Table of Contents:
All communication in the network is based on the OSI (Open system Interconnection model) framework which is the basis for all transmissions in a reliable and secure manner. OSI model is a conceptual model which provides a common framework across disparate systems and established rules about how different network protocols and communication processes work together seamlessly. It is a foundation to design and secure network architectures.
Today we look more in detail about Open systems interconnections (OSI) framework and how it works in cyber security, each layer and what security functionalities are available.
Related: OSI Model CheatSheet
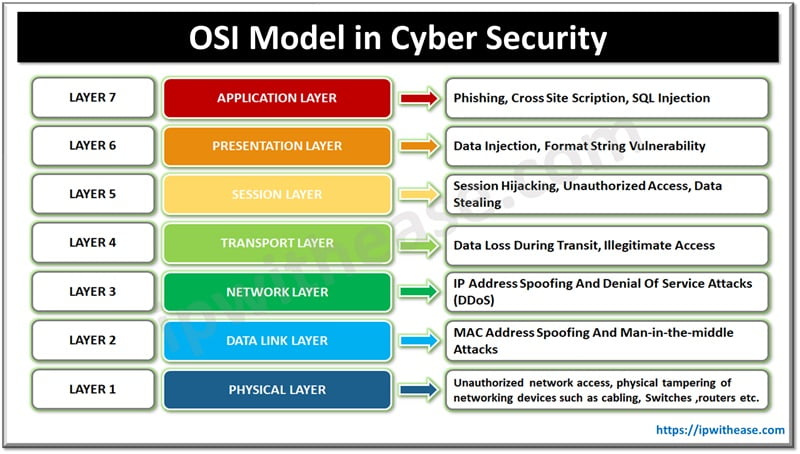
OSI Model in Cyber Security
In this blog we will understand more in detail how at each layer of OSI model what security controls can be implemented. Implementing security controls at each layer ensures a full fledged protection. OSI framework comprises 7 layers as depicted in figure below.
Layer 1: Physical Layer
- Physical layer is responsible for physical infrastructure and physical transmission of data
- It handles in electric, mechanical, and physical aspects of network
- Security considerations at this layer consist of protection against attacks targeting physical layers of the network such as unauthorized access to network communication devices such as switches, routers etc. or it may involve tampering of cable connections.
- Protection mechanism deployed at this layer comprises physical access restrictions such as lock etc.
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
- Data link layer is responsible for reliable and error free transmission of data across the network
- It provides techniques for packet management such as frames, error detection and flow control of data packets
- Security aspects at this layer consider protection against data link layer attacks such as spoofing MAC address, man-in-the-middle attacks etc.
- Protection mechanism deployed at this layer consists of using secure protocols such as IPsec and SSL/TLS to establish secure connections and encrypting data.
Layer 3: Network Layer
- Network layer is responsible for handling logical address management and data packet routing across networks
- It enables communication between several networks. Security aspects of this layer consider protection against network layer attacks such as IP spoofing and Denial of service attacks (DDoS).
- Protection mechanism deployed at this layer comprise of DDOS protection software, firewalls etc.
Related: DOS vs DDOS: Detailed Comparison
Layer 4: Transport Layer
- Transport layer ensures reliable delivery of data between the hosts in a network. It is responsible for establishment of end-to-end connections, segmentation and data reassembly and error correction techniques
- Security aspects of this layer deals with protection against transport layer attacks such as data stealing, illegitimate access , and data protection in transit
- Protection mechanism deployed at this layer comprises encryption techniques such as AES 256, TLS etc.
Layer 5: Session Layer
- Session layer is responsible for management and coordination of sessions between systems.
- Its function is to establish, maintain and terminate connection between applications
- Security aspects of this layer deals with risks associated with session layer attacks such as data stealing, unauthorized access, and session hijacking
- Protection mechanism deployed at this layer comprises Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) etc.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
- Presentation layer is responsible for data presentation, data formatting and encryption and compression
- It ensures data sent from one application is understood by another application
- Security aspects of this layer deals with protection against presentation layer attacks such as data injection and format string vulnerability.
- Protection mechanism deployed at this layer comprise of secure coding practises
Layer 7: Application Layer
- Application layer is the only layer which directly services to end users. It has protocols to support email, web browsing , file transfer services.
- Security aspects of this layer deal with prevention or protection from application layer attacks such as Phishing , cross site scripting, SQL injection etc.
- Protection mechanisms deployed at this layer comprises Anti-phishing software, Data loss prevention software, Antivirus software etc.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj