Table of Contents
Understanding IDS
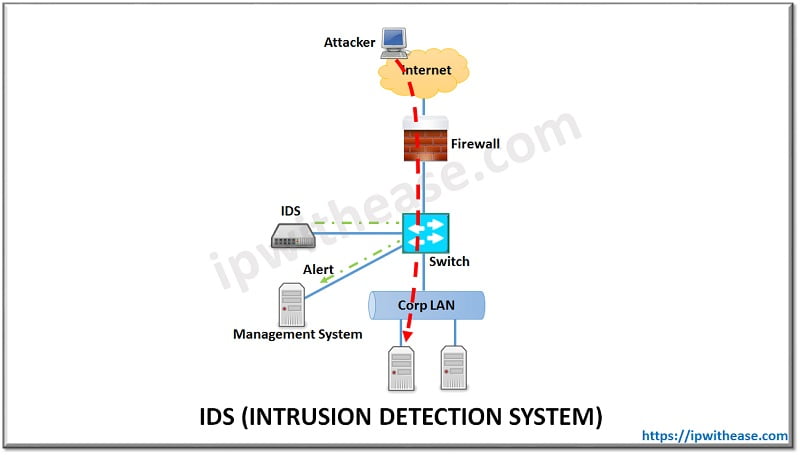
Intrusion Detection System (called IDS in short) is a device or software solution that monitors a network or systems for malicious activity or policy violations. IDS is passive device which watches packets of data traversing the network, comparing with signature patterns and setting off an alarm on detection on suspicious activity. IDS system is mostly employed after the Firewall in a non-Inline mode, where is connects to a switch or a network tap and traffic is spanned (or or sent via tap) to IDS.
IDS is commonly compared to another security solution called IPS. IPS stands for Intrusion Prevention System which functions in contrast to IDS by blocking or remediating flows with malicious traffic.
Related – What is IPS Security?
Many times, IDS solution can also work as an IPS system. Customers can use this dual functionality of IDS and IPS by using the system in two phases. In the 1st phase, when the network, security and application stack is newly setup, IDS feature will be leveraged to see how the system behaves without actually blocking anything. Once the initial phase has settled well, then fine-tuned IPS can be turned on in 2nd phase and the system can be deployed inline to provide full protection from attacks.
Example Scenario: IDS
Below figure depicts one of the most common scenario where IDs is deployed in non-inline mode and traffic is shared with IDS by switch using port mirroring or port span. In some cases, a passive device called Network TAP may also be deployed separately if switch is not used for sending traffic to IDS –
3 key objectives of IDS
- Security Automation – With help of IDS (or IPS system), security vulnerabilities and threats are kept at bay. Network and security admins are rest assured of the safety of network due to IDS presence which captures and automatically takes required step to alert in event of attacks.
- Security Compliance – The IDS system helps meet the security posture of IT infrastructure and also provides valuable audit information used for compliance investigations.
- Policy enforcement – Organizational security policies can be easily implemented and corrective actions can be taken during event of non-complaint traffic flow . With IDS informing the concern about breach of laid down policies, a corrective step can be taken and therefore organizational policies can be strictly adhered to.
Related – IDS vs IPS vs Firewall
FAQs
Q.1 What are the different types of IDS?
The two main types of IDS are:
Network-based IDS (NIDS): Monitors network traffic for signs of intrusion.
Host-based IDS (HIDS): Focuses on monitoring individual devices, system files, and log data to detect abnormal activities.
Q.2 What are the key components of an IDS?
An IDS typically consists of:
Sensors: Collect data from the network or hosts.
Analyzers: Process the data to detect malicious patterns.
Alerting System: Notifies security administrators of any potential threats.
Management Console: Central interface to view alerts, logs, and configure settings.
Q.3 What are false positives and false negatives in IDS?
False Positive: A legitimate activity flagged as suspicious by the IDS.
False Negative: A malicious activity that goes undetected by the IDS. False negatives are more dangerous because they allow threats to remain unnoticed.
Q.4 Can IDS protect against zero-day attacks?
While IDS can detect some anomalies and unusual patterns, it is generally not effective against zero-day attacks on its own. However, with behavioral analysis and integration with threat intelligence, an IDS can potentially spot zero-day exploits based on abnormal behavior.
Q.5 How does an IDS handle encrypted traffic?
An IDS typically cannot inspect encrypted traffic directly. It may monitor metadata, such as traffic patterns, or rely on other security tools (like decryption gateways) to gain visibility into the contents of encrypted packets.
Q.6 How effective is an IDS in modern cybersecurity?
An IDS is still an effective tool for detecting potential threats, especially when integrated with other security technologies. However, it requires skilled personnel to monitor alerts, filter false positives, and respond effectively. Modern IDS can be enhanced with machine learning and threat intelligence feeds for better accuracy.
Watch Related Video for better Understanding
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj