Table of Contents
Zero knowledge proof (ZKP) is a powerful tool that can be used to secure digital transactions, provide authentication, and help protect privacy in digital systems. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of ZKP, its history, and its various applications.
What is Zero Knowledge Proof Protocol?
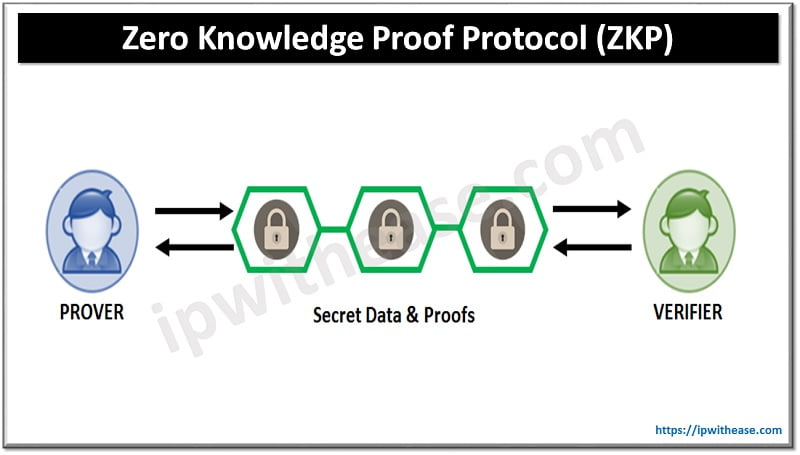
Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) is a cryptographic protocol that allows two parties to prove to one another that a certain statement is true without revealing the actual information behind the statement.
In essence, zero-knowledge proof is a way for two parties to prove the validity of a statement without revealing any of the underlying information. This has a variety of potential applications, such as secure authentication, privacy-preserving digital transactions, and even the secure transmission of digital messages.
History of Zero Knowledge Proof Protocol
The concept of zero-knowledge proof was first proposed by cryptographers Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff in 1985. Their work was based on the assumption that two parties, known as the prover and the verifier, could interact with each other without revealing any additional information about each other beyond the statement being proven.
In recent years, its use has become even more widespread, with the rise of blockchain technology and the development of zero-knowledge proof protocols for use on public blockchains.
Types of Zero-Knowledge Proof
The two fundamental types of zero-knowledge proof are interactive and non-interactive.
Interactive ZKP: In an interactive zero-knowledge proof, the prover and verifier interact with each other to prove the validity of the statement. This type of proof is more secure than non-interactive proofs but can be more cumbersome to implement.
Non-interactive ZKP: In a non-interactive zero-knowledge proof, the prover and verifier do not need to interact with each other to prove the validity of the statement. This type of proof is less secure than interactive proofs, but it is much easier to implement.
How does Zero Knowledge Proof Protocol work?
Zero-knowledge proof protocols use a series of public-key operations to prove the validity of a statement without revealing any of the underlying information. The protocol works by having the prover and verifier exchange messages, which are then verified by a set of cryptographic operations.
The protocol begins with the prover and verifier agreeing on a common set of cryptographic assumptions, known as the Common Reference String (CRS). Once the CRS has been agreed upon, the prover and verifier can then exchange messages, which are then verified by a series of cryptographic operations.
The cryptographic operations used by the protocol can vary depending on the type of zero-knowledge proof being used. In interactive zero-knowledge proofs, the prover and verifier must exchange messages to prove the validity of the statement. In non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs, the prover and verifier do not need to exchange messages to prove the validity of the statement.
Applications of Zero Knowledge Proof Protocol
Zero-knowledge proof protocols have a variety of potential applications:
- Secure Authentication: By using a zero-knowledge proof, two parties can authenticate each other without having to reveal any of their personal information. This allows the parties to authenticate each other without having to trust each other with sensitive information.
- Privacy-preserving Digital Transactions: Zero-knowledge proofs can also be used to create privacy-preserving digital transactions. By using a zero-knowledge proof, two parties can transact with each other without having to reveal any of their personal information. This allows the parties to transact securely without having to trust each other with sensitive information.
- Secure Message Transmission: By using a zero-knowledge proof, two parties can transmit messages to each other without having to reveal any of their personal information. This allows the parties to securely transmit messages without having to trust each other with sensitive information.
Advantages
- Zero-knowledge proofs are much more secure than traditional methods of authentication.
- Zero-knowledge proofs are much more efficient than traditional methods of authentication.
- Zero-knowledge proofs are much more private than traditional methods of authentication.
Disadvantages
Despite their many advantages, zero-knowledge proofs also have some disadvantages:
- ZKPs are much more complex than traditional methods of authentication.
- ZKPs are much more expensive than traditional methods of authentication.
ZKP and its role in Blockchain
Zero-knowledge proofs have become increasingly popular in recent years, thanks to the emergence of blockchain technology. This has many potential applications in the blockchain space.
For example, zero-knowledge proofs can be used to create privacy-preserving digital transactions, allowing users to transact with each other without having to reveal any of their personal information. This has a number of potential applications in the blockchain space, such as the creation of anonymous digital currencies, or the secure transmission of digital messages.
Zero-knowledge proofs can also be used to create secure authentication protocols, allowing users to securely authenticate each other without having to reveal any of their personal information. This has a number of potential applications in the blockchain space, such as the creation of secure authentication protocols for blockchain-based applications.
Conclusion
Zero knowledge proof is a powerful cryptographic protocol. As the use of blockchain technology continues to grow, we can expect to see zero-knowledge proof protocols become increasingly popular in the years to come.
Continue Reading:
What is DeFi in Cryptocurrency?
Hash Functions and What they Offer for Security in Cryptography
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj