Table of Contents
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) play essential roles in protecting networks from various cyberattacks. IDS focuses on detecting suspicious activities, while IPS takes it a step further by actively blocking or preventing those activities. Both systems detect and respond to a wide range of attack types. This blog will explore the most common cyber attacks that IDS can detect and IPS can prevent, providing insights into how these systems protect modern networks.

List of Common Cyber Attacks Detected by IDS and Prevented by IPS
1. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
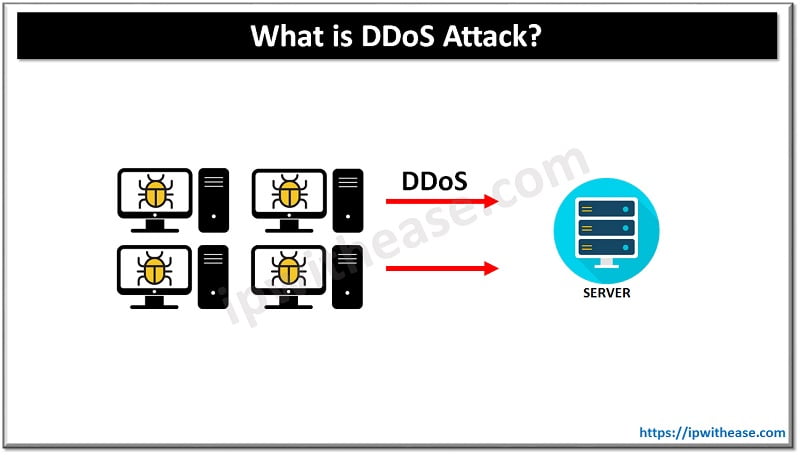
- What It Is: DDoS attacks overwhelm a target network or server with excessive traffic, causing it to slow down or crash.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS monitors network traffic and identifies unusual spikes or patterns that indicate a potential DDoS attack.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can throttle or block the traffic originating from the attacker, protecting the network from being flooded with malicious requests.
2. Malware Infections (Viruses, Worms, Trojans)
- What It Is: Malware includes any software designed to harm or exploit systems, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans. These can be spread through email attachments, downloads, or network vulnerabilities.
- How IDS Detects It: Signature-based IDS can recognize patterns or code snippets that are characteristic of known malware, alerting security teams.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block malicious files or network traffic associated with malware before they reach their target, stopping the infection from spreading.
3. SQL Injection Attacks
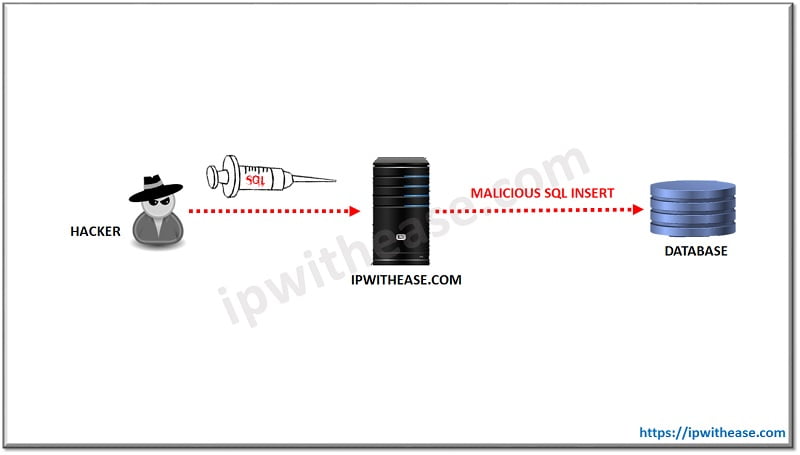
- What It Is: SQL injection occurs when an attacker inserts malicious SQL queries into a web application’s database to gain unauthorized access, delete data, or manipulate database contents.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS can identify SQL injection attempts by monitoring application traffic and flagging anomalous or unexpected SQL commands.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block the attacker’s connection or filter out the malicious SQL queries before they reach the database.
4. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- What It Is: XSS attacks involve injecting malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users, which can result in data theft, session hijacking, or website defacement.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS detects abnormal patterns in web traffic, such as unusual JavaScript or HTML code being sent from users to the server.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block HTTP requests containing malicious scripts, preventing them from being executed in users’ browsers.
5. Brute Force Attacks
- What It Is: In brute force attacks, attackers repeatedly attempt to guess passwords, usernames, or encryption keys by trying various combinations until they succeed.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS can identify repeated login attempts or failed authentication requests, flagging potential brute force activity.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block the attacker’s IP address after detecting a certain threshold of failed login attempts, preventing further brute force attempts.
6. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
- What It Is: In a MitM attack, the attacker secretly intercepts and possibly alters communication between two parties without their knowledge.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS can detect suspicious network behaviors, such as unusual changes in packet routes or unexpected IP addresses in the communication flow.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can terminate the suspicious connection or block network traffic that exhibits signs of interception.
7. Port Scanning
- What It Is: Port scanning is used by attackers to identify open ports and services on a target system, which can be exploited for future attacks.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS can detect multiple connection attempts across various ports, which is indicative of port scanning.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block the source of the port scan, preventing the attacker from gathering further information about open ports.
8. Buffer Overflow Attacks
- What It Is: Buffer overflow attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software by sending more data than a buffer can handle, leading to system crashes or arbitrary code execution.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS can recognize patterns in data packets that suggest buffer overflow attempts, such as oversized packets or abnormal commands.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can stop the malicious input from reaching the target application by dropping the oversized packets or blocking specific network commands.
9. Phishing and Spear Phishing Attacks
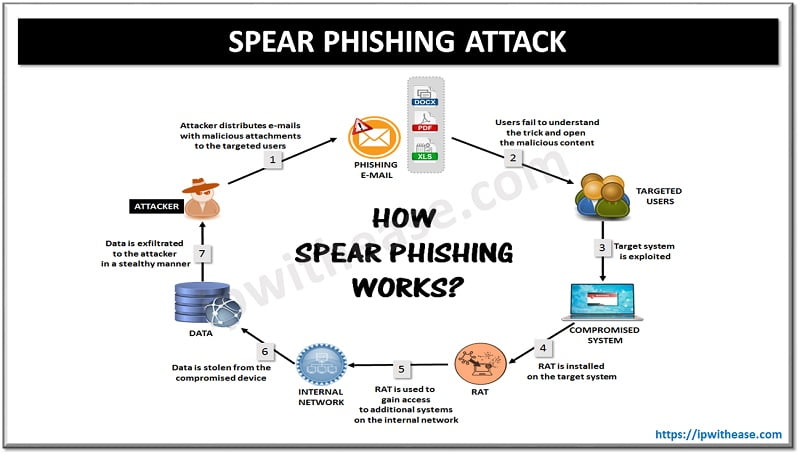
- What It Is: Phishing involves tricking users into providing sensitive information (such as passwords or credit card numbers) by masquerading as a trusted entity. Spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS can flag suspicious emails or web traffic that matches known phishing patterns or blacklisted domains.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block phishing emails, malicious URLs, or suspicious traffic to prevent users from accessing phishing sites or submitting sensitive information.
10. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
- What It Is: APTs are prolonged, targeted cyberattacks where attackers gain and maintain unauthorized access to a network to steal data or disrupt operations.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS monitors network traffic for unusual, continuous, or stealthy activity indicative of an APT, such as lateral movement or data exfiltration.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can disrupt communication between the attacker and the compromised systems by blocking traffic, stopping data theft, and isolating infected machines.
11. Zero-Day Exploits
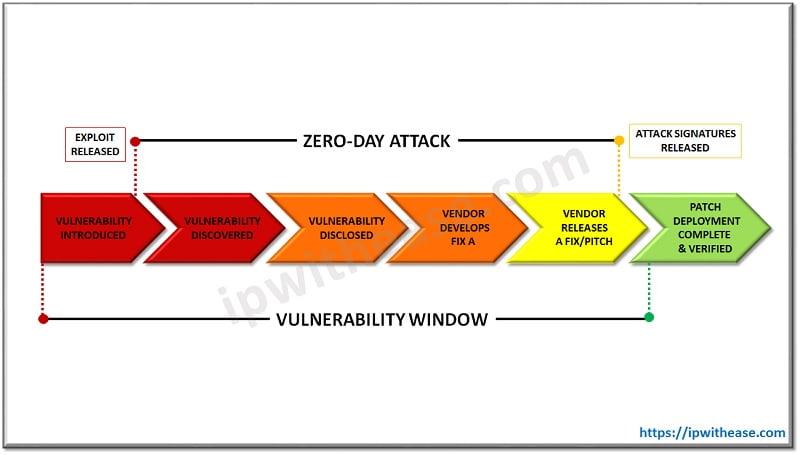
- What It Is: Zero-day exploits take advantage of vulnerabilities that have not yet been patched or publicly disclosed.
- How IDS Detects It: Anomaly-based IDS can detect traffic that deviates from normal behavior, which may signal the exploitation of a zero-day vulnerability.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block unknown traffic patterns or suspicious payloads that exhibit exploit-like behavior, reducing the chance of successful zero-day attacks.
12. Insider Threats
- What It Is: Insider threats arise from individuals within an organization who misuse their access to steal, damage, or compromise sensitive information.
- How IDS Detects It: IDS can monitor for unusual activity from insiders, such as large data transfers or accessing sensitive areas of the network at odd times.
- How IPS Prevents It: IPS can block or limit access to certain network segments or critical data when unusual insider behavior is detected, mitigating the risk of insider attacks.
Conclusion
IDS and IPS systems are powerful tools for detecting and preventing a wide array of cyberattacks. While IDS provides critical visibility into ongoing threats by identifying suspicious activity, IPS takes a proactive stance by blocking or preventing malicious actions before they can cause harm. Together, these systems form a layered defense strategy that significantly enhances network security by protecting against both common and sophisticated attacks.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj