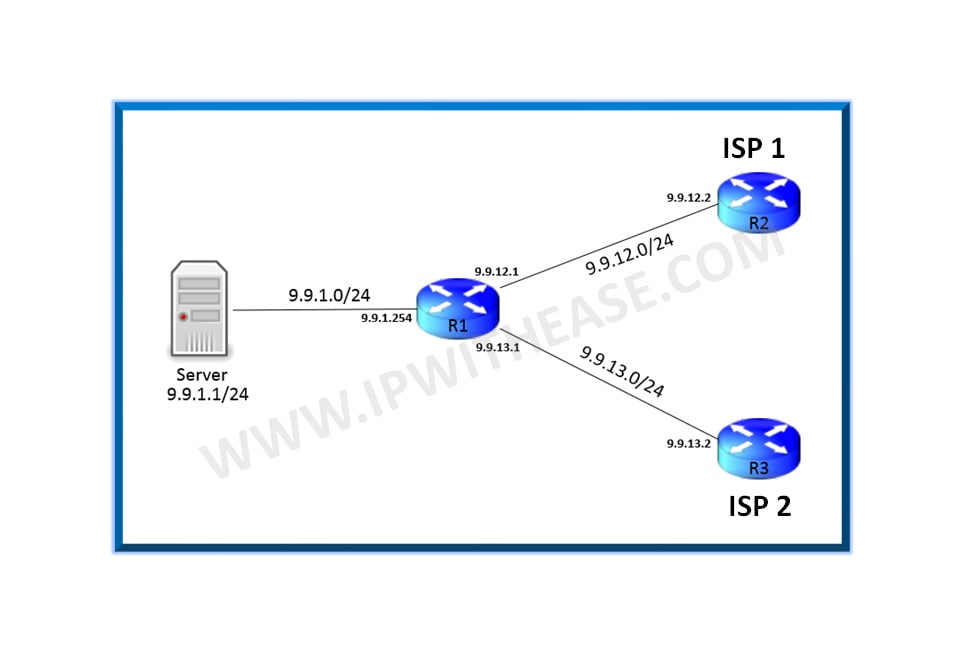
After 2010, the Internet of Things (IoT) and other sensor-activated embedded devices were put into mass production. Global IoT production is expected to grow above 22 billion in 2025.
And this situation created the need for new cost-efficient innovations like LPWAN. Is this the first time you are hearing about the Low Power Wide Area Network? Want to know more about it.
You are in the right place. In this article, you will get to know about the Low Power Wide Area Network and its uses in modern technology development. 
What is LPWAN?
It was specifically created for Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and IoT devices. Its name itself defines it – It is long-distance wireless connectivity with low power consumption. It interconnects the battery-powered devices with low bandwidth and low bit rate over long ranges.
LPWAN is not a completely new technology to our society, it is just a new innovative form of existing Wireless connections and networks. LPWAN refers to the Low Power Wide Area Network.
A normal LPWAN technology has a packet size of 10 -1,000 bites and up to speed up to 200 Kbps. The range of the LPWA network can vary from 2 km to 1,000 km based on the technology and power consumption.
It is mostly used in the majority of IoT devices and especially the ones that are used in smart cities and smart or digital infrastructure.
History of LPWAN Technology
Many smart devices that are interconnected today don’t need the high speed and bandwidth of our normal cellular devices. Using the cellular network will increase the cost and power consumption of the devices.
But at the same time, these devices needed the longevity and coverage range of the traditional LTE Cellular networks. In response to the need, in 2013 LPWAN technology was brought into the market and gained its popularity among the I0T applications in 2015.
And in the same year GSMA wireless Industry association recommended some standards, which helped the network operators to meet the specific cost, coverage, and power consumption needs of IoT applications. The above-said standard also includes the LTE-M and NB – IoT.
At the same time, the LoRa Alliance was formed and added another low bandwidth, low latency wireless option for the IoT applications. Now the LPWAN market is in the early stage of development. The industry is still fragmented, but the situation is changing.
At first (by 2017) the LoRa was the overall market leader and Sigfox was the leader of the public network. However, at the end of 2020, the NB-IoT technology has overtaken LoRa and Sigfox and is expected to dominate the market for the next five years.
Currently, NB-IoT and Lora hold nearly 70% of the market share and it is expected to grow to 85% in the next five years.
Types of LPWAN:
The LPWAN technology cannot be classified easily; there are different types of LPWAN technologies that come in many shapes and sizes. There are 16 types of LPWAN in the market and still counting. For now, the market can be divided into two categories –
Non-Cellular LPWA Networks
There are LPWAN technologies that are not based on cellular solutions such as Sigfox and LoRa. Although there are many other types, these two face fierce competition on the market.
LoRaWAN is a French start-up acquired by the founder of LoRa Alliance. It transmits the small packets between 0.3 and 50Kits at 3 per second. Though it is marketed through commercial operators it remains an open-source network.
On the other hand, SigFox, the main competitor of LoRaWAN is also a French initiative in the Internet of Things created in 2009. You need SigFox certified transmitters and receivers to use this low-speed network but it guarantees interoperability between the countries.
Standardized Cellular Network
There are LPWAN technologies that use the existing cellular networks to alleviate issues between the M2M and IoT applications with low production costs. The two main competitors of this category are LTE –M and NB –IoT.
Final Words
Although there is fierce completion in the market it affects society in a good way. And it is expected that in the next few years’ market will attain a stable growth stage.
The need for IoT applications is increasing due to the development of smart cities, smart agriculture, and other digital development projects. The LPWAN technologies are having a promising future for the next 10 years.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj